Abstract
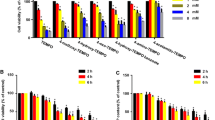
Oxidative cell injury could be induced by different reactive oxygen species (ROS) operating in multiple pathways. The present work is focused on three different models of oxidative stress: the xanthine/xanthine oxidase system (XXO), an extracellular superoxide anion generator; tert-butylhydroperoxide (TBHP), an analogue of lipid hydroperoxides; and doxorubicin (Dox), an anticancer drug. Superoxide and peroxyl radicals, among other ROS, could be effectively scavenged by MnTM-4-PyP, a polyfunctional catalytic antioxidant. In this report, we have addressed the role of MnTM-4-PyP on the protection against the cytotoxicity induced by the three aforementioned oxidants. The effect of MnTM-4-PyP (0.1–100 μM) was evaluated in V79 fibroblasts using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide reduction and the crystal violet assays, as well as the mitotic index. Also, the generation of intracellular ROS was studied by the fluorescent probe dihydroethidium. MnTM-4-PyP has shown significant protective effects against the cytotoxicity of XXO and TBHP, increasing the cell viability in approximately 40% and reducing the intracellular level of ROS. However, no considerable protection occurred against Dox. The three oxidants caused a mitotic index reduction that was not altered by MnTM-4-PyP. In summary, MnTM-4-PyP appears to be a promising agent for the protection against oxidative injury. However, it has shown differential responses, reinforcing the need to study different experimental models for the adequate evaluation of its potentialities as a catalytic antioxidant.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CV:
-
Crystal violet
- DHE:
-
Dihydroethidium
- Dox:
-
Doxorubicin
- MI:
-
Mitotic index
- MnPs:
-
Manganese porphyrins
- MnTM-4-PyP:
-
Manganese(III)tetrakis-(1-methyl-4-pyridyl) porphyrin
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SODm:
-
Superoxide dismutase mimetics
- TBHP:
-
tert-Butylhydroperoxide
- XXO:
-
Xanthine/xanthine oxidase system
References
Awe SO, Adeagbo ASO. Analysis of tert-butyl hydroperoxide induced constrictions of perfused vascular beds in vitro. Life Sci 2002;71:1255–66. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01845-3.
Bai XC, Lu D, Liu AL, Zhang ZM, Li XM, Zou ZP, Zeng WS, Cheng BL, Luo SQ. Reactive oxygen species stimulates receptor activator of NF-κB ligand expression in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 2005;280:17497–506. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409332200.
Batinic-Haberle I, Benov L, Spasojevic I, Fridovich I. The ortho effect makes manganese(III) meso-tetrakis-(N-methylpyridinium-2-yl)porphyrin a powerful and potentially useful superoxide dismutase mimic. J Biol Chem 1998;273:24521–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.38.24521.
Berthiaume JM, Wallace KB. Adriamycin-induced oxidative mitochondrial cardiotoxicity. Cell Biol Toxicol 2007;23:15–25. doi:10.1007/s10565-006-0140-y.
Bienvenue E, Choua S, Lobo-Recio MA, Marzin C, Pacheco P, Seta P, Tarrago G. Structure and superoxide dismutase activity of Ru(lI), Cu(II), and Mn(II) macrocyclic complexes. J Inorg Biochem 1995;57:157–68. doi:10.1016/0162-0134(94)00020-B.
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Mitchell JB. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res 1987;47:936–42.
Chiba K, Kawakami K, Tohyama K. Simultaneous evaluation of cell viability by Neutral Red, MTT and Crystal violet staining assays of the same cells. Toxicol In Vitro 1998;12:251–8. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(97)00107-0.
Day BJ. Catalytic antioxidants: a radical approach to new therapeutics. Drug Discov Today 2004;9:557–66. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(04)03139-3.
Day BJ, Batinic-Haberle I, Crapo JD. Metalloporphyrins are potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation. Free Radic Biol Med 1999;26:730–6. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00261-5.
Denicola A, Radi R. Peroxynitrite and drug-dependent toxicity. Toxicology 2005;208:273–88. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.11.023.
Dumont P, Burton M, Chen QM, Gonos ES, Frippiat C, Mazarati JB, Eliaers F, Remacle J, Toussaint O. Induction of replicative senescence biomarkers by sublethal oxidative stresses in normal human fibroblast. Free Radic Biol Med 2000;28:361–73. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00249-X.
Fattman CL, Schaefer LM, Oury TD. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in biology and medicine. Free Radic Biol Med 2003;35:236–56. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00275-2.
Faulkner KM, Liochev SI, Fridovich I. Stable Mn(III) porphyrins mimic superoxide dismutase in vitro and substitute for it in vivo. J Biol Chem 1994;269:23471–6.
Fernandes AS, Gaspar J, Cabral MF, Caneiras C, Guedes R, Rueff J, Castro M, Costa J, Oliveira NG. Macrocyclic copper(II) complexes: superoxide scavenging activity, structural studies and cytotoxicity evaluation. J Inorg Biochem 2007;101:849–58. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.01.013.
Ferrer-Sueta G, Batinic-Haberle I, Spasojevic I, Fridovich I, Radi R. Catalytic scavenging of peroxynitrite by isomeric Mn(III) N-methylpyridylporphyrins in the presence of reductants. Chem Res Toxicol 1999;12:442–9. doi:10.1021/tx980245d.
Ferrer-Sueta G, Vitturi D, Batinic-Haberle I, Fridovich I, Goldstein S, Czapski G, Radi R. Reactions of manganese porphyrins with peroxynitrite and carbonate radical anion. J Biol Chem 2003;278:27432–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M213302200.
Gauter-Fleckenstein B, Fleckenstein K, Owzar K, Jiang C, Batinic-Haberle I, Vujaskovic Z. Comparison of two Mn porphyrin-based mimics of superoxide dismutase in pulmonary radioprotection. Free Radic Biol Med 2008;44:982–9. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.10.058.
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free radicals in biology and medicine. New York: Oxford University Press; 2007.
Harrington EA, Bruce JL, Harlow E, Dyson N. pRB plays an essential role in cell cycle arrest induced by DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:11945–50. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.20.11945.
Keizer HG, Pinedo HM, Schuurhuis GJ, Joenje H. Doxorubicin (adriamycin): a critical review of free radical-dependent mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther 1990;47:219–31. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(90)90088-J.
Kellogg EW, Fridovich I. Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and singlet oxygen in lipid peroxidation by a xanthine oxidase system. J Biol Chem 1975;250:8812–7.
Kim BY, Han MJ, Chung AS. Effects of reactive oxygen species on proliferation of Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79) cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2001;30:686–98. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00514-1.
Kiyomiya K, Matsuo S, Kurebe M. Differences in intracellular sites of action of adriamycin in neoplastic and normal differentiated cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2001;47:51–6. doi:10.1007/s002800000201.
Konorev EA, Kennedy MC, Kalyanaraman B. Cell-permeable superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase mimetics afford superior protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: the role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates. Arch Biochem Biophys 1999;368:421–8. doi:10.1006/abbi.1999.1337.
Lahaye D, Muthukumaran K, Hung CH, Gryko D, Rebouças JS, Spasojevic I, Batinic-Haberle I, Lindsey JS. Design and synthesis of manganese porphyrins with tailored lipophilicity: investigation of redox properties and superoxide dismutase activity. Bioorg Med Chem 2007;15:7066–86. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.07.015.
Lazzé MC, Pizzala R, Savio M, Stivala LA, Prosperi E, Bianchi L. Anthocyanins protect against DNA damage induced by tert-butyl-hydroperoxide in rat smooth muscle and hepatoma cells. Mutat Res 2003;535:103–15.
Li Y, Cao Z, Zhu H. Upregulation of endogenous antioxidants and phase 2 enzymes by the red wine polyphenol, resveratrol in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells leads to cytoprotection against oxidative and electrophilic stress. Pharmacol Res 2006;53:6–15. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2005.08.002.
Mickuviene I, Kirveliene V, Juodka B. Experimental survey of non-clonogenic viability assays for adherent cells in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro 2004;18:639–48. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2004.02.001.
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L. Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev 2004;56:185–229. doi:10.1124/pr.56.2.6.
Mody N, Parhami F, Sarafian TA, Demer LL. Oxidative stress modulates osteoblastic differentiation of vascular and bone cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2001;31:509–19. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00610-4.
Nilakantan V, Zhou X, Hilton G, Shi Y, Baker JE, Khanna AK, Pieper GM. Antagonizing reactive oxygen by treatment with a manganese(III) metalloporphyrin-based superoxide dismutase mimetic in cardiac transplants. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:898–906. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.11.015.
Park JE, Yang JH, Yoon SJ, Lee JH, Yang ES, Park JW. Lipid peroxidation-mediated cytotoxicity and DNA damage in U937 cells. Biochimie 2003;84:1198–204. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(02)00039-1.
Patel M, Day BJ. Metalloporphyrin class of therapeutic catalytic antioxidants. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1999;20:359–64. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(99)01336-X.
Peshavariya HM, Dusting GJ, Selemidis S. Analysis of dihydroethidium fluorescence for the detection of intracellular and extracellular superoxide produced by NADPH oxidase. Free Radic Res 2007;41:699–712. doi:10.1080/10715760701297354.
Piret JP, Arnould T, Fuks B, Chatelain P, Remacle J, Michiels C. Mitochondria permeability transition-dependent tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced apoptosis in hepatoma HepG2 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2004;67:611–20. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2003.09.026.
Rah DK, Han DW, Baek HS, Hyon SH, Park JC. Prevention of reactive oxygen species-induced oxidative stress in human microvascular endothelial cells by green tea polyphenol. Toxicol Lett 2005;155:269–75. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.10.002.
Rose P, Whiteman M, Huang SH, Halliwell B, Ong CN. β-phenylethyl isothiocyanate-mediated apoptosis in hepatoma HepG2 cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 2003;60:1489–503. doi:10.1007/s00018-003-3150-4.
Santoro A, Lioi MB, Monfregola J, Salzano S, Barbieri R, Ursini MV. l-Carnitine protects mammalian cells from chromosome aberrations but not from inhibition of cell proliferation induced by hydrogen peroxide. Mutat Res 2005;587:16–25.
Scanlon JM, Reynolds IJ. Effects of oxidants and glutamate receptor activation on mitochondrial membrane potential in rat forebrain neurons. J Neurochem 1998;71:2392–400.
Sharma SS, Gupta S. Neuroprotective effect of MnTMPyP, a superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic in global cerebral ischemia is mediated through reduction of oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation. Eur J Pharmacol 2007;561:72–9. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.039.
Takemura G, Fujiwara H. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms to management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2007;49:330–52. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2006.10.002.
Tarpey MM, Wink DA, Grisham MB. Methods for detection of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen: in vitro and in vivo considerations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004;286:R431–R444. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00361.2003.
Wang T, Liu B, Qin L, Wilson B, Hong JS. Protective effect of the SOD/catalase mimetic MnTMPyP on inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mesencephalic neuronal–glial cultures. J Neuroimmunol 2004;147:68–72. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.10.040.
Acknowledgments
A.S.F. acknowledges Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal for the financial support (PhD grant SFRH/BD/28773/2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, A.S., Serejo, J., Gaspar, J. et al. Oxidative injury in V79 Chinese hamster cells: protective role of the superoxide dismutase mimetic MnTM-4-PyP. Cell Biol Toxicol 26, 91–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-009-9120-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-009-9120-3