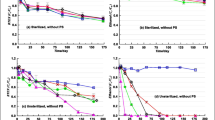
Dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria derive energy needed for growth and function by oxidation of organic compounds or molecular hydrogen coupled with reduction of iron(III) to iron(II) in subsurface environments. In this work, we used the indicated bacteria in an anaerobic environment for oxidation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (a mixture of o-, m-, and p-xylenes) (BETX), which are aquifer contaminants. We show that oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons coupled with bacterial reduction of iron follows first-order kinetics. The rate constant is maximum for an aromatic hydrocarbon:Fe ratio equal to 1. The oxidation rate constant increases in the series benzene < toluene < ethylbenzene < xylenes. The aromatic hydrocarbon degradation efficiency increases as the concentration of the substrate (citric acid) increases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. R. Lovley, J Ind. Microb. Biotechnol. 18, 75–81 (1997).
J. Lemaire, V. Croze, J. Maier, and M. Simonnot, Chemosphere, 84, 1181–1187 (2011).
M. J. Lonborg, P. Engesgaard, P. L. Bjerg, and D. Rosbjerg, J. Contam. Hydrol. 87, 191-210 (2006).
K. Rugge, P. L. Bjerg, and T. H. Christensen, Environ. Sci. Technol., 29, 1395-1400 (1995).
T. B. Hofstetter, C. G. Heijman, S. B. Haderlein, C. Holliger, and R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol., 33, 1479-1487 (1999).
C. M. Hansel, S. G. Benner, J. Neiss, A. Dohnalkova, R. K. Kukkadapu, and S. Fendorf, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 67, 2977–2992 (2003).
N. B. Tobler, T. B. Hofstetter, K. L. Straub, D. Fontana, and R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol., 41, 7765-7772 (2007).
C. G. Heijman, E. Grieder, C. Holliger, and R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol., 29, 775–783 (1995).
N. B. Tobler, T. B. Hofstetter, and R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 7773–7780 (2007).
J. Clement, J. Shrestha, J. G. Ehrenfeld, and P. R. Jaffe, Soil Biol. Biochem., 37, 2323–2328 (2005).
W. R. Villatoro-Monzón, M. G. Morales-Ibarria, E. K. Velázquez, H. Ramírez-Saad, and E. Razo-Flores, Water Air Soil Pollut., 192, 165–172 (2008).
S. Botton and J. R. Parsons, Biodegradation, 18, 371-381 (2007).
D. W. Major, C. I. Mayfield, and J. F. Barker, Ground Water, 26, 8-14 (1987).
M. L. McCormick, E. J. Bouwer, and P. Adriaens, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36, 403-410 (2002).
C. G. Heijman, E. Grieder, C. Holliger, and R. P. Schwarzenbach, Environ. Sci. Technol., 29, 775–783 (1995).
M. Tandukar, S. J. Huber, T. Onodera, and S. G. Pavlostathis, Environ. Sci. Technol., 43, 8159–8165 (2009).
G. Wang, L. P. Huang, and Y. F. Zhang, Biotechnol. Lett., 30, 1959–1966 (2008).
S. Botton and J. R. Parsons, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25, 2630–2638 (2006).
J. M. Tor and D. R. Lovley, Environ. Microbiol., 3, 281–287 (2001).
D. R. Lovley, J. C. Woodward, and F. H. Chapelle, Nature, 370, 128–131 (1994).
D. R. Lovley and D. J. Lonergan, Environ. Microbiol., 56, 1858–1864 (1990).
D. Qu and S. Schnell, Acta Microbiol. Sin., 21, 745–749 (2001).
“Water quality-determination of iron-phenanthroline - spectrophotometry,” Environmental Protection Standard of China, HJ/T 345 (2007).
R. Swisher and G. C. Carroll, Microb. Ecol., 6, 217–226 (1980).
G. Adam and H. Duncan, Soil Biol. Biochem., 33, 943–951 (2001).
C. Liu, S. Kota, J. M. Zachara, J. K. Fredrickson, and C. K. Brinkman, Environ. Sci. Technol., 35, 2482–2490 (2001).
C. Liu, S. Kota, J. M. Zachara, Y. A. Gorby, J. E. Szecsody, and C. F. Brown, Environ. Sci. Technol., 35, 1385–1393 (2001).
S. Bonneville, T. Behrends, P. Van Cappellen, C. Hyacinthe, and W. F. M. Roling, Geochimica, 70, 5842–5854 (2006).
S. Bonneville, P. Van Cappellen, and T. Behrends, Chem. Geol., 212, 255–268 (2004).
M. L. McCormick, E. J. Bouwer, and P. Adriaens, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36, 403–401 (2002).
E. E. Roden and M. M. Urrutia, Environ. Sci. Technol., 33, 1847–1853 (1999).
M. K. Jahn, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71, 3355–3358 (2005).
M. E. Caldwell and J. M. Suflita, Environ. Sci. Technol., 34, 1216–1220 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 1, pp. 44 – 49, January – February, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, D., Xiaolan, M. & Jingjie, L. Removal of aromatic hydrocarbons from aquifers by oxidation coupled with dissimilatory bacterial reduction of iron. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 49, 70–80 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-013-0413-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-013-0413-0