Abstract
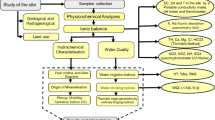
Konya City, located in the central part of Turkey, has grown and urbanized rapidly. A large amount of the water requirement of Konya City is supplied from groundwater. The quality of this groundwater was determined by taking samples from 177 of the wells within the study area. The purposes of this investigation were (1) to provide an overview of present groundwater quality and (2) to determine spatial distribution of groundwater quality parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity, Cl − , SO4 − 2, hardness, and NO3 − concentrations, and (3) to map groundwater quality in the study area by using GIS and Geostatistics techniques. ArcGIS 9.0 and ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst were used for generation of various thematic maps and ArcGIS Spatial Analyst to produce the final groundwater quality map. An interpolation technique, ordinary kriging, was used to obtain the spatial distribution of groundwater quality parameters. The final map shows that the southwest of the city has optimum groundwater quality, and, in general, the groundwater quality decreases south to north of the city; 5.03% (21.51 km2) of the total study area is classified to be at the optimum groundwater quality level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H., & Chon, H. (1999). Assessment of groundwater contamination using geographic information systems. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 21, 273–289. doi:10.1023/A:1006697512090.
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1976). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (14th edition). New York: APHA, AWWA, WPCF.
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1985). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (16th edition). Washington: APHA, AWWA, WPCF.
Buttner, O., Becker, A., Kellner, S., Kuehn, S., Wendt-Potthoff, K., Zachmann, D. W., et al. (1998). Geostatistical analysis of surface sediments in an acidic mining lake. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 108, 297–316. doi:10.1023/A:1005145029916.
Cressie, N. (1990). The origins of kriging. Mathematical Geology, 22, 239–252.
D’agostino, V., Greene, E. A., Passarella, G., Vurro, M. (1998). Spatial and temporal study of nitrate concentration in groundwater by means of coregionalization. Environmental Geology, 36(3–4), 285–295. doi:10.1007/s002540050344.
Ducci, D. (1999). GIS techniques for mapping groundwater contamination risk. Natural Hazards, 20, 279–294. doi:10.1023/A:1008192919933.
Engel, B. A., & Navulur, K. C. S. (1999). The role of geographical information systems in groundwater engineering. In J. W. Delleur (Ed.), The handbook of groundwater engineering (pp. 21, 1–16). Boca Raton: CRC.
EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) (1993). Wellhead protection: a guide for small communities. Office of Research and Development Office of Water, Washington, DC., EPA/625/R-93/002, 144 p.
ESRI (Environmental Systems Research Institute) (2001). Using ArcGIS geostatistical analyst (300 p.), USA.
Fetter, C. W. (1999). Contaminant hydrogeology (p. 500). USA: Prentice Hall.
Fritch, T. G., Yelderman, J. C., Dworkin, S. I., & Arnold, J. G. (2000). A predictive modeling approach to assessing the groundwater pollution susceptibility of the Paluxy Aquifer, Central Texas, using a geographic information system. Environmental Geology, 39(9), 1063–1069. doi:10.1007/s002549900078.
Fytianos, K., & Christophoridis, C. (2004). Nitrate, arsenic and chloride pollution of drinking water in Northern Greece: Elaboration by applying GIS. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 93, 55–67. doi:10.1023/B:EMAS.0000016791.73493.aa.
Gringarten, E., & Deutsch, C. V. (2001). Teacher’s aide variogram interpretation and modeling. Mathematical Geology, 33(4), 507–534. doi:10.1023/A:1011093014141.
Hudak, P. F. (1999). Chloride and nitrate distributions in the Hickory Aquifer, Central Texas, USA. Environment International, 25(4), 393–401. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(99)00016-1.
Hudak, P. F. (2000). Regional trends in nitrate content of Texas groundwater. Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 228(1–2), 37–47. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00206-1.
Hudak, P. F. (2001). Water hardness and sodium trends in Texas aquifers. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 68, 177–185. doi:10.1023/A:1010760413010.
Hudak, P. F., & Sanmanee, S. (2003). Spatial patterns of nitrate, chloride, sulfate, and fluoride concentrations in the woodbine aquifer of North-Central Texas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 82, 311–320. doi:10.1023/A:1021946402095.
Kravchenko, A., & Bullock, D. G. (1999). A comparative study of interpolation methods for mapping soil properties. Agronomy Journal, 91(3), 393–400.
Levallois, P., Thériault, M., Rouffignat, J., Tessier, S., Landry, R., Ayotte, P., et al. (1998). Groundwater contamination by nitrates associated with intensive potato culture in Québec. The Science of the Total Environment, 217, 91–101. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00191-0.
Lin, Y., Tan, Y., & Rouhani, S. (2001). Identifying spatial characteristics of transmissivity using simulated annealing and kriging methods. Environmental Geology, 41(1–2), 189–199. doi:10.1007/s002540100382.
Mcgrath, D., & Zhang, C. (2003). Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of Ireland. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 1629–1639. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00045-3.
Nas, B., & Berktay, A. (2006). Groundwater contamination by nitrates in the City of Konya, (Turkey): A GIS perspective. Journal of Environmental Management, 79, 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.05.010.
Poon, K., Wong, R. W., Lam, M. H., Yeung, H., & Chiu, T. K. (2000). Geostatistical modelling of the spatial distribution of sewage pollution in coastal sediments. Water Research, 32, 99–108. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00119-0.
Pozdnyakova, L., & Zhang, R. (1999). Geostatistical analyses of soil salinity in a large field. Precision Agriculture, 1, 153–165. doi:10.1023/A:1009947506264.
Sawyer, C. N., & Mccarty, P. L. (1978). Chemistry for environmental engineering (p. 532). NY: Mc-Graw Hill.
Stein, M. L. (1999). Interpolation of spatial data: Some theory for kriging (p. 264). Berlin: Springer.
Tranchant, B. J. S., & Vincent, A. P. (2000). Statistical interpolation of ozone measurements from satellite data (TOMS, SBUV and SAGE II) using the kriging method. Annales Geophysicae, 18, 666–678. doi:10.1007/s00585-000-0666-x.
TSE (1997). Drinking water Turkish standards, Turkish standards (TSE-266). Ankara.
Vinten, A. J. A., & Dunn, S. M. (2001). Assessing the effects of land use on temporal change in well water quality in a designated nitrate vulnerable zone. The Science of the Total Environment, 265, 253–268. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00662-8.
Water Authority. Works Report 2000 (2001). Water authority (143 p.). Municipality of Konya City, Konya, Turkey (In Turkish).
WHO (World Health Organization) (1985). Health hazards from nitrates in drinking water. WHO, Regional Office for Europe.
WHO (World Health Organization) (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality, third edition. Geneva: WHO.
Yamamoto, J. K. (2000). An alternative measure of the reliability of ordinary kriging estimates. Mathematical Geology, 32(4), 489–509. doi:10.1023/A:1007577916868.
Zhu, H. C., Charlet, J. M., & Poffijn, A. (2001). Radon risk mapping in Southern Belgium: An application of geostatistical and GIS techniques. The Science of the Total Environment, 272, 203–210. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00693-3.
Zimmerman, D., Pavlik, C., Ruggles, A., & Armstrong, M. P. (1999). An experimental comparison of ordinary and universal kriging and inverse distance weighting. Mathematical Geology, 31(4), 375–390. doi:10.1023/A:1007586507433.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nas, B., Berktay, A. Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ Monit Assess 160, 215–227 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0689-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0689-4