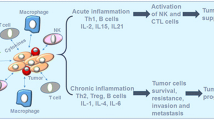
Abstract
Cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF are primarily pro-inflammatory. The inflammation induced by these cytokines is reflected in the type of genes they induce. In the pathogenesis of carcinogenesis as well as tumor growth and spread, cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF induce chemokines that attract neutrophils. Neutrophils are key players in the production of reactive oxygen species and carcinogenesis. Another aspect of pro-inflammatory cytokines is the induction of adhesion molecules and metalloproteinases, both of which provide mechanisms for tumor invasion. Blocking cytokines, however, will reduce tumor growth and spread if administered at sufficient concentrations and will require parenteral therapy. However, blocking cytokines will not kill tumor cells nor prevent carcinogenesis. Blocking cytokines is best as an adjunct therapy together with tumorocidal drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Denventer, S. J. H. (2001). Transmembrane TNFα, induction of apoptosis, and the efficacy of TNF-targeting therapies in Crohn's Disease. Gastroenterology, 121, 1242–1246.
Fleischmann, R. M., Schechtman, J., Bennett, R., Handel, M. L., Burmester, G. R., Tesser, J., et al. (2003). Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (r-metHuIL-1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A large, international, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 48, 927–934.
Mohan, A. K., Cote, T. R., Block, J. A., Manadan, A. M., Siegel, J., & Braun, M. M. (2004). Tuberculosis following the use of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 39, 295–299.
Wallis, R. S., Broder, M. S., Wong, J. Y., Hanson, M. E., & Beenhouwer, D. O. (2004). Granulomatous infectious diseases associated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 38, 1261–1265.
Wallis, R. S., Saliu, O. Y., Sofer, C., Stein, D. S., & Schwander, S. K. (2005). Differential effects of TNF blockers on TB immunity. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 64(suppl 3), 132.
Balkwill, F., Charles, K. A., & Mantovani, A. (2005). Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell, 7, 211–217.
Mantovani, A. (2005). Cancer: Inflammation by remote control. Nature, 435, 752–753.
Colombo, M. P., & Mantovani, A. (2005). Targeting myelomonocytic cells to revert inflammation-dependent cancer promotion. Cancer Research, 65, 9113–9116.
El-Omar, E. M., Carrington, M., Chow, W. H., McColl, K. E., Bream, J. H., Young, H. A., et al. (2001). The role of interleukin-1 polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Nature, 412, 99.
Glas, J., Torok, H. P., Schneider, A., Brunnler, G., Kopp, R., Albert, E. D., et al. (2004). Allele 2 of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene is associated with early gastric cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 22, 4746–4752.
Hamajiama, N., Matsuo, K., Saito, T., Tajima, K., Okujma, K., Yamao, K., et al. (2001). Interleukin-1 polymorphims, lifestyle factors and Helicobacter pylori infection. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research, 92, 383–389.
Riedel, S., Kraft, M., Kucharzik, T., Pauels, H. G., Tiemann, M., Steinbuchel, A., et al. (2001). CD4+ Th1-cells predominate in low-grade B-cell lymphoma of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT type). Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 36, 1198–1203.
Gatti, L. L., Burbano, R. R., de Assumpcao, P. P., Smith Mde, A., & Payao, S. L. (2004). Interleukin-1beta polymorphisms, Helicobacter pylori infection in individuals from Northern Brazil with gastric adenocarcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 4, 93–98.
Chang, Y. W., Jang, J. Y., Kim, N. H., Lee, J. W., Lee, H. J., Jung, W. W., et al. (2005). Interleukin-1B (IL-1B) polymorphisms and gastric mucosal levels of IL-1beta cytokine in Korean patients with gastric cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 114, 465–471.
Chandrasekharan, N. V., Dai, H., Roos, K. L., Evanson, N. K., Tomsik, J., Elton, T. S., et al. (2002). COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: Cloning, structure, and expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 13926–13931.
Dinarello, C. A. (1996). Biological basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood, 87, 2095–2147.
Li, S., Ballou, L. R., Morham, S. G., & Blatteis, C. M. (2001). Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates the febrile response of mice to interleukin-1beta. Brain Research, 910, 163–173.
Li, S., Goorha, S., Ballou, L. R., & Blatteis, C. M. (2003). Intracerebroventricular interleukin-6, macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta and IL-18: Pyrogenic and PGE(2)-mediated? Brain Research, 992, 76–84.
Li, S., Wang, Y., Matsumura, K., Ballou, L. R., Morham, S. G., & Blatteis, C. M. (1999). The febrile response to lipopolysaccharide is blocked in cyclooxygenase-2(−/−), but not in cyclooxygenase-1(−/−) mice. Brain Research, 825, 86–94.
Di Mari, J. F., Mifflin, R. C., Adegboyega, P. A., Saada, J. I., & Powell, D. W. (2003). IL-1alpha-induced COX-2 expression in human intestinal myofibroblasts is dependent on a PKCzeta-ROS pathway. Gastroenterology, 124, 1855–1865.
Netea, M. G., Puren, A. J., & Dinarello, C. A. (2000). A short course of oral aspirin increases IL-18-induced interferon-gamma production in whole blood cultures. European Cytokine Network, 11, 379–382.
Voronov, E., Shouval, D. S., Krelin, Y., Cagnano, E., Benharroch, D., Iwakura, Y., et al. (2003). IL-1 is required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 2645–2650.
Jung, Y. J., Isaacs, J. S., Lee, S., Trepel, J., & Neckers, L. (2003). IL-1beta-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1alpha via an NFkappaB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between inflammation and oncogenesis. Faseb Journal, 17, 2115–2117.
Konturek, P. C., Kania, J., Konturek, J. W., Nikiforuk, A., Konturek, S. J., & Hahn, E. G. (2003). H. pylori infection, atrophic gastritis, cytokines, gastrin, COX-2, PPAR gamma and impaired apoptosis in gastric carcinogenesis. Medical Science Monitor, 9, SR53–SR66.
Carrascal, M. T., Mendoza, L., Valcarcel, M., Salado, C., Egilegor, E., Telleria, N., et al. (2003). Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces b16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelium. Cancer Research, 63, 491–497.
Vidal-Vanaclocha, F., Fantuzzi, G., Mendoza, L., Fuentes, A. M., Anasagasti, M. J., Martin, J., et al. (2000). IL-18 regulates IL-1beta-dependent hepatic melanoma metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 734–739.
Lee, J. K., Kim, S. H., Lewis, E. C., Azam, T., Reznikov, L. L., & Dinarello, C. A. (2004). Differences in signaling pathways by IL-1beta and IL-18. Proceedings of the National Academyof Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 8815–8820.
Dinarello, C. A., Cannon, J. G., Mancilla, J., Bishai, I., Lees, J., & Coceani, F. (1991). Interleukin-6 as an endogenous pyrogen: Induction of prostaglandin E2 in brain but not in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Brain Research, 562, 199–206.
Reznikov, L. L., Kim, S. H., Westcott, J. Y., Frishman, J., Fantuzzi, G., Novick, D., et al. (2000). IL-18 binding protein increases spontaneous and IL-1-induced prostaglandin production via inhibition of IFN-gamma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 2174–2179.
Borrello, M. G., Alberti, L., Fischer, A., Degl'innocenti, D., Ferrario, C., Gariboldi, M., et al. (2005). Induction of a proinflammatory program in normal human thyrocytes by the RET/PTC1 oncogene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 14825–14830.
Zou, J., Rudwaleit, M., Brandt, J., Thiel, A., Braun, J., & Sieper, J. (2003). Down-regulation of the nonspecific and antigen-specific T cell cytokine response in ankylosing spondylitis during treatment with infliximab. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 48, 780–790.
Zou, J., Rudwaleit, M., Brandt, J., Thiel, A., Braun, J., & Sieper, J. (2003). Up regulation of the production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma by T cells in ankylosing spondylitis during treatment with etanercept. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 62, 561–564.
Keane, J., Gershon, S., Wise, R. P., Mirabile-Levens, E., Kasznica, J., Schwieterman, W. D., et al. (2001). Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor-α-neutralizing agent. New England Journal of Medicine, 345, 1098–1104.
Brown, S. L., Greene, M. H., Gershon, S. K., Edwards, E. T., & Braun, M. M. (2002). Tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy and lymphoma development: Twenty-six cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 46, 3151–3158.
Song, X., Krelin, Y., Dvorkin, T., Bjorkdahl, O., Segal, S., Dinarello, C. A., et al. (2005). CD11b+/Gr-1+ immature myeloid cells mediate suppression of T cells in mice bearing tumors of IL-1β-secreting Cells. Journal of Immunology, 175, 8200–8208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinarello, C.A. The paradox of pro-inflammatory cytokines in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25, 307–313 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-006-9000-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-006-9000-8