Abstract
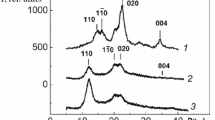
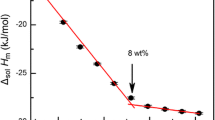
To elucidate the role of urea in dissolution of cellulose in aqueous alkali-urea solvent, the dissolution process was monitored by differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffractometry. Urea had no direct interaction with cellulose in dissolution process, but promoted the decrease of crystallinity. Moreover, the addition of urea increased the dissolved fraction of cellulose in the solvent by 1.5–2.5 times and improved the thermal stability of the solution. Urea might help alkali hydrate to penetrate into crystalline region of cellulose by stabilizing the alkali-swollen cellulose molecules, leading to an increase in dissolved fraction of cellulose. This stabilization may be due to the local accumulation of urea on the hydrophobic surface, preventing the hydrophobic association of dissolved cellulose molecules.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergenstrahle-Wohlert M, Berglund LA, Brady JW, Larsson PT, Westlund P, Wohlert J (2012) Concentration enrichment of urea at cellulose surfaces: results from molecular dynamics simulations and NMR spectroscopy. Cellulose 19:1–12
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5:539–549
Cai J, Zhang L (2006) Unique gelation behavior of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Biomacromolecules 7:183–189
Cai J, Zhang L, Chang C, Cheng G, Chen X, Chu B (2007) Hydrogen-bond-induced inclusion complex in aqueous cellulose/LiOH/urea solution at low temperature. ChemPhysChem 8:1572–1579
Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S, Zhang L (2008) Cellulose aerogels from aqueous alkali hydroxide–urea solution. ChemSusChem 1:149–154
Egal M, Budtova T, Navard P (2008) The dissolution of microcrystalline cellulose in sodium hydroxide-urea aqueous solutions. Cellulose 15:361–370
Glasser WG, Atalla RH, Blackwell J, Brown RM, Burchard W, French AD, Klemm DO, Nishiyama Y (2012) About the structure of cellulose: debating the Lindman hypothesis. Cellulose 19:589–598
Hongo T, Yamane C, Saito M, Okajima K (1996) Super-molecular structures controlling the swelling behavior of regenerated cellulose membranes. Polym J 28:769–779
Isobe N, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S (2012) Mechanism of cellulose gelation from aqueous alkali-urea solution. Carbohydr Polym 89:1298–1300
Isogai A (1997a) NMR analysis of cellulose dissolved in aqueous NaOH solutions. Cellulose 4:99–107
Isogai A (1997b) Properties of handsheets containing cellulose regenerated from cellulose/aqueous NaOH solution. Sen’i Gakkaishi 53:96–100
Isogai A, Atalla RH (1995) Alkaline method for dissolving cellulose. US patent 5410034
Isogai A, Atalla RH (1998) Dissolution of cellulose in aqueous NaOH solutions. Cellulose 5:309–319
Jeffries R, Warwicker JO (1969) The function of swelling in the finishing of cotton. Textile Res J 39:548–559
Kamide K, Saito M (1986) Light scattering and viscometric study of cellulose in aqueous lithium hydroxide. Polym J 18:569–579
Kamide K, Okajima K, Matsui T, Kowsaka K (1984) Study on the solubility of cellulose in aqueous alkali solution by deuteration IR and 13C NMR. Polym J 16:857–866
Kamide K, Kowsaka K, Okajima K (1985) Determination of intramolecular hydrogen bonds and selective coordination of sodium cation in alkalicellulose by CP/MASS 13C NMR. Polym J 17:707–711
Kamide K, Okajima K, Kowsaka K (1992) Dissolution of natural cellulose into aqueous alkali solution: role of super-molecular structure of cellulose. Polym J 24:71–86
Kunze J, Fink HP (2005) Structural changes and activation of cellulose by caustic soda solution with urea. Macromol Symp 223:175–187
Lindman B, Karlström G, Stigsson L (2010) On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J Mol Liq 156:76–81
Lu A, Liu Y, Zhang L, Potthast A (2011) Investigation on metastable solution of cellulose dissolved in NaOH/urea aqueous system at low temperature. J Phys Chem B 115:12801–12808
Lue A, Liu Y, Zhang L, Potthas A (2011) Light scattering study on the dynamic behaviour of cellulose inclusion complex in LiOH/urea aqueous solution. Polymer 52:3857–3864
Medronho B, Romano A, Miguel MG, Stigsson L, Lindman B (2012) Rationalizing cellulose (in)solubility: reviewing basic physicochemical aspects and role of hydrophobic interactions. Cellulose 19:581–587
Nishimura H, Okano T, Sarko A (1991) Mercerization of cellulose. 5. Crystal and molecular structure of Na-cellulose I. Macromolecules 24:759–770
Okano T, Sarko A (1984) Mercerization of cellulose. I. X-ray diffraction evidence for intermediate structures. J Appl Polym Sci 29:4175–4182
Porro F, Bédué O, Chanzy H, Heux L (2007) Solid-state 13C NMR study of Na–cellulose complexes. Biomacromolecules 8:2586–2593
Qi H, Chang C, Zhang L (2008) Effects of temperature and molecular weight on dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Cellulose 15:779–787
Schwarzkoph O (1932) Zur Kenntnis der Alkalicellulose. Z Elektrochem 38:353–358
Shimizu S (2011) The effect of urea on hydrophobic hydration: preferential interaction and the enthalpy of transfer. Chem Phys Lett 517:76–79
Sobue H, Kiessig H, Hess K (1939) Das system cellulose-Natriumhydroxyd-Wasser in abhängigkeit von der temperatur. Z Physik Chem B 43:309–328
Tanford C (1964) Isothermal unfolding of globular proteins in aqueous urea solutions. J Am Chem Soc 86:2050–2059
Wada M, Okano T (2001) Localization of Iα and Iβ phases in algal cellulose revealed by acid treatments. Cellulose 8:183–188
Wada M, Okano T, Sugiyama J (1997) Synchrotron-radiated X-ray and neutron diffraction study of native cellulose. Cellulose 4:221–232
Wang Y, Deng Y (2009) The kinetics of cellulose dissolution in sodium hydroxide solution at low temperatures. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1398–1405
Warwicker JO, Jeffries R, Colbran RL, Robinson RN (1966) A review of the literature on the effect of caustic soda and other swelling agents on the fine structure of cotton. The cotton silk and man-made fibres research association, Manchester
Yamane C, Mori M, Saito M, Okajima K (1996) Structures and mechanical properties of cellulose filament spun from cellulose/aqueous NaOH solution system. Polym J 28:1039–1047
Yamashiki T, Kamide K, Okajima K, Kowsaka K, Matsui T, Fukase H (1988) Some characteristic features of dilute aqueous alkali solutions of specific alkali concentration (2.5 mol l−1) which possess maximum solubility power against cellulose. Polym J 20:447–457
Yamashiki T, Matsui T, Saitoh M, Okajima K, Kamide K, Sawada T (1990) Characterisation of cellulose treated by the steam explosion method. Part 2: effect of treatment conditions on changes in morphology, degree of polymerisation, solubility in aqueous sodium hydroxide and supermolecular structure of soft wood pulp during steam explosion. Br Polym J 22:121–128
Zangi R, Zhou R, Berne BJ (2009) Urea’s action on hydrophobic interactions. J Am Chem Soc 131:1535–1541
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 23580226) and a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS fellows (No. 24-7759). N.I. acknowledges financial support from JSPS Research Fellowship for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isobe, N., Noguchi, K., Nishiyama, Y. et al. Role of urea in alkaline dissolution of cellulose. Cellulose 20, 97–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9800-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9800-7