Abstract
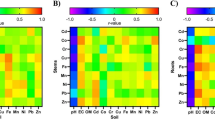
Prediction models were developed to estimate the extent to which aluminium, chromium, copper, iron, manganese, nickel, lead, and zinc were absorbed in the grains, leaves, stems, and roots of Sorghum bicolor cultivated in soil with various amendment rate of sewage sludge (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 g/kg) under greenhouse conditions. It was found that, aside from lead, all the examined metals occurred in significantly higher content in the roots compared to aerial tissues. Furthermore, the r-values were significantly negative between the bioconcentration factors of all metals, apart from aluminium and lead, and soil pH, whereas they were significantly positive between the bioconcentration factors, apart from lead, and soil organic matter content (OM). The r-values were typically significantly positive between the levels of all eight metals in the investigated tissues and in the soil. Moreover, the content of all the eight metals in the tissues exhibited a significant negative r-value with soil pH but a significant positive r-value with soil OM. The eight metal contents in the tissues given by the prediction models were quite similar to the real values, suggesting that the created models performed well, as shown by t-tests. It was thus concluded that prediction models were a viable option for evaluating how safe it was to grow S. bicolor in soils with sewage sludge content and at the same time for keeping track of possible human health hazards.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments: Biochemistry bioavailability and risk of metals. Springer.
Allen, S. (1989). Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Augustsson, A. L., Uddh-Soderberg, T. E., Hogmalm, K. J., & Filipsson, M. E. (2015). Metal uptake by homegrown vegetables – The relative importance in human health risk assessments at contaminated sites. Environmental Research, 138, 181–190.
Basta, N. T., Ryan, J. A., & Chaney, R. L. (2005). Trace element chemistry in residual-treated soil: Key concepts and metal bioavailability. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 49–63.
Bešter, P. K., Lobnik, F., Eržen, I., Kastelec, D., & Zupan, M. (2013). Prediction of cadmium concentration in selected home-produced vegetables. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 96, 182–190.
Binder, D., Dobermann, A., Sander, D., & Cassman, K. (2002). Biosolids as nitrogen source for irrigated maize and rainfed sorghum. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 531–542.
Bonten, L., Groenenberg, J., Weng, L., & van Riemsdijk, W. (2008). Use of speciation and complexation models to estimate heavy metal sorption in soils. Geoderma, 146, 303–310.
Bosch, C. H., & Borus, D. J. (2007). Cereals and pulses of Tropical Africa. Wageningen.
Boshoff, M., De Jonge, M., Scheifler, R., & Bervoets, L. (2014). Predicting As Cd Cu Pb and Zn levels in grasses (Agrostis sp and Poa sp) and stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) applying soil-plant transfer models. Science of the Total Environment, 493, 862–871.
Brunetti, G., Farrag, K., Rovira, P., Nigro, F., & Sensi, N. (2011). Greenhouse and field studies on Cr Cu Pb and Zn phytoextraction by Brassica napus from contaminated soils in the Apulia region Southern Italy. Geoderma, 160, 517–523.
Chaoua, S., Boussaa, S., El Gharmali, A., & Boumezzough, A. (2018). Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 18, 429–436.
Chaudhary, S. A. (1989). Grasses of Saudi Arabia. National Herbarium National Agriculture and Water Research Center Ministry of Agriculture and Water, Riyadh.
Chaudri, A., McGrath, S., Gibbs, P., Chambers, B., Carlton-Smith, C., Godley, A., Bacon, J., Campbell, C., & Aitken, M. (2007). Cadmium availability to wheat grain in soils treated with sewage sludge or metal salts. Chemosphere, 66, 1415–1423.
Cornell, R., & Schwertmann, U. (2003). The iron oxides. Wiley VCH.
Dolgen, D., Alpaslan, M., & Delen, N. (2007). Agricultural recycling of treatment-plant sludge: A case study for a vegetable-processing factory. Journal of Environmental Management, 84, 274–281.
Du Laing, G., van de Moortel, A., Moors, W., De Grauwe, P., Meers, E., Tack, F., & Verloo, M. (2009). Factors affecting metal concentrations in reed plants (Phragmites australis) of intertidal marshes in the Scheldt estuary. Ecological Engineering, 35, 310–318.
Egan, M. (2013). Biosolids management strategies: An evaluation of energy production as an alternative to land application. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 4299–4310.
Eid, E. M., & Shaltout, K. H. (2016). Bioaccumulation and translocation of heavy metals by nine native plant species grown at a sewage sludge dump site. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18, 1075–1085.
Eid, E. M., Alrumman, S. A., Galal, T. M., & El-Bebany, A. F. (2018a). Prediction models for evaluating the heavy metal uptake by spinach (Spinacia oleracea L) from soil amended with sewage sludge. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 20, 1418–1426.
Eid, E. M., Alrumman, S. A., Farahat, E. A., & El-Bebany, A. F. (2018b). Prediction models for evaluating the uptake of heavy metals by cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L) grown in agricultural soils amended with sewage sludge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 501.
Eid, E. M., Alrumman, S. A., Galal, T. M., & El-Bebany, A. F. (2019). Regression models for monitoring trace metal accumulations by Faba sativa Bernh plants grown in soils amended with different rates of sewage sludge. Scientific Reports, 9, 5443.
Eid, E. M., Khedher, K. M., Ayed, H., Arshad, M., Mouldi, A., Shaltout, K. H., Sewelam, N., Galal, T. M., El-Bebany, A. F., & Alshehri, A. M. (2020a). Prediction models based on soil properties for evaluating the heavy metal uptake into Hordeum vulgare L grown in agricultural soils amended with different rates of sewage sludge. International Journal of Environmental Health Research. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2020.1730771
Eid, E. M., Galal, T. M., & El-Bebany, A. F. (2020b). Regression models for monitoring heavy metals accumulation by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants grown in soil amended with different rates of sewage sludge. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 22, 1000–1008.
Eid, E. M., Shaltout, K. H., Alamri, S. A. M., Sewelam, N. A., & Galal, T. M. (2020c). Evaluating the uptake of ten heavy metals by kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L) grown in a soil-sludge mixture using a regression model. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 18, 7021–7039.
Eid, E. M., Shaltout, K. H., Alamri, S. A. M., Sewelam, N. A., Galal, T. M., & Brima, E. I. (2020d). Prediction models for evaluating heavy metal uptake by Pisum sativum L in soil amended with sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 55, 151–160.
Eid, E. M., Shaltout, K. H., Alamri, S. A. M., Sewelam, N. A., Galal, T. M. (2020e). Uptake prediction of ten heavy metals by Corchorus olitorius L cultivated in soil mixed with sewage sludge. Food and Energy Security, 9, e203.
Eid, E. M., Shaltout, K. H., Abdallah, S. M., Galal, T. M., El-Bebany, A. F., & Sewelam, N. A. (2020f). Uptake prediction of ten heavy metals by Eruca sativa Mill cultivated in soils amended with sewage sludge. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 104, 134–143.
Eid, E. M., Shaltout, K. H., Alamri, S. A. M., Alrumman, S. A., Hussain, A. A., Sewelam, N., El-Bebany, A. F., Alfarhan, A. H., Picó, Y., & Barcelo, D. (2021). Prediction models based on soil properties for evaluating the uptake of eight heavy metals by tomato plant (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) grown in agricultural soils amended with sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 105977.
Franz, E., Römkens, P., van Raamsdonk, L., & van der Fels-Klerx, I. (2008). A chain modeling approach to estimate the impact of soil cadmium pollution on human dietary exposure. Journal of Food Protection, 71, 2504–2513.
Handa, S., Thakur, M., & Thakur, K. (2019). Effect of domestic effluents on tomato crop Solanum lycopersicum (L.) production. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 8, 1–7.
He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., & Stoffella, P. J. (2005). Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 19, 125–140.
Huxely, E. (1999). Dictionary of gardening Volume 4: R to Z. The New Royal Horticultural Society Macmillan Reference LTD, London.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press.
Kalis, E. J., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Town, R. M., Unsworth, E. R., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2008). Relationship between metal speciation in soil solution and metal adsorption at the root surface of ryegrass. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 2221–2231.
Karamooz, H., Afshar, A., & Nematpour, F. (2016). Tolerance and accumulation of heavy metals by Descurainia sophia L. Journal of Chemical Health Risks, 6, 69–78.
Kumar, V., Thakur, R., & Kumar, P. (2019a). Assessment of heavy metals uptake by cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var botrytis) grown in integrated industrial effluent irrigated soils: A prediction modelling study. Scientia Horticulturae, 257, 108682.
Kumar, V., Singh, J., & Kumar, P. (2019b). Heavy metal uptake by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.) from paper mill effluent (PME): Experimental and prediction modeling studies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 14400–14413.
Kuo, S., Lai, M., & Lin, C. (2006). Influence of solution acidity and CaCl2 concentration on the removal of heavy metals from metal-contaminated rice soils. Environmental Pollution, 144, 918–925.
Latare, A., Kumar, O., Singh, S., & Gupta, A. (2014). Direct and residual effect of sewage sludge on yield, heavy metals content and soil fertility under rice-wheat system. Ecological Engineering, 69, 17–24.
Li, Y., Wang, H., Wang, H., Yin, F., Yang, X., & Hu, Y. (2014). Heavy metal pollution in vegetables grown in the vicinity of a multi-metal mining area in Gejiu China: Total concentrations speciation analysis and health risk. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 12569–12582.
Matic, N., Jena, V., Sinha, D., Ghosh, S., & Pandey, A. (2019). Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in Coriandrum sativum. Journal of Applied Chemistry, 8, 850–855.
McCauley, A., Jones, C., & Jacobsen, J. (2009). Soil pH and organic matter: Nutrient management modules 8. Montana State University Extension Service.
Michel, K., & Ludwig, B. (2005). Modelling of seepage water composition from experiments with an acid soil and a calcareous sediment. Acta Hydrochimica Et Hydrobiologica, 33, 595–604.
Muchuweti, M., Birkett, J. W., Chinyanga, E., Zvauya, R., Scrimshaw, M. D., & Lester, J. N. (2006). Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: Implications for human health. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 112, 41–48.
Nakamura, K., Yasutaka, T., Kuwatani, T., & Komai, T. (2017). Development of a predictive model for lead, cadmium and fluorine soil-water partition coefficients using sparse multiple linear regression analysis. Chemosphere, 186, 501–509.
Nan, Z., Li, J., Zhang, J., & Cheng, G. (2002). Cadmium and zinc interactions and their transfer in soil-crop system under actual field conditions. Science of the Total Environment, 285, 187–195.
Novotná, M., Mikeš, O., & Komprdová, K. (2015). Development and comparison of regression models for the uptake of metals into various field crops. Environmental Pollution, 207, 357–364.
Pal, R., & Kundu, R. (2016). Risk assessment of some selected vegetables grown in metal contaminated soil supplements. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences India Section B: Biological Sciences, 86, 585–593.
Peles, J. D., Brewer, S. R., & Barret, G. W. (1998). Heavy metal accumulation by old-field plant species during recovery of sludge-treated ecosystems. The American Midland Naturalist, 140, 245–251.
Raguž, V., Jarsjö, J., Grolander, S., Lindborg, R., & Avila, R. (2013). Plant uptake of elements in soil and pore water: Field observations versus model assumptions. Journal of Environmental Management, 126, 147–156.
Ramadan, M. A., & Al-Ashkar, E. A. (2007). The effect of different fertilizers on the heavy metals in soil and tomato plant. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 1, 300–306.
Singh, R., & Agrawal, M. (2009). Use of sewage sludge as fertilizer supplement for Abelmoschus esculentus plants: Physiological, biochemical and growth responses. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 3, 91–106.
Singh, R., & Agrawal, M. (2010a). Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 632–641.
Singh, R., & Agrawal, M. (2010b). Effect of different sewage sludge applications on growth and yield of Vigna radiata L field crop: Metal uptake by plant. Ecological Engineering, 36, 969–972.
Soil Survey Staff. (2014). Keys to soil taxonomy 12th edition. US Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Soriano-Disla, J., Gómez, I., Navarro-Pedreño, J., & Jordán, M. (2014). The transfer of heavy metals to barley plants from soils amended with sewage sludge with different heavy metal burdens. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 14, 687–696.
SPSS. (2006). SPSS base 15.0 user’s guide. SPSS Inc, Chicago.
Tudoreanu, L., & Phillips, C. (2004). Empirical models of cadmium accumulation in maize rye grass and soya bean plants. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 84, 845–852.
Waegeneers, N., Ruttens, A., & de Temmerman, L. (2011). A dynamic model to calculate cadmium concentrations in bovine tissues from basic soil characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 2815–2823.
Wilke, B. M. (2005). Determination of chemical and physical soil properties. In R. Margesin & F. Schinner (Eds.), Manual for soil analysis - monitoring and assessing soil bioremediation (pp. 47–95). Springer-Verlag.
Yang, H., Li, Z., Lu, L., Long, J., & Liang, Y. (2013). Cross-species extrapolation of prediction models for cadmium transfer from soil to corn grain. PLOS ONE, 8, e80855.
Ye, X., Li, H., Ma, Y., Wu, L., & Sun, B. (2014). The bioaccumulation of Cd in rice grains in paddy soils as affected and predicted by soil properties. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 14, 1407–1416.
Zeng, F., Ali, S., Zhang, H., Ouyang, Y., Qiu, B., Wu, F., & Zhang, G. (2011). The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution, 159, 84–91.
Zhang, S., Song, J., Gao, H., Zhang, Q., Lv, M., Wang, S., Liu, G., Pan, Y., Christie, P., & Sun, W. (2016). Improving prediction of metal uptake by Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis L) based on a soil-plant stepwise analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 569, 1595–1605.
Zheng, Y., Shen, D., Wu, S., Han, Y., Li, S., Tang, F., & Liu, Y. (2018). Uptake effects of toxic heavy metals from growth soils into jujube and persimmon of China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 31593–31602.
Zhou, L., Zhao, Y., & Wang, S. (2015). Cadmium transfer and detoxification mechanisms in a soil-mulberry-silkworm system: Phytoremediation potential. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 18031–18039.
Funding
This research work was funded by the Scientific Research Deanship at King Khalid University and the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia through the project number IFP-KKU-2020/3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.H. Shaltout: writing — original draft, supervision; S.A.M. Alamri: project administration, writing — review & editing; S.A. Alrumman: project administration, writing — review and editing; A.A. Hussain: methodology; N. Sewelam: writing — review & editing; E.M. Eid: conceptualisation, formal analysis, investigation, writing — review and editing, visualisation, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaltout, K.H., Alamri, S.A.M., Alrumman, S.A. et al. Evaluation of uptake of eight metals by Sorghum bicolor grown in arable soil combined with sewage sludge based on prediction models. Environ Monit Assess 193, 510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09320-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09320-7