Abstract
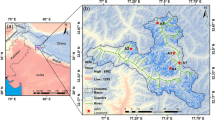
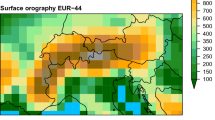
Large basins with relatively wide floors experience heterogeneous nocturnal cooling due to the diversity of the topography and the land use within the basin. Near mountain ranges the drainage flows prevail, but in low areas, river valleys or embedded plateaux, the actual rates of cooling differ as does the behaviour of the local flows in the first few metres above the surface. In this study, the temporal and spatial heterogeneity of the surface cooling is inspected through the analysis of satellite radiative surface temperature, data from a meteorological network and a tall tower. The organisation of the flow within the basin is also studied by means of a high-resolution numerical mesoscale simulation. Although the basin cools almost as a unit, there exists a large diversity of local regimes. Vertical profiles from the mesoscale simulation are analysed and grouped according to their wind structure and stratification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bravo M, Mira A, Soler MR, Cuxart J (2008) Intercomparison and evaluation of MM5 and Meso-NH mesoscale models in the stable boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 128: 77–101
Bromwich DH (1989) Satellite analyses of Antarctic katabatic wind behavior. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 70: 738–749
Clements CB, Whiteman CD, Horel JD (2003) Cold-air-pool structure and evolution in a mountain basin: Peter Sinks, Utah. J Appl Meteorol 42: 752–768
Coll C, Caselles V (1997) A split-window algorithm for land surface temperature from advanced very high resolution radiometer data: validation and algorithm comparison. J Geophys Res 102: 697–713
Coll C, Caselles V, Sobrino JA, Valor E (1994) On the atmospheric dependence of the split-window equation for land surface temperature. Int J Remote Sens 15: 105–122
Conangla L, Cuxart J (2006) On the turbulence in the upper part of the low-level jet: an experimental and numerical study. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118: 379–400
Conangla L, Cuxart J, Soler MR (2008) Characterisation of the nocturnal boundary layer at a site in northern Spain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 128: 255–276
Cuxart J (2008) Nocturnal basin low-level jets: an integrated study. Acta Geophys Pol 56: 100–113
Cuxart J, Yagüe C, Morales G, Terradellas E, Orbe J, Calvo J, Fernandez A, Soler MR, Infante C, Buenestado P, Espinalt A, Joergensen HE, Rees JM, Vilá J, Redondo JM, Cantalapiedra IR, Conangla L (2000a) Stable atmospheric boundary-layer experiment in Spain (SABLES 98): a report. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 96: 337–370
Cuxart J, Bougeault P, Redelsperger J-L (2000b) A turbulence scheme allowing for mesoscale and large-eddy simulations. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 126: 1–30
Cuxart J, Jiménez MA, Martínez D (2007) Nocturnal mesobeta basin and katabatic flows on a midlatitude island. Mon Weather Rev 135: 918–932
Edwards JM (2009) Radiative processes in the stable boundary layer: part II. The development of the nocturnal boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 131: 127–146
Gopalakrishnan SG, Maithili S, McNider RT, Singh MP (1998) Study of radiative and turbulent processes in the stable boundary layer under weak wind conditions. J Atmos Sci 55: 954–960
Grisogono B, Oerlemans J (2001) Katabatic flow: analytic solution for gradually varying eddy diffusivities. J Atmos Sci 58: 3349–3354
Heymann Y, Steenmans C, Croissille G, Bossard M (1994) Corine land cover technical guide. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, 136 pp
Jiménez MA, Mira A, Cuxart J, Luque A, Alonso S, Guijarro JA (2008) Verification of a clear-sky mesoscale simulation using satellite-derived surface temperatures. Mon Weather Rev 136: 5148–5161
Lafore JP, Stein J, Asencio N, Bougeault P, Ducrocq V, Duron J, Fisher C, Héreil P, Mascart P, Pinty JP, Redelsperger J-L, Richard E, Vilá-Gueraude Arellano J (1998) The Meso-NH atmospheric simulation system. Part I: Adiabatic formulation and control simulation. Ann Geophys 16: 90–109
Lundquist JD, Pepin N, Rochford C (2008) Automated algorithm for mapping regions of cold-air pooling in complex terrain. J Geophys Res 113: D22107-1–D22107-15
Mahrt L, Sun J, Blumen W, Delany T, Oncley S (1998) Nocturnal boundary-layer regimes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 88: 255–278
Martínez D, Cuxart J (2009) Assessment of the hydraulic slope flow approach using a mesoscale model. Acta Geophys Pol 57: 882–903
Michelson SA, Bao JW (2008) Sensitivity of low-level winds simulated by the WRF model in California’s Central Valley to uncertainties in the large-scale forcing and soil initialization. J Appl Meteorol Clim 47: 3131–3149
Morcrette J-J (1990) Impact of changes to the radiation transfer parameterizations plus cloud optical properties in the ECMWF model. Mon Weather Rev 118: 847–873
Neff WD, King CW (1989) The accumulation and pooling of drainage flows in a large basin. J Appl Meteorol 28: 518–529
Noilhan J, Planton S (1989) A simple parameterization of land surface processes for meteorological models. Mon Weather Rev 117: 536–549
Prata AJ, Caselles V, Coll C, Sobrino JA, Otllé C (1995) Thermal remote sensing of land surface temperature from satellites: current status and future prospects. Remote Sens Environ 12: 175–224
Savijärvi H (2006) Radiative and turbulent heating rates in the clear-air boundary layer. Q J Roy Meteorol Soc 132: 147–161
Terradellas E, Morales G, Cuxart J, Yagüe C (2001) Wavelet methods: application to the study of the stable atmospheric boundary layer under non-stationary conditions. Dyn Atmos Oceans 34: 225–244
Viana S, Yagüe C, Maqueda G (2009) Propagation and effects of a mesoscale gravity wave over a weakly-stratified nocturnal boundary layer during the SABLES2006 field campaign. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 133: 165–188
Vosper SB, Brown AR (2008) Numerical simulations of sheltering in valleys: the formation of nighttime cold-air pools. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 127: 429–448
Whiteman CD, Bian X, Zhong S (1999) Wintertime evolution of the temperature inversion in the Colorado Plateau basin. J Appl Meteorol 38: 1103–1117
Whiteman CD, Haiden T, Pospichal B, Eisenbach S, Steinacker R (2004) Minimum temperatures, diurnal temperature ranges, and temperature inversions in limestone sinkholes of different sizes and shapes. J Appl Meteorol 43: 1224–1236
Whiteman CD, De Wekker SFL, Haiden T (2007) Effect of dewfall and frostfall on nighttime cooling in a small, closed basin. J Appl Meteorol Clim 46: 3–13
Wolyn PG, McKee TB (1989) Deep stable layers in the intermountain western United States. Mon Weather Rev 117: 461–472
Zängl G (2005a) Formation of extreme cold-air pools in elevated sinkholes: an idealized numerical process study. Mon Weather Rev 133: 925–941
Zängl G (2005b) Dynamical aspects of wintertime cold-air pools in an alpine valley system. Mon Weather Rev 133: 2721–2740
Zhong S, Whiteman CD, Bian X, Shaw WJ, Hubble JM (2001) Meteorological processes affecting the evolution of a wintertime cold air pool in the Columbia basin. Mon Weather Rev 129: 2600–2613
Zhong S, Whiteman CD, Bian X (2004) Diurnal evolution of three-dimensional wind and temperature structure in California’s Central valley. J Appl Meteorol 43: 1679–1699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Mahrt on leave from Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez, D., Jiménez, M.A., Cuxart, J. et al. Heterogeneous Nocturnal Cooling in a Large Basin Under Very Stable Conditions. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 137, 97–113 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-010-9522-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-010-9522-z