Abstract
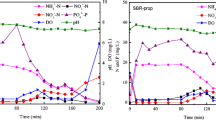
A comparative study on the use of methanol as a supplementary carbon source to enhance denitrification in primary and secondary anoxic zones is reported. Three lab-scale sequencing batch reactors (SBR) were operated to achieve nitrogen and carbon removal from domestic wastewater. Methanol was added to the primary anoxic period of the first SBR, and to the secondary anoxic period of the second SBR. No methanol was added to the third SBR, which served as a control. The extent of improvement on the denitrification performance was found to be dependent on the reactor configuration. Addition to the secondary anoxic period is more effective when very low effluent nitrate levels are to be achieved and hence requires a relatively large amount of methanol. Adding a small amount of methanol to the secondary anoxic period may cause nitrite accumulation, which does not improve overall nitrogen removal. In the latter case, methanol should be added to the primary anoxic period. The addition of methanol can also improve biological phosphorus removal by creating anaerobic conditions and increasing the availability of organic carbon in wastewater for polyphosphate accumulating organisms. This potentially provides a cost-effective approach to phosphorus removal from wastewater with a low carbon content. New fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) probes targeting methanol-utilising denitrifiers were designed using stable isotope probing. Microbial structure analysis of the sludges using the new and existing FISH probes clearly showed that the addition of methanol stimulated the growth of specific methanol-utilizing denitrifiers, which improved the capability of sludge to use methanol and ethanol for denitrification, but reduced its capability to use wastewater COD for denitrification. Unlike acetate, long-term application of methanol has no negative impact on the settling properties of the sludge.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aesoy A, Odegaard H, Bach K, Pujol R, Hamon M (1998) Denitrification in a packed bed biofilm reactor (BIOFOR—Experiments with different carbon sources. Water Res 32:1463–1470. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00358-8
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1919–1925
American Public Health Association American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation, Washington
Bond PL, Erhart R, Wagner M, Keller J, Blackall LL (1999) Identification of some of the major groups of bacteria in efficient and nonefficient biological phosphorus removal activated sludge systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4077–4084
Bouchez T, Patureau D, Dabert P, Wagner M, Delgenes JP, Moletta R (2000) Successful and unsuccessful bioaugmentation experiments monitored by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Water Sci Technol 41(12):61–68
Carucci A, Ramadori R, Rossetti S, Tomei MC (1996) Kinetics of denitrification reactions in single sludge systems. Water Res 30:51–56. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00127-7
Crocetti GR, Hugenholtz P, Bond PL, Schuler A, Keller J, Jenkins D et al (2000) Identification of polyphosphate-accumulating organisms and design of 16S rRNA-directed probes for their detection and quantitation. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1175–1182. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.3.1175-1182.2000
Daims H, Bruhl A, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (1999) The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all bacteria: Development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:434–444
Dennison WC, Abal EG (1999) Moreton Bay study: a scientific basis for the healthy waterways campaign. South East Queensland Regional Water Quality Management Strategy, Brisbane
Erhart R, Bradford D, Seviour RJ, Amann R, Blackall LL (1997) Development and use of fluorescent in situ hybridization probes for the detection and identification of ‘‘Microthrix parvicella’’ in activated sludge. Syst Appl Microbiol 20:310–318
Ginige MP (2003) Identification of denitrifying microbial communities in activated sludge exposed to external carbon sources. PhD dissertation. Advanced Wastewater Management Centre. Brisbane, The University of Queensland
Ginige MP, Hugenholtz P, Daims H, Wagner M, Keller J, Blackall LL (2004) Use of stable-isotope probing, full-cycle rRNA analysis, and fluorescence in situ hybridization-microautoradiography to study a methanol-fed denitrifying microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:588–596. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.1.588-596.2004
Ginige MP, Keller J, Blackall LL (2005) Investigation of an acetate-fed denitrifying microbial community by stable isotope probing, full-cycle rRNA analysis, and fluorescent in situ hybridization-microautoradiography. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8683–8691. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.12.8683-8691.2005
Hallin S, Pell M (1998) Metabolic properties of denitrifying bacteria adapting to methanol and ethanol in activated sludge. Water Res 32:13–18. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00199-1
Hallin S, Rothman M, Pell M (1996) Adaptation of denitrifying bacteria to acetate and methanol in activated sludge. Water Res 30:1445–1450. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(96)00033-4
Hallin S, Throbäck IN, Dicksved J, Pell M (2006) Metabolic profiles and genetic diversity of denitrifying communities in activated sludge after addition of methanol or ethanol. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5445–5452. doi:10.1128/AEM.00809-06
Layton AC, Karanth PN, Lajoie CA, Meyers AJ, Gregory IR, Stapleton RD et al (2000) Quantification of Hyphomicrobium populations in activated sludge from an industrial wastewater treatment system as determined by 16S rRNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1167–1174. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.3.1167-1174.2000
Louzeiro NR, Mavinic DS, Oldham WK, Meisen A, Gardner IS (2002) Methanol-induced biological nutrient removal kinetics in a full-scale sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 36:2721–2732. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00494-8
Louzeiro NR, Mavinic DS, Oldham WK, Meisen A, Gardner IS (2003) Process control and design considerations for methanol-induced denitrification in a sequencing batch reactor. Environ Technol 24:161–169
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer KH (1992) Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of Proteobacteria—problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:593–600
Martin HG, Ivanova N, Kunin V, Warnecke F, Barry KW, Mchardy AC et al (2006) Metagenomic analysis of two enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) sludge communities. Nat Biotechnol 24:1263–1269. doi:10.1038/nbt1247
Nyberg U, Andersson B, Aspegren H (1996) Long-term experiences with external carbon sources for nitrogen removal. Water Sci Technol 33(12):109–116. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(96)00464-7
Pratt S, Yuan ZG, Gapes D, Dorigo M, Zeng RJ, Keller J (2003) Development of a novel titration and off-gas analysis (TOGA) sensor for the study of biological processes in wastewater treatment systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:482–495. doi:10.1002/bit.10490
Purtschert I, Siegrist H, Gujer W (1996) Enhanced denitrification with methanol at WWTP Zürich-Werdhölzli. Water Sci Technol 33(12):117–126. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(96)00465-9
Schmid M, Twachtmann U, Klein M, Strous M, Juretschko S, Jetten M et al (2000) Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:93–106
Seviour RJ, Blackall LL (1999) The microbiology of activated sludge. Kluwer, Boston
Sozen S, Orhon D (1999) The effect of nitrite correction on the evaluation of the rate of nitrate utilization under anoxic conditions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:790–800. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199908)74:8<790::AID-JCTB106>3.0.CO;2-C
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL, Metcalf & Eddy (1991) Wastewater engineering: treatment, disposal, and reuse. McGraw-Hill, New York
Thomas M, Wright P, Blackall L, Urbain V, Keller J (2003) Optimisation of Noosa BNR plant to improve performance and reduce operating costs. Water Sci Technol 47(12):141–148
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the Australian Research Council (ARC), Brisbane Water, Sydney Water, Cab Water and ANOX NV (Sweden) through the ARC grant LP0347793. We are grateful for the above industry partners for their scientific and technical input into this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginige, M.P., Bowyer, J.C., Foley, L. et al. A comparative study of methanol as a supplementary carbon source for enhancing denitrification in primary and secondary anoxic zones. Biodegradation 20, 221–234 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9215-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9215-1