SUMMARY
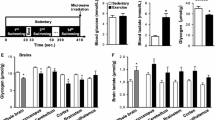
This study was designed to investigate the effect of acute and chronic high-intensity treadmill exercise on changes in plasma lactate and brain neuropeptide (NPY), leucine-enkephalin (L-ENK), and dynorpin A1–13 (DYN A1–13). Avidin–biotin complex (ABC) immunohistochemistry and image pattern analysis were used to observe the effect of chronic (total 7 weeks) and acute treadmill exercise (an initial speed of 15 m min−1 gradually increased to 35 m min−1 with 0°, 20–25 min per day duration) on the changes of NPY, L-ENK, and DYN A1–13 in different areas of rat brain. Plasma lactate was also measured in response to such exercise. Compared with preexercise control (P < 0.01), plasma lactate concentration significantly increased in the immediate postexercise; but it returned to the normal level soon after the 30 min postexercise. The content of NPY in paraventricular (PVN), dorsomedial (DMN), and ventromedial (VMN) hypothalamic nuclei continued to increase in 0, 30, and 180 min postexercise compared with preexercise control (P < 0.01). The content of L-ENK in caudate-putamen (CPu) significantly increased in the immediate postexercise compared with preexercise control (P < 0.01), but it gradually returned to the normal level after the 180 min postexercise. However, the content of DYN A1–13 in PVN rose substantially only in 30 min postexercise in comparison with the preexercise control (P < 0.01). Thus, different changes of NPY, L-ENK, and DYN A1–13 in response to such high-intensity exercise depend on the brain region and the time examined, especially, the contents of NPY in different brain regions continuously remain at a high level after such high-intensity exercise. And this high level might reduce energy expenditure and thus contribute to the stimulation of brain NPY neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Barry, E. L., and Ambrose, A. D. M. (2004). Chronic exercise lowers the defended body weight gain and adiposity in diet-induced obese rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 286:771–778.
Bi, S., Robinson, B. M., and Moran, T. H. (2003). Acute food deprivation and chronic food restriction differentially affect hypothalamic NPY mRNA expression. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 285:R1030–R1036.
Billington, C. J., Briggs, J. E., Grace, M., and Levine, A. S. (1991). Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of neuropeptide Y on energy metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 260:R321–R327.
Bucinskaite, V., Lundeberg, T., Stenfors, C., Ekblom, A., Dahlin, L., and Theodorsson, E. (1994). Effects of electro-acupuncture and physical exercise on regional concentrations of neuropeptides in rat brain. Brain Res. 12(666):128–132.
Chen, J. X., Yang, W. Y., Liang, R., Lu, D. Y., and Zhou, W. A. (1997). Experimental study of the effects of long term and high intensity exercise on plasma β-endorphin, dynorphin A1–13, leucine–enkephalin and lactate in rats. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 14:371.
Chronwall, B. M., DiMaggio, D. A., Massari, V. J., Pickel, V. M., Ruggiero, D. A., and O’Donohue, T. L. (1985). The anatomy of neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience 15:1159–1181.
Corbett, S. W., Stern, J. S., and Keesey, R. E. (1986). Energy expenditure in rats with diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 44:173–180.
Elitsur, Y., Luk, G. D., Colberg, M., Gesell, M. S., Dosescu, J., and Moshier, J. A. (1994). Neuropeptide Y (NPY) enhances proliferation of human colonic lamina propria lymphocytes. Neuropeptides 26(5):289–295.
Gibson, S. J., Polak, J. M., Allen, J. M., Adrian, T. E., Kelly, J. S., and Bloom, S. R. (1984). The distribution and origin of a novel brain peptide, neuropeptide Y in the spinal cord of several mammals. J. Comp. Neurol. 227(1):79–91.
Hill, J. O., Davis, J. R., and Tagliaferro, A. R. (1983). Effects of diet and exercise training on thermogenesis in adult female rats. Physiol. Behav. 31:133–135.
Hill, J. O., Davis, J. R., Tagliaferro, A. R., and Stewart, J. (1984). Dietary obesity and exercise in young rats. Physiol. Behav. 33:321–328.
Hokfelt, T., Lundberg, J. M., Terenius, L., Jancso, G., and Kimmel, J. (1981). Avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP) immunoreactive neurons in the spinal cord and spinal trigeminal nucleus. Peptides 2(1):81–87.
Hughes, J., Smith, T. W., Kosterlitz, H. W., Fothergill, L. A., Morgan, B. A., and Morris, H. R. (1975). Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature 258(5536):577–580.
Jang, M. H., Shin, M. C., Lim, B. V., Chung, J. H., Kang, H. S., Kang, S. A., Choue, R. W., Kim, E. H., and Kim, C. J. (2002). Nicotine administration decreases nitric oxide synthase expression in the hypothalamus of food deprived rats. Neurosci. Lett. 322:29–32.
Jiaxu, C., Weiyi, Y. (2000). Influence of acute and chronic treadmill exercise on rat brain POMC gene expression. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 32:954–957.
Jensen, E. W., Espersen, K., Kanstrup, I. L., and Christensen, N. J. (1994). Exercise-induced changes in plasma catecholamines and neuropeptide Y: Relation to age and sampling times. J. Appl. Physiol. 76(3):1269–1273.
Kalra, S. P., and Crowley, W. R. (1992). Neuropeptide Y: A novel neuroendocrine peptide in the control of pituiary hormone secretion and its relation to luteinizing hormone. Front Neuroendocrinol. 13:1–46.
Karamouzis, I., Karamouzis, M., Vrabas, I. S., Christoulas, K., Kyriazis, N., Giannoulis, E., and Mandroukas, K. (2002). The effects of marathon swimming on serum leptin and plasma neuropeptide Y levels. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 40(2):132–136.
Krukoff, T. L. (1987). Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in cat spinal cord with special reference to autonomic areas. Brain Res. 415:300–308.
Levenson, C. W., Moore, J. B.(1998). Response of rat adrenal neuropeptide Y and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA to acute stress is enhanced by long-term voluntary exercise. Neurosci. Lett. 20(242, 3):177–179.
Levin, B. E. (1999). Arcuate NPY neurons and energy homeostasis in diet-induced obese and resistant rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 276:R382–R387.
Levin, B. E., and Dunn-Meynell, A. A. (1997). Dysregulation of arcuate nucleus preproneuropeptide Y mRNA in diet-induced obese rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 272:R1365–R1370.
Lewis, D. E., Shellard, L., Koeslag, D. G., Boer, D. E., McCarthy, H. D., McKibbin, P. E., Russell, J. C., and Williams, G. (1993). Intense exercise and food restriction cause similar hypothalamic neuropeptide Y increases in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 264:E279–E284.
Li, C., Chen, P., and Smith, M. S. (1998). Neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons in the arcuate nucleus (ARH) and dorsomedial nucleus (DMH), areas activated during lactation, project to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH). Regul. Peptides 75/76:98–100.
Morris, M. J., Russell, A. E., Kapoor, V., Cain, M. D., Elliott, J. M., West, M. J., Wing, L. M., and Chalmers, J. P. (1986). Increases in plasma neuropeptide Y concentrations during sympathetic activation in man. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 17(2):143–149.
O’Donohue, T. L., Chronwall, B. M., and Pruss, R. M. (1985). Neuropeptide Y and peptide YY in neuronal and endocrine system. Peptides 6:755–768.
Richard, D. (1995). Exercise and the neurobiological control of food intake and energy expenditure. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 19(Suppl. 4):S73–S79.
Shin, M. S., Kim, H., Chang, H. K., Lee, T. H., Jang, M. H., Shin, M. C., Lim, B. V., Lee, H. H., Kim, Y. P., Yoon, J. H., Jeong, I. G., Kim, C. J. (2003). Treadmill exercise suppresses diabetes-induced increment of neuropeptide Y expression in the hypothalamus of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 346(3):157–160.
Tatemoto, K., Carlquist, M., Mutt, V. (1982). Neuropeptide Y—A novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pan creatic polypeptide. Nature 296:659–60.
Verger, P., Lanteaume, M. T., and Louis-Sylvestre, J. (1994). Free food choice after acute exercise in men. Appetite 22:159–164.
Walker, H. C., and Romsos, D. R. (1993). Similar effects of NPY on energy metabolism and on plasma insulin in adrenalectomized ob/ob and lean mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 264:E226–E230.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30000216), Teaching and Research Award Program for Outstanding Young Teachers in Higher Education Institutes of Ministry of Education, China, Foundation for the Authors of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertations of China (No. 200059), and Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation (No. 81037). Gratitude is expressed to Associate Professor Min-Juan Wang, working at Department of Educational Technology, San Diego State University, for her kindly revised the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JX., Zhao, X., Yue, GX. et al. Influence of Acute and Chronic Treadmill Exercise on Rat Plasma Lactate and Brain NPY, L-ENK, DYN A1–13 . Cell Mol Neurobiol 27, 1–10 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9110-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9110-4