Abstract
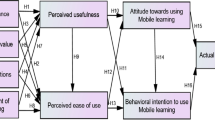
The tremendous and rapid developments in the information and communications technology sector as well as mobile devices have resulted in modern technologies, one of which is Mobile Learning (M-learning). M-learning is a new technique for learning that helps students to do their educational activities and access the learning materials easily without temporal or spatial restrictions, with the help of mobile devices. It is a robust component to make learning easy and flexible. Recently, many applications and services related to it have been developed. Despite the large number of researchers who have dealt with the topic of M-learning, the issue of factors affecting the adoption of M-learning has not been dealt with adequately, especially in Palestine. Therefore, it becomes necessary to explore the factors influencing the intentions of the students of higher education institutions to adopt M-learning. Hence, the goal of this study is to inspect the factors that influence higher education students’ intentions in Palestine to adopt M-learning system in the learning process and use its applications based on Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and some external factors. Wherefore, built on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) integrated with some external factors (mobility, self-efficacy and enjoyment), this paper proposes a hypothesized model of M-learning in Higher education institutes in Palestine. Relevant data were gathered from a sample of 388 students. Participants, using a self-report questionnaire, reported data. Pearson correlation, multiple linear regression and structural equation modeling (SEM) were employed to analyze the collected data. Results indicate that perceived usefulness and attitude have significant influence on M-learning adoption intention, while perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and perceived self-efficacy significantly affect the attitude to use M-learning. Perceived enjoyment and perceived self-efficacy are predictors of perceived ease of use. While mobility and perceived ease of use have significant effect on perceived usefulness. These results validate the capacity of TAM constructs and the external variables used in this research for predicting acceptance of M-learning. Limitations and future work are highlighted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Al-Aish, A., & Love, S. (2013). Factors influencing students’ acceptance of m-learning: An investigation in higher education. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 14(5).
Abu-Shanab, E., & Haider, S. (2015). Major factors influencing the adoption of m-government in Jordan. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 11(4), 223–240.
Adejo, O. W., Ewuzie, I., Usoro, A., & Connolly, T. (2018). E-learning to m-learning: Framework for data protection and security in cloud infrastructure. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci.(IJITCS), 10(4), 1-9.
Al-Emran, M., Al-Maroof, R., Al-Sharafi, M. A., & Arpaci, I. (2020a). What impacts learning with wearables? An integrated theoretical model. Interactive learning environments, 1-21.
Al-Emran, M., Arpaci, I., & Salloum, S. A. (2020b). An empirical examination of continuous intention to use m-learning: An integrated model. Education and Information Technologies, 1-20.
Al-Emran, M., Elsherif, H. M., & Shaalan, K. (2016). Investigating attitudes towards the use of mobile learning in higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 93–102.
Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., & Kamaludin, A. (2020c). Towards a conceptual model for examining the impact of knowledge management factors on mobile learning acceptance. Technology in Society, 101247.
AlHamad, A. Q. M. (2020). Predicting the intention to use Mobile learning: A hybrid SEM-machine learning approach. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)., 9(3).
Ali, R. A., & Arshad, M. R. M. (2016). Perspectives of students’ behavior towards mobile learning (M-learning) in Egypt: An extension of the UTAUT model. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 6(4), 1109–1114.
Ali, R. A., & Arshad, M. R. M. (2018). Empirical analysis on factors impacting on intention to use m-learning in basic education in Egypt. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 19(2), 253–270.
Almaiah, M. A., & Alismaiel, O. A. (2019). Examination of factors influencing the use of mobile learning system: An empirical study. Education and Information Technologies, 24(1), 885–909.
Alrasheedi, M., & Capretz, L. F. (2018). Determination of critical success factors affecting mobile learning: A meta-analysis approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04288.
Alrasheedi, M., Capretz, L. F., & Raza, A. (2015). A systematic review of the critical factors for success of mobile learning in higher education (university students' perspective). Journal of Educational Computing Research, 52(2), 257–276.
Alsswey, A., & Al-Samarraie, H. (2019). M-learning adoption in the Arab gulf countries: A systematic review of factors and challenges. Education and Information Technologies, 1–14.
Althunibat, A. (2015). Determining the factors influencing students’ intention to use m-learning in Jordan higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 52, 65–71.
Ayub, A. F. M., Zaini, S. H., Luan, W. S., & Jaafar, W. M. W. (2017). The influence of mobile self-efficacy, personal innovativeness and readiness towards students’ attitudes towards the use of mobile apps in learning and teaching. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(14), 364–374.
Azizi, S. M., & Khatony, A. (2019). Investigating factors affecting on medical sciences students’ intention to adopt mobile learning. BMC Medical Education, 19(1), 381.
BankMyCell (2020). Available at: https://www.bankmycell.com/blog/how-many-phones-are-in-the-world [accessed 09.01.2020].
Bere, A., & Rambe, P. (2016). An empirical analysis of the determinants of mobile instant messaging appropriation in university learning. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28(2), 172–198.
Buabeng-Andoh, C. (2020). Exploring University students’ intention to use mobile learning: A research model approach. Education and information technologies, 1-16.
Chao, C. M. (2019). Factors determining the behavioral intention to use mobile learning: An application and extension of the UTAUT model. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1652.
Chin, L. P., & Ahmad, Z. A. (2015). Perceived enjoyment and Malaysian consumers’ intention to use a single platform e-payment. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 18, p. 01009). EDP sciences.
Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Modern Methods for Business Research, 295(2), 295–336.
Chung, H. H., Chen, S. C., & Kuo, M. H. (2015). A study of EFL college students‟ acceptance of mobile learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 176, 333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.479.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Daniel, W. W., & Cross, C. L. (2013). Biostatistics: A foundation for analysis in the health sciences, 10th ed. Wiley.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS quarterly, 319-340.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1992). Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace 1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 22(14), 1111–1132.
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003.
Fagan, M. H. (2019). Factors influencing student acceptance of mobile learning in higher education. Computers in the Schools, 36(2), 105–121.
Gómez-Ramirez, I., Valencia-Arias, A., & Duque, L. (2019). Approach to M-learning acceptance Among University students: An integrated model of TPB and TAM. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 20(3).
Hair Jr, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage publications.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2014). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Los Angeles: Sage Publication.
Huang, J. H., Lin, Y. R., & Chuang, S. T. (2007). Elucidating user behavior of mobile learning: A perspective of the extended technology acceptance model. The Electronic Library, 25(5), 585–598.
Huang, Y. (2014) Empirical analysis on factors impacting Mobile learning acceptance in higher engineering education, PhD dissertation.
Iqbal, S., & Qureshi, I. A. (2012). M-learning adoption: A perspective from a developing country. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 13(3), 147–164.
Khanh, N. T. V., & Gim, G. (2014). Factors influencing mobile-learning adoption intention: An empirical investigation in high education. Journal of Social Sciences, 10(2), 51–62.
Liu, Y., Han, S., & Li, H. (2010). Understanding the factors driving m-learning adoption: A literature review. Campus-Wide Information Systems, 27(4), 210–226.
Mac Callum, K., & Jeffrey, L. (2013). The influence of students' ICT skills and their adoption of mobile learning. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 29(3).
Mubuke, F., Ogenmungu, C., Masaba, A. K., & Andrew, W. (2017). The predictability of perceived enjoyment and its impact on the intention to use Mobile learning systems. Asian Journal of Computer Science And Information Technology, 1(1), 7.
Nikou, S. A., & Economides, A. A. (2017). Mobile-based assessment: Investigating the factors that influence behavioral intention to use. Computers & Education, 109, 56–73.
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS) (2019). PCBS & MTIT Issue A Joint Press Release On The Eve Of The International Day For Telecommunication And Information Society 17/05/2019. Available at: http://www.pcbs.gov.ps/site/512/default.aspx?lang=en&ItemID=3462 [accessed 09.01.2020].
Park, S. Y., Nam, M. W., & Cha, S. B. (2012). University students' behavioral intention to use mobile learning: Evaluating the technology acceptance model. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(4), 592–605.
Patten, M. L. (2016). Questionnaire research: A practical guide. Routledge.
Qashou, A., & Saleh, Y. (2018). E-marketing implementation in small and medium-sized restaurants in Palestine. Arab Economic and Business Journal, 13(2), 93–110.
Rimale, Z., El Habib, B. L., & Tragha, A. (2016). A brief survey and comparison of m-learning and e-learning. International Journal of Computer Networks and Communications Security, 4(4), 89.
Rodrigues, L. F., Oliveira, A., & Costa, C. J. (2016). Does ease-of-use contributes to the perception of enjoyment? A case of gamification in e-banking. Computers in Human Behavior, 61, 114–126.
Sabah, N. M. (2016). Exploring students' awareness and perceptions: Influencing factors and individual differences driving m-learning adoption. Computers in Human Behavior, 65, 522–533.
Saroia, A. I., & Gao, S. (2019). Investigating university students’ intention to use mobile learning management systems in Sweden. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 56(5), 569–580.
Senaratne, S. I., Samarasinghe, S. M., & Jayewardenepura, G. (2019). Factors affecting the intention to adopt m learning. International Business Research, 12(2), 150–164.
Suki, N. M., & Suki, N. M. (2011). Users’ behavior towards ubiquitous M-learning. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 12(3), 118–129.
Tan, G., Ooi, K., Sim, J., & Phusavat, K. (2012). Determinants of Mobile learning adoption: An empirical analysis. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 52.
Vega, A., Ramírez-Benavidez, K., & Guerrero, L. A. (2019). Tool UTAUT applied to measure interaction experience with NAO robot. In international conference on human-computer interaction (pp. 501-512). Springer, Cham.
Wang, W. T., & Li, H. M. (2012). Factors influencing mobile services adoption: A brand-equity perspective. Internet Research: Electronic Networking Applications and Policy, 22(2), 142–179.
Yadegaridehkordi, E., & Iahad, N. A. (2012). Influences of demographic information as moderating factors in adoption of m-learning. International Journal of Technology Diffusion (IJTD), 3(1), 8–21.
Yadegaridehkordi, E., Iahad, N. A., & Baloch, H. Z. (2013). Success factors influencing the adoption of M-learning. International Journal of Continuing Engineering Education and Life Long Learning, 23(2), 167–178.
Yang, S. H. (2012). Exploring college students' attitudes and self-efficacy of mobile learning. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 11(4), 148–154.
Yeap, J. A., Ramayah, T., & Soto-Acosta, P. (2016). Factors propelling the adoption of m-learning among students in higher education. Electronic Markets, 26(4), 323–338.
Yousafzai, A., Chang, V., Gani, A., & Noor, R. M. (2016). Multimedia augmented m-learning: Issues, trends and open challenges. International Journal of Information Management, 36(5), 784–792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author of the article confirms that there are no conflict of interest in the submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendex 1
Appendex 1

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qashou, A. Influencing factors in M-learning adoption in higher education. Educ Inf Technol 26, 1755–1785 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10323-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10323-z