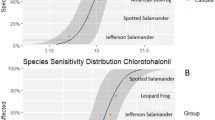
Abstract
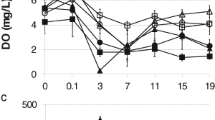
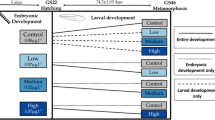
Agricultural fungicide application has increased tenfold since 2005 in the United States. Active ingredients and formulations of strobilurin fungicides at environmentally relevant concentrations cause mortality to larval and metamorph amphibians; however, little is known about chronic exposure effects in amphibians. We exposed larval amphibians (Bufo cognatus) throughout metamorphosis to the common fungicide formulations Headline®, Stratego®, Quilt®, and a control to determine effects on development and growth. Formulations were tested at 1.7, 50, and 400 μg/L of the active strobilurin ingredient for Headline®, Stratego®, and Quilt®, respectively. Fungicide exposure did not affect body mass or snout–vent length at metamorphosis. However, exposure to Headline® at 1.7 μg/L increased the development rate of tadpoles by approximately 5 days compared to the control, an effect not observed for Stratego® and Quilt®. Stratego® also caused approximately 35 % cumulative mortality. Results from the experiment suggest that chronic effects of strobilurin fungicides on development, growth, and mortality to B. cognatus are apparent at environmentally relevant concentrations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altwegg R, Reyer HU (2003) Patterns of natural selection on size at metamorphosis in water frogs. Evolution 57:872–882. doi:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00298.x
Balba H (2007) Review of strobilurin fungicide chemicals. J Environ Sci Health Part B 42:441–451. doi:10.1080/03601230701316465
Bartlett DW, Clough JM, Godwin JR, Hall AA, Hamer M, Parr-Dobrzanski B (2002) The strobilurin fungicides. Pest Manag Sci 58:649–662. doi:10.1002/ps.520
BASF Corporation (2008a) Headline fungicide label. NVA 2008-04-088-0262. Research Triangle Park, NC
BASF Corporation (2008b) Headline fungicide supplemental label. NVA 2008-04-088-0327. Research Triangle Park, NC
Battaglin WA, Sandstrom MW, Kuivila KM, Kolpin DW, Meyer MT (2011) Occurrence of azoxystrobin, propiconazole, and selected other fungicides in US streams, 2005–2006. Water Air Soil Pollut 218:307–322. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0643-2
Bayer Crop Science (2008) Stratego fungicide label. EPA Reg. No. 264-799. Research Triangle, NC
Belden J, McMurry S, Smith L, Reilley P (2010) Acute toxicity of fungicide formulations to amphibians at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2477–24880. doi:10.1002/etc.297
Boone MD, Bridges CM, Rothermel BB (2001) Growth and development of larval green frogs (Rana clamitans) exposed to multiple doses of an insecticide. Oecologia 129:518–524. doi:10.1007/s004420100749
Boone MD, Semlitsch RD, Fairchild JF, Rothermel BB (2004) Effects of an insecticide on amphibians in large-scale experimental ponds. Ecol Appl 14:685–691. doi:10.1890/02-5308
Bridges CM (2000) Long-term effects of pesticide exposure at various life stages of the southern leopard frog (Rana sphenocephala). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:91–96. doi:10.1007/s002440010084
Deb D, Engel BA, Harbor J, Hahn L, Lim KJ, Zhai T (2010) Investigation potential water quality impacts of fungicides used to combat soybean rust in Indiana. Water Air Soil Pollut 207:273–288. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0135-4
Denver RJ (1995) Environmental neuroendocrine interactions in the control of amphibian metamorphosis. Neth J Zool 45:195–200
Denver RJ (1997a) Environmental stress as a developmental cue: corticotropin-releasing hormone is a proximate mediator of adaptive phenotypic plasticity in amphibian metamorphosis. Horm Behav 31:169–179. doi:10.1006/hbeh.1997.1383
Denver RJ (1997b) Proximate mechanisms of phenotypic plasticity in amphibian metamorphosis. Am Zool 37:172–184. doi:10.1093/icb/37.2.172
Denver RJ, Mirhadi N, Phillips M (1998) Adaptive plasticity in amphibian metamorphosis: response of Scaphiopus hammondii tadpoles to habitat desiccation. Ecology 79:1859–1872
Diana SG, Resetarits WJ Jr, Schaeffer DJ, Beckmen KB, Beasley VR (2000) Effects of atrazine on amphibian growth and survival in artificial aquatic communities. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2961–2967. doi:10.1002/etc.5620191217
Fioramonti E, Semlitsch RD, Reyer HU, Fent K (1997) Effects of triphenyltin and pH on the growth and development of Rana lessonae and Rana esculenta tadpoles. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1940–1947. doi:10.1002/etc.5620160925
Gervasi SS, Foufopoulos J (2008) Costs of plasticity: responses to desiccation decrease post-metamorphic immune function in a pond-breeding amphibian. Funct Ecol 22:100–108. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2007.01340.x
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Greulich K, Pflugmacher S (2003) Differences in susceptibility of various life stages of amphibians to pesticide exposure. Aquat Toxicol 65:329–336. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(03)00153-X
Hooser EA, Belden JB, Smith LM, McMurry ST (2012) Acute toxicity of three strobilurin fungicides and their active ingredients to tadpoles. Ecotoxicology 21:1458–1464. doi:10.1007/s10646-012-0899-y
Howe CM, Berrill M, Pauli BD, Helbing CC, Werry K, Veldhoen N (2004) Toxicity of glyphosate-based pesticides to four North American frog species. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1928–1938. doi:10.1897/03-71
Jarvinen AW, Nordling BR, Henry ME (1983) Chronic toxicity of Dursban (chlorpyrifos) to the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) and the resultant acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 7:423–434. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(83)90008-8
Krupa JJ (1994) Breeding biology of the Great Plains toad in Oklahoma. J Herpetol 28:217–224
Martin LB, Hopkins WA, Mydlarz LD, Rohr JR (2010) The effects of anthropogenic global change on immune functions and disease resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1195:129–148. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05454.x
McMahon TA, Halstead NT, Johnson S, Raffel TR, Romansic JM, Crumrine PW, Boughton RK, Martin LB, Rohr JR (2011) The fungicide chlorothalonil is nonlinearly associated with corticosterone, immunity, and mortality in amphibians. Environ Health Perspect 119:1098–1103. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002956
McMurry ST, Smith LM, Dupler KD, Gutierrez MB (2009) Influence of land use on body size and splenic cellularity in wetland breeding Spea spp. J Herpetol 43:421–430. doi:10.1670/07-126R2.1
Morrison SA, McMurry ST, Smith LM, Belden JB (2013) Acute toxicity of pyraclostrobin and trifloxystrobin to Hyalella azteca. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1516–1525. doi:10.1002/etc.2228
O’Connel JL, Johnson LA, Smith LM, McMurry ST, Haukos DA (2011) Influence of land-use and conservation programs on wetland plant communities of the semiarid United States Great Plains. Biol Conserv. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2011.11.03
Ochoa-Acuna HG, Bialkowski W, Yale G, Hahn L (2009) Toxicity of soybean rust fungicides to freshwater algae and Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 18:440–446. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0298-1
Olsvik PA, Kroglund F, Fenstad B, Kirstensen T (2010) Effects of the fungicide azoxystrobin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) smolt. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1852–1861. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.07.017
Relyea RA (2004) Growth and survival of five amphibian species exposed to combinations of pesticides. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1737–1742. doi:10.1897/03-493
Russell PE (2005) A century of fungicide evolution. J Agric Sci 143:11–25. doi:10.1017/S0021859605004971
Semlitsch RD, Foglia M, Mueller A, Steiner I, Fioramonti E, Fent K (1995) Short-term exposure to triphenyltin affects the swimming and feeding behavior of tadpoles. Enivron Toxicol Chem 14:1419–1423. doi:10.1002/etc.5620140819
Shaner GE, Alexander C, Christmas E, Conley SP, Dobbins CL, Hurt CA, Patrick GF, Rane KK, Ruhl GE (2005) Preparing for Asian soybean rust. Purdue extension. http://www.extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/ID/ID-324.pdf. Accessed 20 March 2011
Skelly DK, Werner EE (1990) Behavioral and life-historical responses of larval American toads to an odonate predator. Ecology 71:2313–2322. doi:10.2307/1938642
Syngenta Crop Protection (2009) Quilt fungicide label. EPA Reg. No. 100-1178. SC P 1178A-L6D 0209. Greensboro, NC, USA
Thomas DG, Breslow N, Gart JJ (1977) Trend and homogeneity analysis of proportions and life table data. Comput Biomed Res 10:373–381
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2007) ECOTOX User Guide: ECOTOXicology Database System. Version 4.0
Warming TP, Mulderij G, Christoffersen KS (2009) Clonal variation in physiological responses of Daphnia magna to the strobilurin fungicide azoxystrobin. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:374–380. doi:10.1897/08-279.1
Werner EE (1986) Metamorphosis growth rate, predation risk, and the optimal size at transformation. Am Nat 128:319–341
Wilbur HM (1980) Complex life cycles. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:67–93. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.11.110180.000435
Wilbur HM, Collins JP (1973) Ecological aspects of amphibian metamorphosis. Science 182:1305–1314. doi:10.1126/science.182 4119.1305
Acknowledgments
Funding for this Project was provided by the National Science Foundation (Award No. 0718302) and the CEAP Wetlands Program, US Department of Agriculture-Natural Resource Conservation Service. Dr. Barney Luttbeg provided tremendous provision in the statistical analysis of this research. Special thanks go to Michael Cobbs, Shella Swain, Cleo Szmygiel, Dale Daniel, Brandon Hartman and Blake Stevison for aiding in collecting data and collecting toads.
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartman, E.A.H., Belden, J.B., Smith, L.M. et al. Chronic effects of strobilurin fungicides on development, growth, and mortality of larval Great Plains toads (Bufo cognatus). Ecotoxicology 23, 396–403 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1203-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1203-0