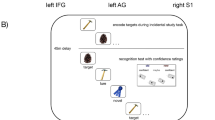
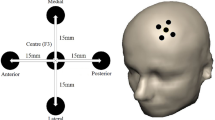
Abstract
There is evidence that the human prefrontal cortex is asymmetrically involved in long-term episodic memory processing. Moreover, abstract and concrete words processing has been reported to differentially involve prefrontal and parietal areas. We implemented a two-stages functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)–repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) paradigm to investigate the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices (DLPFCs) and parietal cortices (PARCs) in encoding and retrieval of abstract and concrete words. Using this paradigm we could select areas to be stimulated on the basis of single-subject (SS) anatomical and functional data, investigating the usefulness of this integration approach. With respect to fMRI, abstract and concrete words differed only for a greater left fusiform gyrus activation for concrete words. In turn, significant rTMS effects were found, but only for the retrieval of abstract words. Consistent with previous findings, repetitive stimulation of the right DLPFC had a specific impact on episodic retrieval. Memory retrieval performance was also disrupted when rTMS was applied to the left PARC. Finally, we found a significant positive correlation between the effect sizes of SS right PARC activations for abstract word retrieval and the consequent rTMS interference effects. Taken together these data provide for the first time evidence that also the PARC has a necessary role in episodic retrieval of abstract words. Importantly, from a methodological perspective, our data demonstrate that fMRI-guided rTMS with a SS approach provides a powerful tool to investigate the neural underpinnings of cognitive functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson JL, Hutton C, Ashburner J, Turner R, Friston K (2001) Modeling geometric deformations in EPI time series. Neuroimage 13:903–919
Bastings EP, Gage HD, Greenberg JP, Hammond G, Hernandez L, Santago P, Hamilton CA, Moody DM, Singh KD, Ricci PE, Pons TP, Good DC (1998) Co-registration of cortical magnetic stimulation and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroreport 9:1941–1946
Buckner RL, Wheeler ME (2001) The cognitive neuroscience of remembering. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:624–634
Cabeza R, Nyberg L (2003) Functional neuroimaging of memory. Neuropsychologia 41:241–244
Cabeza R, Locantore JK, Anderson ND (2003) Lateralization of prefrontal activity during episodic memory retrieval: evidence for the production-monitoring hypothesis. J Cogn Neurosci 15:249–259
Epstein CM, Sekino M, Yamaguchi K, Kamiya S, Ueno S (2002) Asymmetries of prefrontal cortex in human episodic memory: effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on learning abstract patterns. Neurosci Lett 320:5–8
Feredoes E, Postle BR (2007) Localization of load sensitivity of working memory storage: quantitatively and qualitatively discrepant results yielded by single-subject and group-averaged approaches to fMRI group analysis. Neuroimage 35:881–903
Feredoes E, Tononi G, Postle BR (2006) Direct evidence for a prefrontal contribution to the control of proactive interference in verbal working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19530–19534
Feredoes E, Tononi G, Postle BR (2007) The neural bases of the short-term storage of verbal information are anatomically variable across individuals. J Neurosci 27:11003–11008
Fletcher PC, Henson RN (2001) Frontal lobes and human memory: insights from functional neuroimaging. Brain 124:849–881
Fliessbach K, Weis S, Klaver P, Elger CE, Weber B (2006) The effect of word concreteness on recognition memory. Neuroimage 32:1413–1421
Flitman SS, Grafman J, Wassermann EM, Cooper V, O’Grady J, Pascual-Leone A, Hallett M (1998) Linguistic processing during repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 50:175–181
Friston KJ, Glaser DE, Henson RN, Kiebel S, Phillips C, Ashburner J (2002) Classical and Bayesian inference in neuroimaging: applications. Neuroimage 16:484–512
Herwig U, Abler B, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C, Wunderlich A, Grothe J, Spitzer M, Walter H (2003a) Verbal storage in a premotor-parietal network: evidence from fMRI-guided magnetic stimulation. Neuroimage 20:1032–1041
Herwig U, Satrapi P, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C (2003b) Using the international 10–20 EEG system for positioning of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr 16:95–99
Jessen F, Heun R, Erb M, Granath DO, Klose U, Papassotiropoulos A, Grodd W (2000) The concreteness effect: evidence for dual coding and context availability. Brain Lang 74:103–112
Kapur S, Craik FI, Tulving E, Wilson AA, Houle S, Brown GM (1994) Neuroanatomical correlates of encoding in episodic memory: levels of processing effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2008–2011
Kelley WM, Miezin FM, McDermott KB, Buckner RL, Raichle ME, Cohen NJ, Ollinger JM, Akbudak E, Conturo TE, Snyder AZ, Petersen SE (1998) Hemispheric specialization in human dorsal frontal cortex and medial temporal lobe for verbal and nonverbal memory encoding. Neuron 20:927–936
Laudanna A, Thornton AM, Brown G, Burani C, Marconi L (1995) Un corpus dell’italiano scritto contemporaneo dalla parte del ricevente. In: Bolasco S, Lebart L, Salem A (eds) III Giornate internazionali di Analisi Statistica dei Dati Testuali. Cisu, Roma
Liljestrom M, Hulten A, Parkkonen L, Salmelin R (2009) Comparing MEG and fMRI views to naming actions and objects. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1845–1856
Manenti R, Cappa SF, Rossini PM, Miniussi C (2008) The role of the prefrontal cortex in sentence comprehension: an rTMS study. Cortex 44:337–344
Mottaghy FM, Krause BJ, Kemna LJ, Topper R, Tellmann L, Beu M, Pascual-Leone A, Muller-Gartner HW (2000) Modulation of the neuronal circuitry subserving working memory in healthy human subjects by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurosci Lett 280:167–170
Mottaghy FM, Doring T, Muller-Gartner HW, Topper R, Krause BJ (2002a) Bilateral parieto-frontal network for verbal working memory: an interference approach using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Eur J Neurosci 16:1627–1632
Mottaghy FM, Gangitano M, Sparing R, Krause BJ, Pascual-Leone A (2002b) Segregation of areas related to visual working memory in the prefrontal cortex revealed by rTMS. Cereb Cortex 12:369–375
Mottaghy FM, Pascual-Leone A, Kemna LJ, Topper R, Herzog H, Muller-Gartner HW, Krause BJ (2003) Modulation of a brain-behavior relationship in verbal working memory by rTMS. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 15:241–249
Nyberg L, Persson J, Habib R, Tulving E, McIntosh AR, Cabeza R, Houle S (2000) Large scale neurocognitive networks underlying episodic memory. J Cogn Neurosci 12:163–173
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Osaka N, Otsuka Y, Hirose N, Ikeda T, Mima T, Fukuyama H, Osaka M (2007) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) applied to left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex disrupts verbal working memory performance in humans. Neurosci Lett 418:232–235
Pascual-Leone A, Wassermann EM, Grafman J, Hallett M (1996) The role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in implicit procedural learning. Exp Brain Res 107:479–485
Postle BR, Ferrarelli F, Hamidi M, Feredoes E, Massimini M, Peterson M, Alexander A, Tononi G (2006) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation dissociates working memory manipulation from retention functions in the prefrontal, but not posterior parietal, cortex. J Cogn Neurosci 18:1712–1722
Rossi S, Cappa SF, Babiloni C, Pasqualetti P, Miniussi C, Carducci F, Babiloni F, Rossini PM (2001) Prefrontal [correction of Prefontal] cortex in long-term memory: an “interference” approach using magnetic stimulation. Nat Neurosci 4:948–952
Rossi S, Miniussi C, Pasqualetti P, Babiloni C, Rossini PM, Cappa SF (2004) Age-related functional changes of prefrontal cortex in long-term memory: a repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation study. J Neurosci 24:7939–7944
Rossi S, Pasqualetti P, Zito G, Vecchio F, Cappa SF, Miniussi C, Babiloni C, Rossini PM (2006) Prefrontal and parietal cortex in human episodic memory: an interference study by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 23:793–800
Rossi S, Ferro M, Cincotta M, Ulivelli M, Bartalini S, Miniussi C, Giovannelli F, Passero S (2007) A real electro-magnetic placebo (REMP) device for sham transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Clin Neurophysiol 118:709–716
Rugg MD, Wilding EL (2000) Retrieval processing and episodic memory. Trends Cogn Sci 4:108–115
Sack AT, Linden DE (2003) Combining transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional imaging in cognitive brain research: possibilities and limitations. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 43:41–56
Sack AT, Kadosh RC, Schuhmann T, Moerel M, Walsh V, Goebel R (2009) Optimizing functional accuracy of TMS in cognitive studies: a comparison of methods. J Cogn Neurosci 21:207–221
Sandrini M, Cappa SF, Rossi S, Rossini PM, Miniussi C (2003) The role of prefrontal cortex in verbal episodic memory: rTMS evidence. J Cogn Neurosci 15:855–861
Simons JS, Spiers HJ (2003) Prefrontal and medial temporal lobe interactions in long-term memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:637–648
Sparing R, Buelte D, Meister IG, Paus T, Fink GR (2008) Transcranial magnetic stimulation and the challenge of coil placement: a comparison of conventional and stereotaxic neuronavigational strategies. Hum Brain Mapp 29:82–96
Tulving E, Kapur S, Craik FI, Moscovitch M, Houle S (1994) Hemispheric encoding/retrieval asymmetry in episodic memory: positron emission tomography findings. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2016–2020
Wagner AD, Desmond JE, Glover GH, Gabrieli JD (1998a) Prefrontal cortex and recognition memory. Functional-MRI evidence for context-dependent retrieval processes. Brain 121(Pt 10):1985–2002
Wagner AD, Poldrack RA, Eldridge LL, Desmond JE, Glover GH, Gabrieli JD (1998b) Material-specific lateralization of prefrontal activation during episodic encoding and retrieval. Neuroreport 9:3711–3717
Walsh V, Pascual-Leone A (2003) Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a neurochronometrics of mind. MIT, Cambridge, MA
Walsh V, Rushworth M (1999) A primer of magnetic stimulation as a tool for neuropsychology. Neuropsychologia 37:125–135
Wassermann EM (1998) Risk and safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: report and suggested guidelines from the international workshop on the safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, June 5–7, 1996. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:1–16
Weis S, Klaver P, Reul J, Elger CE, Fernandez G (2004) Temporal and cerebellar brain regions that support both declarative memory formation and retrieval. Cereb Cortex 14:256–267
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by a EEC-NEST grant (ABSTRACT) to SFC. We wish to thank Dr Marco Calabria for his help with experimental assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manenti, R., Tettamanti, M., Cotelli, M. et al. The Neural Bases of Word Encoding and Retrieval: A fMRI-Guided Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study. Brain Topogr 22, 318–332 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-009-0126-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-009-0126-1