Abstract
A series of cerium-tungsten oxide catalysts was prepared by the co-precipitation method and was evaluated for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x by ammonia (NH3-SCR) over a wide temperature range. These catalysts were characterized by BET, XRD, XPS and H2-TPR analyses. The experimental studies demonstrated that, among cerium-tungsten oxides, CeO2–WO3 with a Ce/W molar ratio of 3/2 exhibited the best activity toward NH3-SCR reactions, N2 selectivity and SO2 durability over a broad temperature range of 175–500 °C at a space velocity of 47,000 h−1. The strong interaction between Ce and W could be the main factor leading to the high activity of the CeO2–WO3 mixed oxide catalyst.
Graphical Abstract
A series of cerium-tungsten oxide catalysts was prepared by the co-precipitation method and was evaluated for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x by ammonia (NH3-SCR) over a wide temperature range. These catalysts were characterized by BET, XRD, XPS and H2-TPR analyses. The experimental studies demonstrated that, among cerium-tungsten oxides, CeO2–WO3 with a Ce/W molar ratio of 3/2 exhibited the best activity toward NH3-SCR reactions, N2 selectivity and SO2 durability over a broad temperature range of 175–500 °C at a space velocity of 47,000 h−1. The strong interaction between Ce and W could be the main factor leading to the high activity of the CeO2–WO3 mixed oxide catalyst.

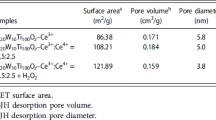
a NO x conversion over pure CeO2, pure WO3 and CeO2–WO3 mixed oxides. b NO conversion as a function of time at 300 °C over CeO2/TiO2, CeO2–WO3/TiO2 and CeO2–WO3 catalyst in the presence of SO2






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch H, Janssen F (1988) Catal Today 2:369
Schneider H, Scharf U, Wokaun A, Baiker A (1994) J Catal 146:545
Busca G, Lietti L, Ramis G, Berti F (1998) Appl Catal B 18:1
Dunn JP, Koppula PR, Stenger HG, Wachs IE (1998) Appl Catal B 19:103
Liu FD, He H, Zhang CB (2008) Chem Commun 17:2043
Xu WQ, Yu YB, Zhang CB, He H (2008) Catal Commun 9:1453
Gao X, Jiang Y, Zhong Y, Luo ZY, Cen KF (2010) J Hazard Mater 174:734
Shen YS, Zhu SM, Qiu T, Shen SB (2009) Catal Commun 11:20
Si ZC, Weng D, Wu XD, Li J, Li G (2010) J Catal 271:43
Qi GS, Yang RT (2004) J Phys Chem B 108:15738
Long RQ, Yang RT (2000) Appl Catal B 27:87
Reddy BM, Khan A, Yamada Y, Kobayashi T, Loridant S, Volta JC (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:162
Xu WQ, He H, Yu YB (2009) J Phys Chem C 113:4426
Chen L, Li JH, Ge MF, Zhu RH (2010) Catal Today 153:77
Chen L, Li JH, Ge MF (2010) Environ Sci Technol 44:9590
Marrero-Lo′pez D, Canales-Va′zquez J, Zhou WZ, Irvine JTS, Nu′n˜ez P (2006) J Solution Chem 179:278
Mamede AS, Payen E, Grange P, Poncelet G, Ion A, Alifanti M, Pârvulescu VI (2004) J Catal 223:1
Noronha FB, Fendley EC, Soares RR, Alvarez WE, Resasco DE (2001) Chem Eng J 82:21
He H, Dai HX, Au CT (2004) Catal Today 90:245
Baek Y, Yong K (2007) J Phys Chem C 111:1213
Leftheriotis G, Papaefthimiou S, Yianoulis P, Siokou A (2001) Thin Solid Films 384:298
Logie V, Maire G, Michel D, Vignes JL (1999) J Catal 188:90
Chen L, Li JH, Ge MF (2009) J Phys Chem C 113:21177
Wu ZB, Jin RB, Liu Y, Wang HQ (2008) Catal Commun 9:2217
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science fund of China (Grant NO. 51078203) and the National High-Tech Research and Development (863) Program of China (Grant No. 2010AA065001 and 2010AA065002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Li, J., Ablikim, W. et al. CeO2–WO3 Mixed Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO x by NH3 Over a Wide Temperature Range. Catal Lett 141, 1859–1864 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-011-0701-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-011-0701-4