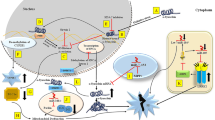
Abstract
Epigenetics play an essential role in the occurrence and improvement of many diseases. Evidence shows that epigenetic modifications are crucial to the regulation of gene expression. DNA methylation is closely linked to embryonic development in mammalian. In recent years, epigenetic drugs have shown unexpected therapeutic effects on neurological diseases, leading to the study of the epigenetic mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases. Unlike genetics, epigenetics modify the genome without changing the DNA sequence. Research shows that epigenetics is involved in all aspects of neurodegenerative diseases. The study of epigenetic will provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanism of neurodegenerative diseases, which may lead to new treatments and diagnoses. This article reviews the role of epigenetic modifications neurodegenerative diseases with dyskinesia, and discusses the therapeutic potential of epigenetic drugs in neurodegenerative diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AGO2:
-
Argonaute 2
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ALKHB5/10B:
-
AlkB homolog 5/10B
- B RG 1 :
-
Brahma-related gene 1
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CpG:
-
Cytosine-phosphate-guanine
- D2:
-
Dopamine receptor 2
- D3:
-
Dopamine receptor 3
- DNMT:
-
DNA methyl-transferase
- ELP3:
-
Elongator protein 3
- eIF3:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3
- FRDA:
-
Friedreich ataxia
- FTD:
-
Frontotemporal dementia
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- FUS:
-
Fused in sarcoma
- HATs:
-
Histone acetyltransferases
- HDACs:
-
Histone deacetylases
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- HDACi:
-
HDAC inhibitor
- H3K9:
-
Histone H3 lysine 9
- HnRNP:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- IGF2BP 1/2/3:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1/2/3
- JmjC:
-
Family and members of the Jumonji C
- lncRNAs:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- LSD:
-
Lysine-specific demethylase
- m6A:
-
N6-Methyladenosine
- METTL3/14/16:
-
Methyltransferase like 3/14/16
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- nBAF:
-
Neuronal BRG1-associated factor complex
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate
- NURD:
-
Nucleosome remodeling histone deacetylase
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- piRNA:
-
Piwi related RNA
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb-repressive complex 2
- PTM:
-
Post-transcriptional modifier
- PRRC2A:
-
Proline rich coiled-coil 2A
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- SMA:
-
Spinal muscular atrophy
- SMN1 :
-
Survival motor neuron 1
- SNCA:
-
α-Synuclein
- snRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- snoRNA:
-
Small nucleolar RNA
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- SOD1:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SIRT:
-
Sirtuins
- TDP-43:
-
TAR-DNA Binding Protein 43
- TET:
-
Ten-eleven translocation
- tsRNA:
-
TRNA derived small RNA
- TUG1 :
-
Taurine-upregulated gene 1
- YTHDF1/2/3:
-
YTH domain-containing family protein 1/2/3
- YTHDC1/2:
-
YTH domain-containing protein ½
- 5caC:
-
5-Carboxylcytosine
- 5hmC:
-
5MC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
- 5mC:
-
5-Methylcytosine
References
Abel T, Zukin RS (2008) Epigenetic targets of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2007.12.002
Adams JM, Cory S (1975) Modified nucleosides and bizarre 5’-termini in mouse myeloma mRNA. Nature 255:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/255028a0
Alarcon CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF (2015) N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 519:482–485. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14281
Al-Mahdawi S, Pinto RM, Ismail O, Varshney D, Lymperi S, Sandi C, Trabzuni D, Pook M (2008) The Friedreich ataxia GAA repeat expansion mutation induces comparable epigenetic changes in human and transgenic mouse brain and heart tissues. Hum Mol Genet 17:735–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm346
Alunni A, Bally-Cuif L (2016) A comparative view of regenerative neurogenesis in vertebrates. Development 143:741–753. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.122796
Arney KL, Fisher AG (2004) Epigenetic aspects of differentiation. J Cell Sci 117:4355–4363. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01390
Audia JE, Campbell RM (2016) Histone modifications and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8(4):a019521. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a019521
Aumiller V, Forstemann K (2008) Roles of microRNAs beyond development–metabolism and neural plasticity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779:692–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.04.008
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T (2011) Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res 21(3):381–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.22
Bennett SA, Tanaz R, Cobos SN, Torrente MP (2019) Epigenetics in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a role for histone post-translational modifications in neurodegenerative disease. Transl Res 204:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2018.10.002
Berger SL (2002) Histone modifications in transcriptional regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00279-4
Berson A, Nativio R, Berger SL, Bonini NM (2018) Epigenetic regulation in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 41:587–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.05.005
Berson A, Sartoris A, Nativio R, Van Deerlin V, Toledo JB, Porta S, Liu S, Chung CY, Garcia BA, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Johnson FB, Berger SL, Bonini NM (2017) TDP-43 promotes neurodegeneration by impairing chromatin remodeling. Curr Biol 27:3579–3590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.10.024
Bestor TH (2000) The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Genet 9:2395–2402. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/9.16.2395
Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16:6–21. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.947102
Bochtler M, Kolano A, Xu GL (2017) DNA demethylation pathways: additional players and regulators. BioEssays 39:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201600178
Bodi Z, Button JD, Grierson D, Fray RG (2010) Yeast targets for mRNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res 38:5327–5335. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq266
Bourinaris T, Houlden H (2018) C9orf72 and its relevance in parkinsonism and movement disorders: a comprehensive review of the literature. Mov Disord Clin Pract 5:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12677
Brenner C, Fuks F (2006) DNA methyltransferases: facts, clues, mysteries. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 301:45–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-31390-7_3
Bronisz A, Carey HA, Godlewski J, Sif S, Ostrowski MC, Sharma SM (2014) The multifunctional protein fused in sarcoma (FUS) is a coactivator of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF). J Biol Chem 289:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.493874
Canaani D, Kahana C, Lavi S, Groner Y (1979) Identification and mapping of N6-methyladenosine containing sequences in simian virus 40 RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 6:2879–2899. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/6.8.2879
Carey HA, Bronisz A, Cabrera J, Hildreth BR, Cuitino M, Fu Q, Ahmad A, Toribio RE, Ostrowski MC, Sharma SM (2016) Failure to target RANKL signaling through p38-MAPK results in defective osteoclastogenesis in the microphthalmia cloudy-eyed mutant. J Cell Physiol 231:630–640. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25108
Carissimi C, Fulci V, Macino G (2009) MicroRNAs: novel regulators of immunity. Autoimmun Rev 8:520–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2009.01.008
Che XQ, Zhao QH, Huang Y, Li X, Ren RJ, Chen SD, Guo QH, Wang G (2018) Mutation screening of the CHCHD2 gene for Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia in Chinese Mainland population. J Alzheimers Dis 61:1283–1288. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170692
Chen CC, Wang KY, Shen CK (2012) The mammalian de novo DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B are also DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine dehydroxymethylases. J Biol Chem 287:33116–33121. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C112.406975
Chen X, Yu C, Guo M, Zheng X, Ali S, Huang H, Zhang L, Wang S, Huang Y, Qie S, Wang J (2019) Down-regulation of m6A mRNA methylation is involved in dopaminergic neuronal death. Acs Chem Neurosci 10:2355–2363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00657
Cheng X (1995) Structure and function of DNA methyltransferases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 24:293–318. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.001453
Chen-Kiang S, Nevins JR, Darnell JJ (1979) N-6-methyl-adenosine in adenovirus type 2 nuclear RNA is conserved in the formation of messenger RNA. J Mol Biol 135:733–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(79)90174-8
Chestnut BA, Chang Q, Price A, Lesuisse C, Wong M, Martin LJ (2011) Epigenetic regulation of motor neuron cell death through DNA methylation. J Neurosci 31:16619–16636. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1639-11.2011
Chou CC, Zhang Y, Umoh ME, Vaughan SW, Lorenzini I, Liu F, Sayegh M, Donlin-Asp PG, Chen YH, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, Powers MA, Kukar T, Hales CM, Gearing M, Cairns NJ, Boylan KB, Dickson DW, Rademakers R, Zhang YJ, Petrucelli L, Sattler R, Zarnescu DC, Glass JD, Rossoll W (2018) TDP-43 pathology disrupts nuclear pore complexes and nucleocytoplasmic transport in ALS/FTD. Nat Neurosci 21:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0047-3
Chuang DM, Leng Y, Marinova Z, Kim HJ, Chiu CT (2009) Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative conditions. Trends Neurosci 32:591–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2009.06.002
Cobos SN, Bennett SA, Torrente MP (2019) The impact of histone post-translational modifications in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1865:1982–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.019
Coppede F (2014) The potential of epigenetic therapies in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Genet 5:220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00220
Cudkowicz ME, Andres PL, Macdonald SA, Bedlack RS, Choudry R, Brown RJ, Zhang H, Schoenfeld DA, Shefner J, Matson S, Matson WR, Ferrante RJ (2009) Phase 2 study of sodium phenylbutyrate in ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10(2):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/17482960802320487
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB (2003) Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J 370:737–749. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20021321
Desplats P, Spencer B, Coffee E, Patel P, Michael S, Patrick C, Adame A, Rockenstein E, Masliah E (2011) Alpha-synuclein sequesters Dnmt1 from the nucleus: a novel mechanism for epigenetic alterations in Lewy body diseases. J Biol Chem 286:9031–9037. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C110.212589
Dharap A, Bowen K, Place R, Li LC, Vemuganti R (2009) Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:675–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.157
Dias BG, Ressler KJ (2014) Parental olfactory experience influences behavior and neural structure in subsequent generations. Nat Neurosci 17:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3594
Dietz KC, Casaccia P (2010) HDAC inhibitors and neurodegeneration: at the edge between protection and damage. Pharmacol Res 62:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2010.01.011
Dion MF, Altschuler SJ, Wu LF, Rando OJ (2005) Genomic characterization reveals a simple histone H4 acetylation code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5501–5506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500136102
Du ZW, Chen H, Liu H, Lu J, Qian K, Huang CL, Zhong X, Fan F, Zhang SC (2015) Generation and expansion of highly pure motor neuron progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun 6:6626. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7626
Ehrnhoefer DE, Skotte NH, Ladha S, Nguyen YT, Qiu X, Deng Y, Huynh KT, Engemann S, Nielsen SM, Becanovic K, Leavitt BR, Hasholt L, Hayden MR (2014) p53 increases caspase-6 expression and activation in muscle tissue expressing mutant huntingtin. Hum Mol Genet 23:717–729. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt458
Engel M, Chen A (2018) The emerging role of mRNA methylation in normal and pathological behavior. Genes Brain Behav 17:e12428. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12428
Esteller M (2002) CpG island hypermethylation and tumor suppressor genes: a booming present, a brighter future. Oncogene 21:5427–5440. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205600
Fang MY, Markmiller S, Vu AQ, Javaherian A, Dowdle WE, Jolivet P, Bushway PJ, Castello NA, Baral A, Chan MY, Linsley JW, Linsley D, Mercola M, Finkbeiner S, Lecuyer E, Lewcock JW, Yeo GW (2019) Small-molecule modulation of TDP-43 recruitment to stress granules prevents persistent TDP-43 accumulation in ALS/FTD. Neuron 103:802–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.048
Felsenfeld G, Groudine M (2003) Controlling the double helix. Nature 421(6921):448–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01411
Ferlita A, Battaglia R, Andronico F, Caruso S, Cianci A, Purrello M, Pietro CD (2018) Non-coding RNAs in endometrial physiopathology. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072120
Fleming AB, Kao CF, Hillyer C, Pikaart M, Osley MA (2008) H2B ubiquitylation plays a role in nucleosome dynamics during transcription elongation. Mol Cell 31(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.025
Floris G, Borghero G, Cannas A, Di Stefano F, Murru MR, Corongiu D, Cuccu S, Tranquilli S, Cherchi MV, Serra A, Loi G, Marrosu MG, Chio A, Marrosu F (2015) Clinical phenotypes and radiological findings in frontotemporal dementia related to TARDBP mutations. J Neurol 262:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7575-5
Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Ropero S, Setien F, Ballestar ML, Heine-Suner D, Cigudosa JC, Urioste M, Benitez J, Boix-Chornet M, Sanchez-Aguilera A, Ling C, Carlsson E, Poulsen P, Vaag A, Stephan Z, Spector TD, Wu YZ, Plass C, Esteller M (2005) Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10604–10609. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500398102
Gao J, Wang L, Yan T, Perry G, Wang X (2019) TDP-43 proteinopathy and mitochondrial abnormalities in neurodegeneration. Mol Cell Neurosci 100:103396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2019.103396
Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M (1987) CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol 196:261–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9
Govin J, Caron C, Lestrat C, Rousseaux S, Khochbin S (2004) The role of histones in chromatin remodelling during mammalian spermiogenesis. Eur J Biochem 271:3459–3469. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04266.x
Greaves CV, Rohrer JD (2019) An update on genetic frontotemporal dementia. J Neurol 266:2075–2086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09363-4
Grunstein M (1997) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/38664
Guo J, Tang HW, Li J, Perrimon N, Yan D (2018a) Xio is a component of the Drosophila sex determination pathway and RNA N(6)-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:3674–3679. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720945115
Guo P, Chen W, Li H, Li M, Li L (2018b) The histone acetylation modifications of breast cancer and their therapeutic implications. Pathol Oncol Res 24:807–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0433-5
Hahnen E, Hauke J, Trankle C, Eyupoglu IY, Wirth B, Blumcke I (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: possible implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 17:169–184. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.17.2.169
Hashimoto H, Liu Y, Upadhyay AK, Chang Y, Howerton SB, Vertino PM, Zhang X, Cheng X (2012) Recognition and potential mechanisms for replication and erasure of cytosine hydroxymethylation. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4841–4849. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks155
Hassig CA, Schreiber SL (1997) Nuclear histone acetylases and deacetylases and transcriptional regulation: HATs off to HDACs. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1:300–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-5931(97)80066-x
Hauke J, Riessland M, Lunke S, Eyupoglu IY, Blumcke I, El-Osta A, Wirth B, Hahnen E (2009) Survival motor neuron gene 2 silencing by DNA methylation correlates with spinal muscular atrophy disease severity and can be bypassed by histone deacetylase inhibition. Hum Mol Genet 18:304–317. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn357
Hess ME, Hess S, Meyer KD, Verhagen LA, Koch L, Bronneke HS, Dietrich MO, Jordan SD, Saletore Y, Elemento O, Belgardt BF, Franz T, Horvath TL, Ruther U, Jaffrey SR, Kloppenburg P, Bruning JC (2013) The fat mass and obesity associated gene (Fto) regulates activity of the dopaminergic midbrain circuitry. Nat Neurosci 16:1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3449
Hockly E, Richon VM, Woodman B, Smith DL, Zhou X, Rosa E, Sathasivam K, Ghazi-Noori S, Mahal A, Lowden PA, Steffan JS, Marsh JL, Thompson LM, Lewis CM, Marks PA, Bates GP (2003) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, ameliorates motor deficits in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(4):2041–2046. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0437870100
Hsieh J, Gage FH (2005) Chromatin remodeling in neural development and plasticity. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(6):664–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2005.09.002
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y, Qi M, Lu Z, Shi H, Wang J, Cheng Y, Luo G, Dai Q, Liu M, Guo X, Sha J, Shen B, He C (2017) Ythdc2 is an N(6)-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res 27:1115–1127. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.99
Hu Y, Chopra V, Chopra R, Locascio JJ, Liao Z, Ding H, Zheng B, Matson WR, Ferrante RJ, Rosas HD, Hersch SM, Scherzer CR (2011) Transcriptional modulator H2A histone family, member Y (H2AFY) marks Huntington disease activity in man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17141–17146. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1104409108
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, Hu YC, Huttelmaier S, Skibbe JR, Su R, Deng X, Dong L, Sun M, Li C, Nachtergaele S, Wang Y, Hu C, Ferchen K, Greis KD, Jiang X, Wei M, Qu L, Guan JL, He C, Yang J, Chen J (2018) Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol 20:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Hwang JY, Aromolaran KA, Zukin RS (2017) The emerging field of epigenetics in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:347–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.46
Imhof A, Yang XJ, Ogryzko VV, Nakatani Y, Wolffe AP, Ge H (1997) Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases. Curr Biol 7:689–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00296-x
Intihar TA, Martinez EA, Gomez-Pastor R (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction in huntington’s disease; interplay between HSF1, p53 and PGC-1alpha transcription factors. Front Cell Neurosci 13:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00103
Iyer LM, Abhiman S, Aravind L (2011) Natural history of eukaryotic DNA methylation systems. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 101:25–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-387685-0.00002-0
Janssen C, Schmalbach S, Boeselt S, Sarlette A, Dengler R, Petri S (2010) Differential histone deacetylase mRNA expression patterns in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181ddd404
Jeyaseelan K, Lim KY, Armugam A (2008) MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 39:959–966. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.500736
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG, He C (2011) N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 7:885–887. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.687
Johnson R (2012) Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 46:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.006
Jowaed A, Schmitt I, Kaut O, Wullner U (2010) Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson’s disease patients’ brains. J Neurosci 30:6355–6359. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6119-09.2010
Kaminsky ZA, Tang T, Wang SC, Ptak C, Oh GH, Wong AH, Feldcamp LA, Virtanen C, Halfvarson J, Tysk C, McRae AF, Visscher PM, Montgomery GW, Gottesman II, Martin NG, Petronis A (2009) DNA methylation profiles in monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Nat Genet 41:240–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.286
Kaneko S, Son J, Bonasio R, Shen SS, Reinberg D (2014) Nascent RNA interaction keeps PRC2 activity poised and in check. Genes Dev 28:1983–1988. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.247940.114
Kazantsev AG, Thompson LM (2008) Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:854–868. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2681
Kennedy EM, Bogerd HP, Kornepati A, Kang D, Ghoshal D, Marshall JB, Poling BC, Tsai K, Gokhale NS, Horner SM, Cullen BR (2017a) Posttranscriptional m(6)A editing of HIV-1 mRNAs enhances viral gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 22:830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.010
Kennedy EM, Courtney DG, Tsai K, Cullen BR (2017b) Viral epitranscriptomics. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02263-16
Kennerdell JR, Liu N, Bonini NM (2018) MiR-34 inhibits polycomb repressive complex 2 to modulate chaperone expression and promote healthy brain aging. Nat Commun 9:4188. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06592-5
Konsoula Z, Barile FA (2012) Epigenetic histone acetylation and deacetylation mechanisms in experimental models of neurodegenerative disorders. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 66:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2012.08.001
Kooistra SM, Helin K (2012) Molecular mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3327
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128:693–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005
Kuo MH, Allis CD (1998) Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. BioEssays 20:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199808)20:8%3c615::AID-BIES4%3e3.0.CO;2-H
Lazo-Gomez R, Ramirez-Jarquin UN, Tovar-Y-Romo LB, Tapia R (2013) Histone deacetylases and their role in motor neuron degeneration. Front Cell Neurosci 7:243. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00243
Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, Benichou B, Cruaud C, Millasseau P, Zeviani M, Et A (1995) Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 80:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90460-3
Lence T, Akhtar J, Bayer M, Schmid K, Spindler L, Ho CH, Kreim N, Andrade-Navarro MA, Poeck B, Helm M, Roignant JY (2016) m(6)A modulates neuronal functions and sex determination in drosophila. Nature 540:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20568
Levis R, Penman S (1978) 5’-terminal structures of poly(A)+ cytoplasmic messenger RNA and of poly(A)+ and poly(A)- heterogeneous nuclear RNA of cells of the dipteran Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 120:487–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(78)90350-9
Li E, Zhang Y (2014) DNA methylation in mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6:a19133. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a019133
Li J, Hart RP, Mallimo EM, Swerdel MR, Kusnecov AW, Herrup K (2013) EZH2-mediated H3K27 trimethylation mediates neurodegeneration in ataxia-telangiectasia. Nat Neurosci 16:1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3564
Li J, Sun Y, Chen J (2018) Identification of critical genes and miRNAs associated with the development of Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 65:527–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1129-8
Li L, Zang L, Zhang F, Chen J, Shen H, Shu L, Liang F, Feng C, Chen D, Tao H, Xu T, Li Z, Kang Y, Wu H, Tang L, Zhang P, Jin P, Shu Q, Li X (2017) Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) protein regulates adult neurogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 26:2398–2411. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx128
Li SH, Su SY, Liu JL (2015) Differential regulation of microRNAs in patients with ischemic stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res 12:214–221. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567202612666150605121709
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, Dai Q, Chen W, He C (2014) A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol 10:93–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1432
Liutkeviciute Z, Lukinavicius G, Masevicius V, Daujotyte D, Klimasauskas S (2009) Cytosine-5-methyltransferases add aldehydes to DNA. Nat Chem Biol 5:400–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.172
Marques SC, Oliveira CR, Pereira CM, Outeiro TF (2011) Epigenetics in neurodegeneration: a new layer of complexity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.08.008
Martin C, Zhang Y (2005) The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:838–849. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1761
Matsuda T, Irie T, Katsurabayashi S, Hayashi Y, Nagai T, Hamazaki N, Adefuin A, Miura F, Ito T, Kimura H, Shirahige K, Takeda T, Iwasaki K, Imamura T, Nakashima K (2019) Pioneer factor NeuroD1 rearranges transcriptional and epigenetic profiles to execute microglia-neuron conversion. Neuron 101:472–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.12.010
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Olson EN (2001) Control of muscle development by dueling HATs and HDACs. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00224-0
Merkerova M, Belickova M, Bruchova H (2008) Differential expression of microRNAs in hematopoietic cell lineages. Eur J Haematol 81:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2008.01111.x
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J, Zinoviev A, Skabkin MA, Elemento O, Pestova TV, Qian SB, Jaffrey SR (2015) 5’ UTR m(6)A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell 163:999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.012
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2012) Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 149:1635–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003
Migliore L, Coppede F (2009) Genetics, environmental factors and the emerging role of epigenetics in neurodegenerative diseases. Mutat Res 667:82–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.10.011
Min SW, Cho SH, Zhou Y, Schroeder S, Haroutunian V, Seeley WW, Huang EJ, Shen Y, Masliah E, Mukherjee C, Meyers D, Cole PA, Ott M, Gan L (2010) Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron 67:953–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044
Mitropoulos K, Merkouri PE, Xiromerisiou G et al (2017) Genomic variants in the FTO gene are associated with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Greek patients. Hum Genomics 11:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-017-0126-2
Morahan JM, Yu B, Trent RJ, Pamphlett R (2007) Are metallothionein genes silenced in ALS? Toxicol Lett 168:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.11.003
Narayan P, Ayers DF, Rottman FM, Maroney PA, Nilsen TW (1987) Unequal distribution of N6-methyladenosine in influenza virus mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol 7:1572–1575. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.7.4.1572
Nathan D, Ingvarsdottir K, Sterner DE, Bylebyl GR, Dokmanovic M, Dorsey JA, Whelan KA, Krsmanovic M, Lane WS, Meluh PB et al (2006) Histone sumoylation is a negative regulator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and shows dynamic interplay with positive-acting histone modifications. Genes Dev 20(8):966–976. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1404206
Outeiro TF, Kontopoulos E, Altmann SM, Kufareva I, Strathearn KE, Amore AM, Volk CB, Maxwell MM, Rochet JC, McLean PJ, Young AB, Abagyan R, Feany MB, Hyman BT, Kazantsev AG (2007) Sirtuin 2 inhibitors rescue alpha-synuclein-mediated toxicity in models of Parkinson’s disease. Science 317(5837):516–519. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1143780
Piunti A, Smith ER, Morgan M, Ugarenko M, Khaltyan N, Helmin KA, Ryan CA, Murray DC, Rickels RA, Yilmaz BD, Rendleman EJ, Savas JN, Singer BD, Bulun SE, Shilatifard A (2019) CATACOMB: An endogenous inducible gene that antagonizes H3K27 methylation activity of Polycomb repressive complex 2 via an H3K27M-like mechanism. Sci Adv 5:x2887. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax2887
Pradhan S, Bacolla A, Wells RD, Roberts RJ (1999) Recombinant human DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase. I. Expression, purification, and comparison of de novo and maintenance methylation. J Biol Chem 274:33002–33010. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.46.33002
Ragazzini R, Perez-Palacios R, Baymaz IH, Diop S, Ancelin K, Zielinski D, Michaud A, Givelet M, Borsos M, Aflaki S, Legoix P, Jansen P, Servant N, Torres-Padilla ME, Bourc’His D, Fouchet P, Vermeulen M, Margueron R (2019) EZHIP constrains polycomb repressive complex 2 activity in germ cells. Nat Commun 10:3858. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11800-x
Rideout WR, Eggan K, Jaenisch R (2001) Nuclear cloning and epigenetic reprogramming of the genome. Science 293:1093–1098. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1063206
Ronan JL, Wu W, Crabtree GR (2013) From neural development to cognition: unexpected roles for chromatin. Nat Rev Genet 14:347–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3413
Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T, He C (2017a) Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell 169:1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045
Roundtree IA, Luo GZ, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhou T, Cui Y, Sha J, Huang X, Guerrero L, Xie P, He E, Shen B, He C (2017b) YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N(6)-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31311
Ryu H, Lee J, Hagerty SW, Soh BY, McAlpin SE, Cormier KA, Smith KM, Ferrante RJ (2006) ESET/SETDB1 gene expression and histone H3 (K9) trimethylation in Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19176–19181. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606373103
Sanulli S, Justin N, Teissandier A, Ancelin K, Portoso M, Caron M, Michaud A, Lombard B, Da RS, Offer J, Loew D, Servant N, Wassef M, Burlina F, Gamblin SJ, Heard E, Margueron R (2015) Jarid2 methylation via the PRC2 complex regulates H3K27me3 deposition during cell differentiation. Mol Cell 57:769–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.020
Savas JN, Makusky A, Ottosen S, Baillat D, Then F, Krainc D, Shiekhattar R, Markey SP, Tanese N (2008) Huntington’s disease protein contributes to RNA-mediated gene silencing through association with Argonaute and P bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10820–10825. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800658105
Scekic-Zahirovic J, Sendscheid O, El OH, Jambeau M, Sun Y, Mersmann S, Wagner M, Dieterle S, Sinniger J, Dirrig-Grosch S, Drenner K, Birling MC, Qiu J, Zhou Y, Li H, Fu XD, Rouaux C, Shelkovnikova T, Witting A, Ludolph AC, Kiefer F, Storkebaum E, Lagier-Tourenne C, Dupuis L (2016) Toxic gain of function from mutant FUS protein is crucial to trigger cell autonomous motor neuron loss. Embo J 35:1077–1097. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201592559
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter-Ovanesyan D, Habib N, Cacchiarelli D, Sanjana NE, Freinkman E, Pacold ME, Satija R, Mikkelsen TS, Hacohen N, Zhang F, Carr SA, Lander ES, Regev A (2014) Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5’ sites. Cell Rep 8:284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.048
Seeler JS, Dejean A (2003) Nuclear and unclear functions of SUMO. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(9):690–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1200
Shan Y, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Wang T, Zhang J, Yao J, Ma N, Liang Z, Huang W, Huang K, Zhang T, Su Z, Chen Q, Zhu Y, Wu C, Zhou T, Sun W, Wei Y, Zhang C, Li C, Su S, Liao B, Zhong M, Zhong X, Nie J, Pei D, Pan G (2020) JMJD3 and UTX determine fidelity and lineage specification of human neural progenitor cells. Nat Commun 11:382. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14028-x
Shen L, Song CX, He C, Zhang Y (2014) Mechanism and function of oxidative reversal of DNA and RNA methylation. Annu Rev Biochem 83:585–614. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035513
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu PJ, Liu C, He C (2017) YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N(6)-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res 27:315–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.15
Shimojo M (2008) Huntingtin regulates RE1-silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer factor (REST/NRSF) nuclear trafficking indirectly through a complex with REST/NRSF-interacting LIM domain protein (RILP) and dynactin p150 Glued. J Biol Chem 283:34880–34886. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804183200
Shmakova A, Batie M, Druker J, Rocha S (2014) Chromatin and oxygen sensing in the context of JmjC histone demethylases. Biochem J 462:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140754
Simpson CL, Lemmens R, Miskiewicz K, Broom WJ, Hansen VK, van Vught PW, Landers JE, Sapp P, Van Den Bosch L, Knight J, Neale BM, Turner MR, Veldink JH, Ophoff RA, Tripathi VB, Beleza A, Shah MN, Proitsi P, Van Hoecke A, Carmeliet P, Horvitz HR, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, van den Berg LH, Sham PC, Powell JF, Verstreken P, Brown RJ, Robberecht W, Al-Chalabi A (2009) Variants of the elongator protein 3 (ELP3) gene are associated with motor neuron degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 18:472–481. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn375
Sledz P, Jinek M (2016) Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)A writer complex. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18434
Smiley JA, Kundracik M, Landfried DA, Barnes VS, Axhemi AA (2005) Genes of the thymidine salvage pathway: thymine-7-hydroxylase from a Rhodotorula glutinis cDNA library and iso-orotate decarboxylase from Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta 1723:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.02.001
Smith ZD, Meissner A (2013) DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet 14:204–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3354
Son EY, Crabtree GR (2014) The role of BAF (mSWI/SNF) complexes in mammalian neural development. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 166C:333–349. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31416
Sorensen SS, Nygaard AB, Nielsen MY, Jensen K, Christensen T (2014) miRNA expression profiles in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 5:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0364-8
Soreq L, Guffanti A, Salomonis N, Simchovitz A, Israel Z, Bergman H, Soreq H (2014) Long non-coding RNA and alternative splicing modulations in Parkinson’s leukocytes identified by RNA sequencing. Plos Comput Biol 10:e1003517. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003517
Staahl BT, Tang J, Wu W, Sun A, Gitler AD, Yoo AS, Crabtree GR (2013) Kinetic analysis of npBAF to nBAF switching reveals exchange of SS18 with CREST and integration with neural developmental pathways. J Neurosci 33:10348–10361. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1258-13.2013
Stack EC, Del SS, Luthi-Carter R, Soh BY, Goldstein DR, Matson S, Goodrich S, Markey AL, Cormier K, Hagerty SW, Smith K, Ryu H, Ferrante RJ (2007) Modulation of nucleosome dynamics in Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 16:1164–1175. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm064
Stoica R, De Vos KJ, Paillusson S, Mueller S, Sancho RM, Lau KF, Vizcay-Barrena G, Lin WL, Xu YF, Lewis J, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L, Mitchell JC, Shaw CE, Miller CC (2014) ER-mitochondria associations are regulated by the VAPB-PTPIP51 interaction and are disrupted by ALS/FTD-associated TDP-43. Nat Commun 5:3996. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4996
Suchy J, Lee S, Ahmed A, Shea TB (2010) Dietary supplementation with S-adenosyl methionine delays the onset of motor neuron pathology in a murine model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuromolecular Med 12(1):86–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-009-8089-7
Suh N, Blelloch R (2011) Small RNAs in early mammalian development: from gametes to gastrulation. Development 138:1653–1661. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.056234
Szyf M (2005) DNA methylation and demethylation as targets for anticancer therapy. Biochemistry (mosc) 70:533–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10541-005-0147-7
Tan M, Luo H, Lee S, Jin F, Yang JS, Montellier E, Buchou T, Cheng Z, Rousseaux S, Rajagopal N et al (2011) Identification of 67 histone marks and histone lysine crotonylation as a new type of histone modification. Cell 146(6):1016–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.008
Tibshirani M, Zhao B, Gentil BJ, Minotti S, Marques C, Keith J, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rouaux C, Robertson J, Durham HD (2017) Dysregulation of chromatin remodelling complexes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 26:4142–4152. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx301
Tokiyoshi E, Watanabe M, Inoue N, Hidaka Y, Iwatani Y (2018) Polymorphisms and expression of genes encoding Argonautes 1 and 2 in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity 51:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916934.2017.1416468
Tremolizzo L, Carboni G, Ruzicka WB, Mitchell CP, Sugaya I, Tueting P, Sharma R, Grayson DR, Costa E, Guidotti A (2002) An epigenetic mouse model for molecular and behavioral neuropathologies related to schizophrenia vulnerability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(26):17095–17100. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.262658999
Trojer P, Reinberg D (2006) Histone lysine demethylases and their impact on epigenetics. Cell 125:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.003
Uckelmann M, Sixma TK (2017) Histone ubiquitination in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair (amst) 56:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.06.011
Valinluck V, Sowers LC (2007) Endogenous cytosine damage products alter the site selectivity of human DNA maintenance methyltransferase DNMT1. Cancer Res 67:946–950. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3123
Valle C, Salvatori I, Gerbino V, Rossi S, Palamiuc L, Rene F, Carri MT (2014) Tissue-specific deregulation of selected HDACs characterizes ALS progression in mouse models: pharmacological characterization of SIRT1 and SIRT2 pathways. Cell Death Dis 5:e1296. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.247
Valor LM (2015) Epigenetic-based therapies in the preclinical and clinical treatment of Huntington’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 67:45–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2015.04.009
Vogel CA, Kramar EA, Matheos DP, Havekes R, Hemstedt TJ, Magnan CN, Sakata K, Tran A, Azzawi S, Lopez A, Dang R, Wang W, Trieu B, Tong J, Barrett RM, Post RJ, Baldi P, Abel T, Lynch G, Wood MA (2017) Mutation of neuron-specific chromatin remodeling subunit BAF53b: rescue of plasticity and memory by manipulating actin remodeling. Learn Mem 24:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.044602.116
von Schimmelmann M, Feinberg PA, Sullivan JM, Ku SM, Badimon A, Duff MK, Wang Z, Lachmann A, Dewell S, Ma’Ayan A, Han MH, Tarakhovsky A, Schaefer A (2016) Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) silences genes responsible for neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 19:1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4360
Wang F, Fischhaber PL, Guo C, Tang TS (2014a) Epigenetic modifications as novel therapeutic targets for Huntington’s disease. Epigenomics 6(3):287–297. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.14.19
Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Vidal M, Tempst P, Jones RS, Zhang Y (2004) Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing. Nature 431(7010):873–878. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02985
Wang J, Ho WY, Lim K, Feng J, Tucker-Kellogg G, Nave KA, Ling SC (2018) Cell-autonomous requirement of TDP-43, an ALS/FTD signature protein, for oligodendrocyte survival and myelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E10941–E10950. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1809821115
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, Ren B, Pan T, He C (2014b) N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505:117–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12730
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H, He C (2015) N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161:1388–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014
Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Hackert P, Lenz C, Urlaub H, Hobartner C, Sloan KE, Bohnsack MT (2017) Human METTL16 is a N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. Embo Rep 18:2004–2014. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201744940
Wei CM, Gershowitz A, Moss B (1975) Methylated nucleotides block 5’ terminus of HeLa cell messenger RNA. Cell 4:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(75)90158-0
Weng MK, Zimmer B, Poltl D, Broeg MP, Ivanova V, Gaspar JA, Sachinidis A, Wullner U, Waldmann T, Leist M (2012) Extensive transcriptional regulation of chromatin modifiers during human neurodevelopment. PLoS One 7:e36708. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036708
Willyard C (2017) An epigenetics gold rush: new controls for gene expression. Nature 542:406–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/542406a
Wu H, Zhang Y (2014) Reversing DNA methylation: mechanisms, genomics, and biological functions. Cell 156:45–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.019
Wu P, Zuo X, Deng H, Liu X, Liu L, Ji A (2013) Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull 97:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001
Wu SC, Zhang Y (2010) Active DNA demethylation: many roads lead to Rome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:607–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2950
Xiao W, Adhikari S, Dahal U, Chen YS, Hao YJ, Sun BF, Sun HY, Li A, Ping XL, Lai WY, Wang X, Ma HL, Huang CM, Yang Y, Huang N, Jiang GB, Wang HL, Zhou Q, Wang XJ, Zhao YL, Yang YG (2016) Nuclear m(6)A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 61:507–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.012
Zhang F, Kang Y, Wang M, Li Y, Xu T, Yang W, Song H, Wu H, Shu Q, Jin P (2018) Fragile X mental retardation protein modulates the stability of its m6A-marked messenger RNA targets. Hum Mol Genet 27:3936–3950. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy292
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, Vagbo CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, Lu Z, Bosmans RP, Dai Q, Hao YJ, Yang X, Zhao WM, Tong WM, Wang XJ, Bogdan F, Furu K, Fu Y, Jia G, Zhao X, Liu J, Krokan HE, Klungland A, Yang YG, He C (2013) ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell 49:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015
Zheng YC, Ma J, Wang Z, Li J, Jiang B, Zhou W, Shi X, Wang X, Zhao W, Liu HM (2015) A Systematic review of histone lysine-specific demethylase 1 and Its inhibitors. Med Res Rev 35:1032–1071. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21350
Zhong S, Li H, Bodi Z, Button J, Vespa L, Herzog M, Fray RG (2008) MTA is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 20:1278–1288. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058883
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR, Qian SB (2015) Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature 526:591–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15377
Zuccato C, Tartari M, Crotti A, Goffredo D, Valenza M, Conti L, Cataudella T, Leavitt BR, Hayden MR, Timmusk T, Rigamonti D, Cattaneo E (2003) Huntingtin interacts with REST/NRSF to modulate the transcription of NRSE-controlled neuronal genes. Nat Genet 35:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1219
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Hui Yuan, Haiying Wang, Bingchen Liu, Xuda Liu, Yi Wen, Rong Cui, Tingwei Pan, Binbin Liu, and Miaoling Wu for their valuable advices.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province [2020-MS-152], the Basic Research Fund of Young Program of Higher Education of Liaoning Province (Grant No. QNK201735), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81302406) and the Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists in School of Public Health, China Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author substantially contributed to the review. ZQ: conception and design, drafting the manuscript; JL, ML, XD, LZ, SW, BX, WL, and ZX: revising the manuscript; YD: conception and design, revising it critically for important intellectual content, and final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Z., Li, J., Li, M. et al. The Essential Role of Epigenetic Modifications in Neurodegenerative Diseases with Dyskinesia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 2459–2472 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01133-z