Abstract
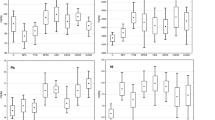
A study was performed to evaluate the pH and the availability of Zn, Cu, Mn, Pb, and Ni in soil amended with increasing doses of composted solid wastes, collected in Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro State and in Coimbra, Minas Gerais State, Brazil. The influence of the time elapsed between compost application to the soil and the sampling of the plant growth substrate (soil + compost) for pH and metal availability analyses was also examined. The availability of heavy metals in the soil, in the compost and in the substrate was evaluated using DTPA solution for metal extraction. The increase of the compost doses added to the soil resulted in the increase of the pH in the substrate. The addition of the compost from the bigger city, Rio de Janeiro, resulted in higher increase in soil pH and available Zn, Cu, Pb, and Ni levels as compared to the addition of the compost from the smaller city, Coimbra. Increasing the time elapsed between the compost application to the soil and the sampling of the mixture resulted in higher available Zn, Cu, Mn, and Pb levels. The addition of the compost from Rio de Janeiro resulted in substrate metal concentrations in the order Zn > Pb > Ni > Cu > Mn and for the Coimbra compost the metal concentrations in the substrate was Zn > Pb > Cu > Ni > Mn. The higher values of pH and available metals obtained for the bigger city were attributed to the greatest metal contamination of its compost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Associação Brasileira das Indústrias da Alimentação – ABIA: 1985, ‘Compêndio da Legislação de Alimentos’, São Paulo, Brasil, 185 pp.
AbdelSabour, M. F. and ElSeoud, M. A. A.: 1996, ‘Effects of organic-waste compost addition on sesame growth, yield and chemical composition’, Agric. Ecos. Environ. 60(2–3), 157–164.
Adriano, D. C.: 1986, Trace Elements in the Terrestrial Environment, Springer Verlag, New York, pp. 421.
Aguilar, F. J., Gonzalez, P., Revilla, J., deLeon, J. J. and Porcel, O.: 1997, ‘Agricultural use of municipal solid waste on tree and bush crops’, J. Agric. Eng. Res. 67(1), 73–79.
Alloway, B. J.: 1993, Heavy Metals in Soils, Black Academic, New York, 339 pp.
Alves, W. L. and Passoni. A. A.: 1997, ‘Compost and vermicompost of urban solid waste in Licania tomentosa (Benth) seedlings production to arborization’, Pesq. Agropec. Brasileira 32(10), 1053–1058.
Andrade, V. M. M., Lourenço, R.S., Muraoka, T. and Malavolta, E.: 1975, ‘Estudos sobre a nutrição mineral do cafeeiro. Influência do cobre do substrato no crescimento e composição mineral do cafeeiro var. Mundo Novo e Catuí’, Anais da ESALQ 32, 647–656.
Borges Jr., M., de Mello, J. W. V., Abrahão, W. A. P., Jordão, C. P. and Simas, F. N. B.: 2001, ‘Methods for evaluation of easily-reducible iron and manganese in paddy soils’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 32(19&20), 3009–3022.
Brady, N. C.: 1989, Natureza e Propriedades dos Solos, Freitas Bastos, Rio de Janeiro, pp. 647.
Businelli, M., Gigliotti, G. and Giusquiani, P. L.: 1996, “Trace element fate in soil profile and corn plant after massive applications of urban waste compost: A six-year study’, Agrochimica 40(4), 145–152.
Comissão de Fertilidade do Solo do Estado de Minas Gerais: 1989, ‘Recomendações para o uso de corretivo e fertilizantes em Minas Gerais, 4a aproximação’, Ed. Nagy, Lavras, Minas Gerais, Brasil, 159 pp.
Costa, C. A. C., Casali, V. W. D., Loures, E. G., Cecon, P. R. and Jordão, C. P.: 1994a, ‘Teor de metais pesados em alface (Lactuca sativa L.), adubada com composto orgânico de lixo urbano’, Rev. Ceres 41(238), 629–640.
Costa, C. A. C.: 1994b, ‘Crescimento e teores de sódio e de metais pesados da alface e da cenoura adubadas com composto orgânico de lixo urbano’, Dissertation, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Brasil, 89 p.
Costa, C. A. C., Casali, V. W. D., Loures, E. G., Cecon, P. R. and Jordão, C. P.: 1997, ‘Teor de zinco, cobre e cádmio em cenoura em função de doses crescentes de composto de lixo urbano’, Hortic. Bras. 15(1), 10–14.
Cuevas, G., Blazquez, R., Martinez, F. and Walter, I.: 2000, ‘Composted MSW effects on soil properties and native vegetation in a degraded semiarid shrubland’, Compost Sci. Utilization 8(4), 303–309.
Eira, A. F. and Carvalho, P. C. T.: 1970, ‘A decomposição da matéria orgânica pelos microrganismos do solo e sua influência nas variações do pH’, Revista da Agricultura 45, 15–21.
Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária – Embrapa: 1979, ‘Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solos’, Serviço Nacional de Levantamento e Conservação de Solos, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil.
Eneji, A. E., Honna, T. and Yamamoto, S.: 2001, ‘Manuring effect on rice grain, yield and extractable trace elements in soils’, J. Plant Nutr. 24(7), 967–977.
Furlani, A. M. C., Furlani, P. R. and Bataglia, O. C.: 1978, ‘Composição mineral de diversas hortaliças’, Bragantia 37(5), 33–44.
Garcia, C., Hernández, T., Costa, F. and Ayuso, M.: 1991, ‘Compostaje de la fracción orgánica de un resíduo sólido urbano. Evolución de su contenido de diversas fracciones de metales pesados’, Suelo Planta 1, 1–13.
Gaudette, H. E., Flight, W. R., Toner, L. and Folger, D. W.: 1974, ‘An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments’, J. Sediment Petrol. 44, 249–253.
Gigliotti, G., Businelli, D. and Giusquiani, P. L.: 1996, ‘Trace metals uptake and distribution in corn plants grown on a 6-year urban waste compost amended soil’, Agric. Ecos. Environ. 21(3), 199–206.
Giusquiani, P. L., Gigliotti, G. and Businelli, D.: 1992, ‘Heavy-metals in the environment – mobility of heavy-metals in urban waste-amended soils’, J. Environ. Qual. 21(3), 330–335.
Haque, I., Lupwayi, N. Z. and Tadesse, T.: 2000, ‘Soil nutrient contents and relation to other soil properties in Ethiopia’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 31(17–18), 2751–2762.
Hernández, T., García, C., Costa, F., Valero, J. A. and Ayuso, M.: 1992, ‘Utilización de resíduos urbanos como fertilizantes orgánicos’, Suelo y Planta 2, 373–383.
Hernando, S., Lobo, M. C. and Polo, A.: 1989, ‘Effect of the application of a municipal refuse compost on the physical and chemical properties of a soil’, Sci.Total Ernviron. 81, 589–596.
Holtzclaw, K. M., Keech, D. A., Page, A. L., Sposito, G., Ganje, T. J. and Ball, N. B.: 1978, ‘Trace metal distributions among the humic acid, the fulvic acid and precipitable fractions extracted with NaOH from sewage sludges’, J. Environ. Qual. 7, 124–127.
Jones, L. H. P. and Jarvis, S. C.: 1981, ‘The Fate of Heavy Metals’, in: D. J. Greeenland and M. H .B. Hayers (eds.), The Chemistry of Soil Process, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 593–620.
Jordão, C. P., Pereira, M. G., Einloft, R., Santana, M. B., Bellato, C. R. and de Mello, J. W. V.: 2002, ‘Removal of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Zn from electroplating wastes and synthetic solutions by vermicompost of cattle manure’, J. Environ. Sci. Health A37(5), 875–892.
Karam, N. S., Ereifej, K. I., Shibli, R. A., AbuKudais, H., Alkofahi, A. and Malkawi, Y.: 1998, ‘Metal concentrations, growth, and yield of potato produced from in vitro plantlets or microtubers and grown in municipal solid-waste-amended substrates’, J. Plant Nutr. 21(4), 725–739.
Kiehl, E. J.: 1985, Fertilizantes Orgânicos, Agronômica Ceres, Piracicaba, Brasil, p. 417–431.
Klock-Moore, K. A. and Fitzpatrick. G. E.: 2000, ‘Management of urban compost amendments in ornamental production systems in Florida’, Soil Crop Sci. Soc. Florida Proc. 59, 14–16.
Knezek, B. D. and Ellis, B. G.: 1980, ‘Essential Micronutrients. IV: Copper, Iron, Manganese and Zinc’, in: B. E. Davies (ed.), Applied Soil Trace Elements, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 482 pp.
Lagerwerff, J. V., Biersdorf, G. T., Milberg, R. P. and Brower, D. L.: 1977, ‘Effects of incubation and liming on yield and heavy metal uptake by rye from sewage-sludge soil’, J. Environ. Qual. 6, 427–431.
Lake, D. J., Kirk, P. W. W. and Lester, J. N.: 1984, ‘Fractionation, characterization and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils: A review’, J. Environ. Qual. 13, 175–183.
Lelis, M. P. N.: 2001, “Compostagem de resíduos orgânicos em Minas Gerais’, Seminário e Exposição sobre os Desafios Técnicos e Econômicos para a Reciclagem, 2, Cempre/Abimaq, São Paulo, Brasil.
Lindsay, W. L. and Norvell, W. A.: 1978, ‘Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper’, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 421–428.
Lucas, R. E. and Knezek, B. D.: 1972, ‘Climate and Soil Conditions Promoting Micronutrient Deficiencies in Plants’, in: Micronutrients in Agriculture, J. J. Mortvedt, P. M. Giordano and W. L. Lindsay (eds.), Soil Sci. Soc. America, Inc., Madison, 666 pp.
Malavolta, E.: 1981, Manual de Química Agrícola – Adubos e Adubação. Ceres: São Paulo, 478 pp.
Malavolta, E.: 1994, Fertilizantes e seu Impacto Ambiental: Micronutrientes e Metais Pesados, Mitos, Mistificação e Fatos, ProduQuímica, São Paulo, 153 pp.
Ministério da Saúde: 1998, Portaria no 685, de 27 de agosto de 1998, Secretaria de Vigilância Sanitária, Brasília, Brasil.
Moreno, J. L., Garcia, C., Hernandez, T. and Pascual, J. A.: 1996, ‘Transference of heavy metals from a calcareous soil amended with sewage-sludge compost to barley plants’, Bioresource Technol. 55(3), 251–258.
Mortvedt, J. J., Cox, F. R., Shuman, L. M. and Welch, R. M.: 1991, Micronutrients in Agriculture, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, 760 pp.
O Saneamento no Brasil do ano 2000: 2002, ‘Pesquisa Nacional de Saneamento Básico’, Bio, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, ano IX, n. 22, pp. 19–34.
Ozoreshampton, M., Schaffer, B., Bryan, H. H. and Hanlon. E. A.: 1994, ‘Nutrient concentrations, growth, and yield of tomato and squash in municipal solid-waste-amended soil’, Hortscience 29(7), 785–788.
Pinamonte, F., Stringari, G., Gasperi, F. and Zorzi, G.: 1997, ‘The use of compost: Its effects on heavy metal levels in soil and plants’, Res. Conserv. Rec. 21(2), 129–143.
Ranwa, R. S. and Singh, K.P.: 1999, ‘Effect of integrated management with vermicompost on productivity of wheat (Triticum aestivum)’, Indian J. Agronomy 44(3), 554–559.
Reyzabal, L., Andrade, L., Marcet, P. and Montero, M. J.: 2000, ‘Effect of long-term cultivation on zinc and copper contents in soils from the Bahia Blanca horticultural belt (Argentina)’, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 31(9–10), 1155–1167.
Sáinz, M. J., Taboada-Castro, M. T. and Vilariño, A.: 1988, ‘Growth, mineral nutrition and mycorrhizal colonization of red clover and cucumber plants grown in a soil amended with composted urban wastes’, Plant Soil 205, 85–92.
Santos, I. Z., Casali, V. W. D. and Miranda, G. V.: 1999, ‘Teores de metais pesados, K e Na no substrato, em função de doses de composto orgânico de lixo urbano e de cultivares de alface’, Ciência Rural 29(3), 415–421.
Shuman, L. M. and. Li, Z. B.: 1972, ‘Amelioration of zinc in cotton using lime or mushroom compost’J. Soil Cont. 6, 425–438.
Smith, S. R.: 1992, ‘Sewage-sludge and refuse composts as peat alternatives for conditioning impoverished soils – Effects on the growth response and mineral status of Petunia grandiflora’, J. Hort. Sci. 67(5), 703–716.
Tomé Jr., J. B.: 1997, Manual para Interpretação de Análise de Solo, Agropecuária, Guaíba, São Paulo, 247 pp.
Zinati, G. M., Li, Y. C. and Bryan, H. H.: 2001, ‘Utilization of compost increases organic carbon and its humin, humic and fulvic acid fractions in calcareous soil’, Compost Sci. Utilization 9(2), 156–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordão, C.P., Nascentes, C.C., Cecon, P.R. et al. Heavy Metal Availability in Soil Amended with Composted Urban Solid Wastes. Environ Monit Assess 112, 309–326 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1072-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1072-y