Abstract
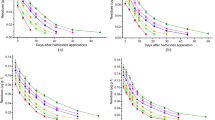
Clay loam soil from agricultural field of Gangetic alluvial zone of West Bengal was investigated to evaluate the effect of chlorpyrifos application at field rate (0.5 mg kg − 1 soil) and 100 times of the field rate (50 mg kg − 1 soil) on soil microbial variables under laboratory conditions. Acetone-induced stress on soil microorganisms was evident in the initial stages in terms of microbial biomass carbon (MBC) content in soil and basal soil respiration (BSR) in control soil samples which received acetone only as compared to control soil without acetone. The soil MBC content increased significantly by application of chlorpyrifos. The BSR and the fluorescein diacetate hydrolysing activity (FDHA) were not adversely affected by chlorpyrifos at field rate, whilst the chemical at higher dosage significantly decreased the metabolic activities of soil microbes in terms of BSR and FDHA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, G., & Duncan, H. (2001). Development of a sensitive and rapid method for the measurement of total microbial activity using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) in a range of soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 33, 943–951. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00244-3.
Adityachaudhury, N., Banerjee, H., & Kole, R. K. (1997). An appraisal of pesticide use in Indian agriculture with special reference to their consumption in West Bengal. Science and Culture, 63, 223–228.
Alef, K. (1995a). Estimation of soil respiration. In K. Alef, & P. Nannipieri (Eds.), Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry (pp. 215–216). London: Academic.
Alef, K. (1995b). Estimation of FDA acitivity. In K. Alef, & P. Nannipieri (Eds.), Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry (pp. 132–135). London: Academic.
Federle, T., Dobbins, D. C., Thornton-Manning, J. R., & Jones, D. C. (1986). Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in subsurface soils. Ground Water, 24, 365–374. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1986.tb01013.x.
Federle, T. W. (1988). Mineralization of mono-substituted aromatic compounds in unsaturated and saturated subsurface soils. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 34, 1037–1042.
Gray, T. R. G. (1990). Methods for studying the microbial ecology of soil. In R. Grigorova, & J. R. Norris (Eds.), Methods in microbiology (vol. 22, pp. 309–342). London: Academic.
Gregorich, E. A., Carter, M. A., Augers, D. A., Monreal, C. M., & Ellert B. H. (1994). Towards a minimum dataset to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 74, 367–385.
Handa, S. K., Agnihotri, N. P., & Kulshrestha, G. (1999). Pesticide residues: Significance, management and analysis (pp. 184–198). Texas, USA: Research Periodicals and Book Publishing House.
Ingram, C. W., Coyne, M. S., & Williams, D. W. (2005). Effects of commercial diazinon and imidacloprid on microbial urease activity in soil and sod. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 1573–1580. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0433.
Joergensen, R. G. (1995). Microbial biomass. In K. Alef, & P. Nannipieri (Eds.), Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry (pp. 382–386). London: Academic.
Kale, S. P., & Raghu, K. (1989). Effect of carbofuran and its degradation products on microbial numbers and respiration in soils. Chemosphere, 18, 2345–2351.
Lethbridge, G., & Burns, R. G. (1975). Inhibition of soil urease by organophosphorus insecticides. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 8, 99–102. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(76)90072-9.
Lethbridge, G., Pettit, N. M., Smith, A. R. J., & Burns, R. G. (1976). The effect of organic solvents on soil urease activity. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 85, 449–450. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(76)90049-3.
Linan, C. (1994). Vademecum de products fitosanitarios 10th edn. Madrid, Spain: Ediciones Agrotecnicas.
Martinez, T. M. V., Salmeron, V., & Gonzalez, J. (1992a). Effect of an organo-phosphorus insecticide, phenophos on agricultural soil microflora. Chemosphere, 24, 71–80. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(92)90568-C.
Martinez, T. M. V., Salmeron, V., & Gonzalez, J. (1992b). Effect of the insecticides methyl-pyrimifos and chlorpyrifos on soil micro-flora in an agricultural loam. Plant and Soil, 147, 25–30. doi:10.1007/BF00009367.
Moorman, T. B. (1989). A review of pesticide effects on microorganisms and microbial processes related to soil fertility. Journal of Production Agriculture, 2, 14–23.
Pandey, S., & Singh, D. K. (2004). Total bacterial and fungal population after chlorpyrifos and quinalphos treatments in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) soils. Chemosphere, 55, 283–290. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.052.
Perucci, P., Scarponi, L., Anderson, J. P. E., Arnold, D. J., Lewis, F., & Torstenson, L. (1992). Interference on soil microbial biomass and persistence of trifluralin in a clay soil. In Proceedings of the international symposium on environmental aspects of pesticide microbiology, 17–21 August 1992, Sigtuna, Sweden, pp. 129–134.
Pozo, C., Martinez, T. M. V., Salmeron, V., Rodelas, B., & Gonzalez, L. J. (1995). Effect of chlorpyrifos on soil microbial activity. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 14, 187–192. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1995)14[187:EOCOSM]2.0.CO;2.
Racke, K. D., Fontaine, D. D., Yoder, R. N., & Miller, J. R. (1994). Chlorpyrifos degradations in soil at termiticidal application rates. Pesticide Science, 42, 43–51. doi:10.1002/ps.2780420108.
Racke, K. D., Laskowski, D. A., & Schultz, M. R. (1990). Resistance of chlorpyrifos to enhanced biodegradation in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 38, 1430–1436. doi:10.1021/jf00096a029.
Rangaswamy, V., Reddy, B. R., & Venkateswarlu, K. (1994). Activities of dehydrogenase and protease in soil as influenced by monocrotophos, quinalphos, cypermethrin and fenvalerate. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 47(4), 319–326. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(94)90098-1.
Robson, H., & Gijnner, H. B. (1970). Differential response of soil microflora to diazinon. Plant and Soil, 33, 613–621. doi:10.1007/BF01378250.
Salonius, P. O. (1972). Effect of DDT and fenitrothion on forest-soil microflora. Journal of Economic Entomology, 65, 1089–1090.
Sardar, D., & Kole, R. K. (2005). Metabolism of chlorpyrifos in relation to its effect on the availability of some plant nutrients in soil. Chemosphere, 61, 1273–1280. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.078.
Schnurer, J., & Rosswall, T. (1982). Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 1256–1261.
Sivasithamparam, K. (1969). Some effects of an insecticide (Dursban) and a weedicide (Linuron) on the microflora of a submerged soil. Ceylon Association for Advancement in Science, 25, 1–8.
Sivasithamparam, K. (1970). Some effects of an insecticide (Dursban) and a weedkiller (Linuron) on the microflora of a submerged soil. Riso, 19, 339–346.
Sommerville, L. (1987). Perspective on side effect testing. In L. Sommerville, & M. P. Greaves (Eds.), Pesticide effects in soil microflora (pp. 5–13). London: Taylor and Francis.
Sylvestre, G. S., & Fournier, J. C. (1979). Effect of pesticides on the soil microflora. In N. C. Brady (Ed.), Advances in agronomy (Vol. 31, pp. 1–81). USA: Academic.
Tu, C. M. (1970). Effect of four organophosphorus insecticides on microbial activities in soil. Applied Microbiology, 19, 479–484.
Tu, C. M. (1972). Effect of four nematocides on activities of microorganisms in soil. Applied Microbiology, 23, 398–401.
Van De Warf, H., & Verstraete, W. (1987a). Estimation of active soil microbial biomass by mathematical analysis of respiration curves: Development and verification of the model. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 19, 253–260. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90006-X.
Van De Warf, H., & Verstraete, W. (1987b). Estimation of active soil microbial biomass by mathematical analysis of respiration curves: Calibration of the test procedure. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 19, 261–265. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90007-1.
Vance, E. D., Brookes, P. C., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1987). An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 19, 703–707. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, M., Sardar, D., Pal, R. et al. Effect of chlorpyrifos on microbial biomass and activities in tropical clay loam soil. Environ Monit Assess 160, 385–391 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0702-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0702-y