Abstract
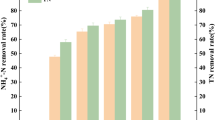
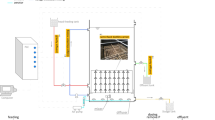
For municipal wastewater treatment, main stream biological nutrient removal (BNR) process is becoming more and more important. This lab-scale study, novel MBR_based BNR processes (named A2N-MBR and A2NO-MBR) were built. Comparison of the COD removal, results obtained demonstrated that COD removal efficiencies were almost the same in three processes, with effluent concentration all bellowed 30 mg L−1. However, the two-sludge systems (A2N-MBR and A2NO-MBR) had an obvious advantage over the A2/O for denitrification and phosphorus removal, with the average TP removal rates of 91.20, 98.05% and TN removal rates of 73.00, 79.49%, respectively, higher than that of 86.45 and 61.60% in A2/O process. Illumina Miseq sequencing revealed that Candidatus_Accumulibacter, which is capable of using nitrate as an electron acceptor for phosphorus and nitrogen removal simultaneously, was the dominant phylum in both A2N-MBR and A2NO-MBR process, accounting for 28.74 and 23.98%, respectively. Distinguishingly, major organism groups related to nitrogen and phosphorus removal in A2/O system were Anaerolineaceae_uncultured, Saprospiraceae_uncultured and Thauera, with proportions of 11.31, 8.56 and 5.00%, respectively. Hence, the diversity of dominant PAOs group was likely responsible for the difference in nitrogen and phosphorus removal in the three processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Daidou T, Tsuneda S, Hirata A (2002) Characterization of denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms cultivated under different electron acceptor conditions using polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis assay. Water Res 36:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00222-6
APHA (2012) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater 2012. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bortone G, Libelli SM, Tilche A, Wanner J (1999) Anoxic phosphate uptake in the dephanox process. Water Sci Technol 40:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00500-4
Broughton A, Pratt S, Shilton A (2008) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal for high-strength wastewater with a low rbCOD: P ratio. Bioresour Technol 99:1236–1241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.02.013
Carvalho G, Lemos PC, Oehmen A, Reis MA (2007) Denitrifying phosphorus removal: linking the process performance with the microbial community structure. Water Res 41:4383–4396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.065
Chen Y, Zhao Z, Peng Y, Li J, Xiao L, Yang L (2016) Performance of a full-scale modified anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process: high-throughput sequence analysis of its microbial structures and their community functions. Bioresour Technol 220:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.095
Dabert P, Sialve B, Delgenès JP, Moletta R, Godon JJ (2001) Characterisation of the microbial 16S rDNA diversity of an aerobic phosphorus-removal ecosystem and monitoring of its transition to nitrate respiration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:500–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000529
Deng Q, Liao BH, Chen JY, Huang RX (2010) Effect of N/P ratios on integration and simultaneous denitrifying nitrogen and phosphorus removal process. Technol Water Treat (China) 36:29–33
Goel RK, Sanhueza P, Noguera DR (2005) Evidence of Dechloromonas sp. participating in enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) in a bench-scale aerated-anoxic reactor. Proc Water Environ Fed 2005:3864–3871. https://doi.org/10.2175/193864705783866261
Hauduc H, Rieger L, Oehmen A, Loosdrecht MCMV, Comeau Y, Héduit A, Vanrolleghem PA, Gillot S (2013) Critical review of activated sludge modeling: state of process knowledge, modeling concepts, and limitations. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:24–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24624
He S, Gall DL, Mcmahon KD (2007) “Candidatus Accumulibacter” population structure in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludges as revealed by polyphosphate kinase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5865–5874. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01207-07
Hill VR, Kahler AM, Jothikumar N, Johnson TB, Hahn D, Cromeans TL (2007) Multistate evaluation of an ultrafiltration-based procedure for simultaneous recovery of enteric microbes in 100-liter tap water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4218–4225. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02713-06
Jeongmyeong K, Hyojung L, Sunyoung K, Song JJ, Woojun P, Cheok J (2010) Analysis of the fine-scale population structure of “Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis” in enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludge, using fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometric sorting. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3825–3835. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00260-10
Jin Z, Ji FY, Xu X, Xu XY, Chen QK, Li Q (2014) Microbial and metabolic characterization of a denitrifying phosphorus-uptake/side stream phosphorus removal system for treating domestic sewage. Biodegradation 25:777–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9698-x
Judd S, Judd S (2010) MBR book: principles and applications of membrane bioreactors for water and wastewater treatment. Elsevier, Oxford
Kuba T, Loosdrecht MCMV, Heijnen JJ (1996) Phosphorus and nitrogen removal with minimal COD requirement by integration of denitrifying dephosphatation and nitrification in a two-sludge system. Water Res 30:1702–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(96)00050-4
Lee DS, Jeon CO, Park JM (2001) Biological nitrogen removal with enhanced phosphate uptake in a sequencing batch reactor using single sludge system. Water Res 35:3968–3976. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00132-4
Lee N, Nielsen PH, Aspegren H, Henze M, Schleifer KH, La CJJ (2003) Long-term population dynamics and in situ physiology in activated sludge systems with enhanced biological phosphorus removal operated with and without nitrogen removal. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:211–227. https://doi.org/10.1078/072320203322346065
Li J (2016) Denitrifying phosphorus removal for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater with low C/N ratios and microbial community structure analysis. Desalin Water Treat 57:1890–1899. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.979235
Li W, Zheng P, Ji J, Zhang M, Guo J, Zhang J, Abbas G (2014) Floatation of granular sludge and its mechanism: a key approach for high-rate denitrifying reactor. Bioresour Technol 152:414–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.056
Li W, Shan XY, Wang ZY, Lin XY, Li CX, Cai CY, Abbas G, Zhang M, Shen LD, Hu ZQ, Zhao HP, Zheng P (2016) Effect of self-alkalization on nitrite accumulation in a high-rate denitrification system: performance, microflora and enzymatic activities. Water Res 88:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.003
Liu X, Chen Q, Liu W, Zhu L (2014) Using the method of wastewater acidification to improve the efficiency of carbon utilization and nutrient removal in A2N process from a lab-scale operation. Desalin Water Treat 57:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.986530
Ma Y, Peng YZ, Wang LX (2009) Improving nutrient removal of the AAO process by an influent bypass flow by denitrifying phosphorus removal. Desalination 246:534–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.047
Mcilroy SJ, Szyszka A, Starnawski P, Saunders AM, Nierychlo M, Nielsen PH, Nielsen JL (2014) Identification of active denitrifiers in full-scale nutrient removal wastewater treatment systems by application of stable-isotope probing, microautoradiography and FISH. Environ Microbiol 18:50. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12614
Nguyen HTT, Le VQ, Hansen AA, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2011) High diversity and abundance of putative polyphosphate-accumulating Tetrasphaera -related bacteria in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:256–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01049.x
Ong YH, Chua AS, Fukushima T, Ngoh GC, Shoji T, Michinaka A (2014) High-temperature EBPR process: the performance, analysis of PAOs and GAOs and the fine-scale population study of Candidatus “Accumulibacter phosphatis”. Water Res 64:102–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.038
Peng YZ, Wang Y, Ozaki M, Pan M (2004) Denitrifying phosphorus removal in a continuously-flow A2N two-sludge process. J Environ Sci Heal A 39:703–715. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-120027736
Peng YZ, Wu CY, Wang RD, Li XL (2011) Denitrifying phosphorus removal with nitrite by a real-time step feed sequencing batch reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:541–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2548
Peterson SB, Warnecke F, Madejska J, Mcmahon KD, Hugenholtz P (2008) Environmental distribution and population biology of Candidatus Accumulibacter, a primary agent of biological phosphorus removal. Environ Microbiol 10:2692–2703. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01690.x
Saunders AM, Larsen P, Nielsen PH (2013) Comparison of nutrient-removing microbial communities in activated sludge from full-scale MBRs and conventional plants. Water Sci Technol 68:366–371. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.183
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Sun SP, Pellicer INC, Merkey B, Qi Z, Xia SQ, Yang DH, Sun JH, Smets BF (2010) Effective biological nitrogen removal treatment processes for domestic wastewaters with low C/N ratios: a review. Environ Eng Sci 27:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2009.0100
Tsuneda S, Ohno T, Soejima K, Hirata A (2006) Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal using denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms in a sequencing batch reactor. Biochem Eng J 27:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2005.07.004
Wachtmeister A, Kuba T, Loosdrecht MCMV, Heijnen JJ (1997) A sludge characterization assay for aerobic and denitrifying phosphorus removing sludge. Water Res 31:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00281-3
Wang Y, Geng J, Ren Z, Guo G, Wang C, Wang H (2013) Effect of COD/N and COD/P ratios on the PHA transformation and dynamics of microbial community structure in a denitrifying phosphorus removal process. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1228–1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3962
Wang Z, Meng Y, Fan T, Du Y, Tang J, Fan S (2015) Phosphorus removal and N2O production in anaerobic/anoxic denitrifying phosphorus removal process: long-term impact of influent phosphorus concentration. Bioresour Technol 179:585–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.016
Yin J, Zhang P, Li F, Li G, Hai B (2015) Simultaneous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal with a sequencing batch reactor–biofilm system. Int Biodeter Biodegr 103:221–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.02.019
Zeng RJ, Saunders AM, Yuan Z, Blackall LL, Keller J (2003) Identification and comparison of aerobic and denitrifying polyphosphate-accumulating organisms. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10652
Zeng W, Zhang J, Wang A, Peng Y (2016) Denitrifying phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater and dynamics of “Candidatus Accumulibacter” and denitrifying bacteria based on genes of ppk 1, narG, nirS and nirK. Bioresour Technol 207:322–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.016
Zhang W, Peng Y, Ren N, Liu Q, Chen Y (2013) Improvement of nutrient removal by optimizing the volume ratio of anoxic to aerobic zone in AAO-BAF system. Chemosphere 93:2859–2863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.047
Zhu S, Wu H, Wei C, Zhou L, Xie J (2016) Contrasting microbial community composition and function perspective in sections of a full-scale coking wastewater treatment system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7009-z
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012QNB12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Xu, X., Zhao, K. et al. Novel MBR_based main stream biological nutrient removal process: high performance and microbial community. Biodegradation 29, 11–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9810-0