Abstract
Objectives
To be competitive with common chemical surfactants, the cost of rhamnolipid production must be minimized by selecting suitable substrates and optimizing the fermentation process.
Results
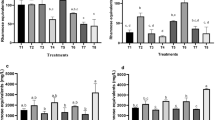
With different plant oils as substrates, Pseudomonas aeruginosa TIB-R02 can produce rhamnolipids with different structural characteristics that were confirmed by HPLC/MS analysis. Different rhamnolipids had different performances in interfacial tension. The production of rhamnolipid was greatly enhanced by fermentation optimization with palm oil as substrate. A fermentation-defoaming tandem system was developed to resolve the problems of foaming and medium overflow during scale-up. Finally, the titer of rhamnolipid reached 60 g/l and the yield reached 80 % in a 300 l fermentation-defoaming tandem system.
Conclusions
The work reveals the potential for producing high-performance rhamnolipids from renewable resources on a large scale.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Hausmann R, Lépine F, Müller MM, Déziel E (2011) Rhamnolipids: detection, analysis, biosynthesis, genetic regulation, and bioengineering of production. In: Soberón-Chávez G (ed) Biosurfactants: from genes to applications. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 13–55
Benincasa M, Abalos A, Oliveira I, Manresa A (2004) Chemical structure, surface properties and biological activities of the biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI from soapstock. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 85:1–8
Chandrasekaran EV, Bemiller JN (1980) Constituent analyses of glycosamino-glycans. In: Whister RL (ed) Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, vol VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 89–96
Gudiña EJ, Rodrigues AI, Alves E, Domingue MR, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2015) Bioconversion of agro-industrial by-products in rhamnolipids toward applications in enhanced oil recovery and bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 177:87–93
Iglauer S, Wu Y, Shuler PJ, Tang Y, Goddard WA (2010) New surfactant classes for enhanced oil recovery and their tertiary oil recovery potential. J Pet Sci Eng 71:23–29
Lindhardt TJ, Bakhit R, Danies L, Mayerl R, Pickenhagen W (1989) Microbially produced rhamnolipid as a source of rhamnose. Biotechnol Bioeng 33:365–368
Makkar RS, Cameotra SS, Banat IM (2011) Advances in utilization of renewable substrates for biosurfactant production. AMB Express 1:5
Müller MM, Kügler JH, Henkel M, Gerlitzki M, Hörmann B, Pöhnlein M, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2012) Rhamnolipids-next generation surfactants? J Biotechnol 162:366–380
Nitschke M, Costa SG, Contiero J (2005) Rhamnolipid surfactants: an update on the general aspects of these remarkable biomolecules. Biotechnol Prog 21:1593–1600
Noh NA, Salleh SM, Yahya AR (2014) Enhanced rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa USM-AR2 via fed-batch cultivation based on maximum substrate uptake rate. Lett Appl Microbiol 58:617–623
Rahman KS, Rahman TJ, McClean S, Marchant R, Banat IM (2002) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant production by strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using low-cost raw materials. Biotechnol Prog 18:1277–1281
Raza ZA, Rehman A, Khan MS, Khalid ZM (2007) Improved production of biosurfactant by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant using vegetable oil refinery wastes. Biodegradation 18:115–121
Reis RS, Pereira AG, Neves BC, Freire DM (2011) Gene regulation of rhamnolipid production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa–a review. Bioresour Technol 102:6377–6384
Robert M, Mercade ME, Bosch MP, Parra JL, Espiny MJ, Manresa MA, Guinea J (1989) Effect of the carbon source on biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 44T1. Biotechnol Lett 11:871–874
Schenk T, Schuphan I, Schmidt B (1995) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of the rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Chromatogr A 693:7–13
Sekhon Randhawa KK, Rahman PK (2014) Rhamnolipid biosurfactants-past, present, and future scenario of global market. Front Microbiol 5:454
Wang Q, Fang X, Bai B, Liang X, Shuler PJ, Goddard WA 3rd, Tang Y (2007) Engineering bacteria for production of rhamnolipid as an agent for enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:842–853
Zhu L, Yang X, Xue C, Chen Y, Qu L, Lu W (2012) Enhanced rhamnolipids production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on a pH stage-controlled fed-batch fermentation process. Bioresour Technol 117:208–213
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program 2014AA022104) and Industrial Biotechnology Program of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (12ZCZDSY13000).
Supporting information
Supplementary Figure 1—Base peak ion intensity chromatograms of rhamnolipids from various sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Z., Peng, Y. & Wang, Q. Rhamnolipid production, characterization and fermentation scale-up by Pseudomonas aeruginosa with plant oils. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2033–2038 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1885-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1885-2