Abstract
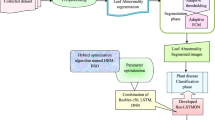
Nowadays, the economy of countries highly depends on the agriculture productivity which has a great effect on the development of human civilization. Sometimes, plant diseases cause a major reduction in agricultural products. This paper proposes a new approach for the automatic detection and classification of plant leaf diseases based on using the ELM deep learning algorithm on a real dataset of plant leaf images. The proposed approach uses the k-means clustering algorithm for image segmentation and applies the GLCM for feature extraction. The BDA optimization algorithm is employed for feature selection, and lastly the ELM algorithm is used for plant leaf diseases classification. The presented approach optimizes the input weights and hidden biases for ELM. The dataset used in this study includes 73 plant leaf images, such that we tested our approach on four diseases that usually affect plants, including: Alternaria alternata, Anthracnose, Bacterial blight, and Cercospora leaf spot. The experimental results show that the proposed approach has achieved encouraging results in terms of these classification measures: accuracy, error rate, recall, F score, and AUC which are 94%, 6%, 92%, 95%, and 96% respectively. Babu






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data set used in the work will be available upon request
Change history
26 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03485-z
References
Weizheng, S., Yachun, W., Zhanliang, C., Hongda, W.: Grading method of leaf spot disease based on image processing. In: 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, pp. 491–494. IEEE, Wuhan (2008)
Babu, M., Rao, B.: Leaves recognition using back propagation neural network-advice for pest and disease control on crops. Expert Advisory System, IndiaKisan Net (2007)
Camargo, A., Smith, J.: An image-processing based algorithm to automatically identify plant disease visual symptoms. Biosyst. Eng. 102(1), 9–21 (2009)
Hillnhutter, C., Mahleni, A.: Early detection and localisation of sugar beet diseases. New Approach. Gesunde Pflanzen 60(4), 143–149 (2008)
Russel, S., Norvig, P.: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Pearson Education Limited, London (2013)
Al Bashish, D., Braik, M., Bani-Ahmad, S.: Detection and classification of leaf diseases using k-means-based segmentation and neural networks—based classifications. Inform. Technol. J. 10(2), 267–275 (2011)
Al-Zu’bi, S., Hawashin, B., Mughaid, A., Baker, T.: Efficient 3d medical image segmentation algorithm over a secured multimedia network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80, 16887–16905 (2020)
Al-Zu’bi, S., Hawashin, B., Mujahed, M., Jararweh, Y., Gupta, B.B.: An efficient employment of internet of multimedia things in smart and future agriculture. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78(20), 29581–29605 (2019)
Liu, W.: Smart sensors, sensing mechanisms and platforms of sustainable smart agriculture realized through the big data analysis. Cluster Comput. 12, 1–15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03295-3
Muthukannan, K., Latha, P., Selvi, R., Nisha, P.: Classification of diseased plant leaves using neural network algorithms. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 10(4), 1913–1919 (2015)
Vijayalakshmi, S., Murugan, D.: An effective approach for diagnosis of plant disease using elm. (2018)
Aqel, D., Hawashin, B.: Arabic relative clauses parsing based on inductive logic programming. Recent Pat. Comput. Sci. 11(2), 121–133 (2018)
Aqel, D., Vadera, S.: A framework for employee appraisals based on sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Intelligent Semantic Web-Services and Applications, pp 1–6 (2010)
Aqel, D., Vadera, S.: A framework for employee appraisals based on inductive logic programming and data mining methods. In: International Conference on Application of Natural Language to Information Systems, pp. 404–407. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Shuja, J., Bilal, K., Alasmary, W., Sinky, H., Alanazi, E.: Applying machine learning techniques for caching in next-generation edge networks: a comprehensive survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 181, 103005 (2021)
Kruppa, J., Schwarz, A., Arminger, G., Ziegler, A.: Consumer credit risk: Individual probability estimates using machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(13), 5125–5131 (2013)
Kulkarni, A., Patil, A.: Applying image processing technique to detect plant diseases. Int. J. Modern Eng. Res. 2(5), 3661–3664 (2012)
Revathi, P., Hemalatha, M.: Identification of cotton diseases based on cross information gain deep forward neural network classifier with pso feature selection. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 5(6), 4637–4642 (2014)
Rumpf, T., Mahlein, A., Steiner, U., Oerke, E., Dehne, H., Plümer, L.: Early detection and classification of plant diseases with support vector machines based on hyperspectral reflectance. Comput. Electron. Agric. 74(1), 91–99 (2010)
Saragih, T., Mahmudy, W., Latief, A., Abadi, Y.: Application of extreme learning machine and modified simulated annealing for Jatropha curcas disease identification. Int. J. Adv. Soft Comput. Appl. 10(2), 108–119 (2018)
Singh, V., Misra, A.: Detection of plant leaf diseases using image segmentation and soft computing techniques. Inform. Process. Agric. 4(1), 41–49 (2017)
McCulloch, W., Pitts, W.: A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 5(4), 115–133 (1943)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Suykens, J., Vandewalle, J.: Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 9(3), 293–300 (1999)
MacQueen, J.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, pp. 281–297. IEEE, Oakland (1967)
Altman, N.: An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 46(3), 175–185 (1992)
Huang, G., Zhu, Q., Siew, C.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3), 489–501 (2006)
Akhtar, K., Saleem, M., Asghar, M., Haq, M.: New report of alternaria alternata causing leaf blight of tomato in Pakistan. Plant Pathol. 53(6), 816–816 (2004)
Rangaswami, G., Mahadevan, A.: Diseases of Crop Plants in India. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi (1998)
Martens, J., Seaman, W., Atkinson, T.: Diseases of field crops in Canada. Canadian Phytopathological. Society (1988)
Horst, R.: Westcott’s Plant Disease Handbook. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Haralick, R., Shanmugam, K., Dinstein, I.: Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 6, 610–621 (1973)
Mirjalili, S.: Dragonfly algorithm: a new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 27(4), 1053–1073 (2016)
Sokolova, M., Lapalme, G.: A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inform. Process. Manag. 45(4), 427–437 (2009)
Rumelhart, D., Hinton, G., Williams, R.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088), 533–536 (1986)
Broomhead, D.S., Lowe, D.: Radial basis functions, multi-variable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Tech. rep, Royal Signals and Radar Establishment Malvern (United Kingdom) (1988)
Sanger, T.: Optimal unsupervised learning in a single-layer linear feedforward neural network. Neural Netw. 2(6), 459–473 (1989)
Popescu, M., Balas, V., Perescu-Popescu, L., Mastorakis, N.: Multilayer perceptron and neural networks. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 8(7), 579–588 (2009)
Devi, T.G., Neelamegam, P.: Image processing based rice plant leaves diseases in Thanjavur, Tamilnadu. Cluster Comput. 22(6), 13415–13428 (2019)
Dubey, A.K., Ratan, R., Rocha, A., et al.: Computer vision based analysis and detection of defects in fruits causes due to nutrients deficiency. Cluster Comput. 23, 1–10 (2019)
Al-Hiary, H., Bani-Ahmad, S., Reyalat, M., Braik, M., Alrahamneh, Z.: Fast and accurate detection and classification of plant diseases. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 17(1), 31–38 (2011)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1942–1948. IEEE, Perth (1995)
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, C., Vecchi, M.: Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598), 671–680 (1983)
Karaboga, D.: An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Tech. rep., Technical report-tr06, Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer (2005)
Shrivastava, V., Pradhan, M., Minz, S., Thakur, M.: Rice plant disease classification using transfer learning of deep convolution neural network. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences (2019)
Valueva, M., Nagornov, N., Lyakhov, P., Valuev, G., Chervyakov, N.: Application of the residue number system to reduce hardware costs of the convolutional neural network implementation. Math. Comput. Simul. 177, 232–243 (2020)
Pham, T., VanTran, L., Dao, S.: Early disease classification of mango leaves using feed-forward neural network and hybrid metaheuristic feature selection. IEEE Access 8, 189960–189973 (2020)
Hemalatha, S., Maheswaran, R.: Recognition of poultry disease in real time using extreme learning machine. In: International Conference of Disciplinary Research in Engineering and Technology (CIDRET2014), pp 44–50 (2014)
Huang, G., Zhou, H., Ding, X., Zhang, R.: Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 42(2), 513–529 (2011)
Yang, X.: Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms. Luniver press, Beckington (2010)
Pham, D., Ghanbarzadeh, A., Koc, E., Otri, S., Rahim, S., Zaidi, M.: The bees algorithm. Technical Note. Manufacturing Engineering Centre, Cardiff University, Cardiff (2005)
Mehrabian, A., Lucas, C.: A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Ecol. Inform. 1(4), 355–366 (2006)
Atashpaz-Gargari, E., Lucas, C.: Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: 2007 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, Ieee, pp 4661–4667 (2007)
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Global Optim. 11(4), 341–359 (1997)
Reynolds, R.: An introduction to cultural algorithms. In: Proceedings of the third annual conference on evolutionary programming, pp. 131–139. World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Dixon, L.: The global optimization problem. an introduction. Toward Global Optim. 2, 1–15 (1978)
Molga, M., Smutnicki, C.: Test functions for optimization needs. Test Funct. Optim. Needs 101, 48 (2005)
Schumer, M., Steiglitz, K.: Adaptive step size random search. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 13(3), 270–276 (1968)
Ackley, D.: A connectionist machine for genetic hillclimbing, vol. 28. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Back, T.: Evolutionary algorithms in theory and practice: evolution strategies, evolutionary programming, genetic algorithms. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1996)
Laguna, M., Martí, R.: Experimental testing of advanced scatter search designs for global optimization of multimodal functions. J. Global Optim. 33(2), 235–255 (2005)
Mühlenbein, H., Schomisch, M., Born, J.: The parallel genetic algorithm as function optimizer. Parallel Comput. 17(6–7), 619–632 (1991)
Törn, A., Žilinskas, A.: Global Optimization. Springer, Berlin (1989)
Branin, F.: Widely convergent method for finding multiple solutions of simultaneous nonlinear equations. IBM J. Res. Dev. 16(5), 504–522 (1972)
Rosenbrock, H.: An automatic method for finding the greatest or least value of a function. Comput. J. 3(3), 175–184 (1960)
Griewank, A.: Generalized descent for global optimization. J. Opt. Theory Appl. 34(1), 11–39 (1981)
Funding
This work was supported by AL Zaytoonah University of Jordan
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All four Authors worked in an equivalent load at all stages to produce this research
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
I have read and I understand the journal information and have agreed to all mentioned terms and conditions.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The affiliation of the author Ala Mughaid has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aqel, D., Al-Zubi, S., Mughaid, A. et al. Extreme learning machine for plant diseases classification: a sustainable approach for smart agriculture. Cluster Comput 25, 2007–2020 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03397-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03397-y