Abstract
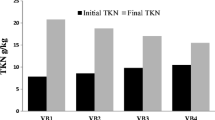
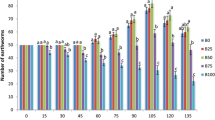
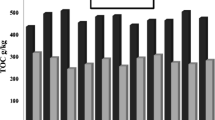
The animal, agro-wastes and water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) are a serious problem for the society and ecosystem. The present study carried out the management of water hyacinth and observation of nutritional status like pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total organic carbon (TOC), total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), C/N ratio, total phosphorus and total calcium (TCa) of liquid bio-fertilizer (vermiwash) before and after vermicomposting of feed materials of different combinations of buffalo dung (BD) with water hyacinth (WH) and gram bran (GB). After vermicomposting of different combinations of BD with WH and agro-wastes, significant decrease in level of pH, EC, TOC and C/N ratio was observed, whereas significant increase in TKN, TK, TAP and TCa level in vermiwash of final vermicompost with respect to initial feed material was observed. The pH of initial mixture in all combinations has tended to basic in nature, while in final vermicompost, it becomes neutral/basic. The significant increase was observed in the level of TKN, TK, TAP in BD + GB + WH (1:2:1) and TCa in BD + GB + WH (1:1:2) vermiwash of final vermicompost of combination, whereas decrease was observed in TOC, C/N ratio, pH and EC in BD + WH (1:1), BD + GB + WH (1:1:1), BD + GB + WH (1:2:1) and BD + GB (1:1), respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok, K. C. (1994). State of art report on vermicomposting in India. New Delhi: Council for Advancement of People action and Rural Technology (CPART).
Atiyeh, R. M., Dominguez, J., Subler, S., & Edwards, C. A. (2000). Change in the biochemical properties of cow manure during processing by earthworm Eisenia andrei (Bouch) and effect of seeding growth. Pedobiologia, 44, 709–724.
Benitez, E., Nogales, R., Masciandaro, G., & Ceccanti, B. (1999). Enzyme activities as indicators of the stabilization of sewage sludge composting with Eisenia fetida. Bioresource Technology, 67, 297–303.
Bharadwaj, A. (2010). Management of kitchen waste material through vermicomposting. Asian Journal of Experimental Biological Sciences, 1(1), 175–177.
Bhartiya, D. K., & Singh, K. (2012). Heavy metals accumulation from municipal solid wastes with different animal dung through vermicomposting by earthworm Eisenia fetida. World Applied Sciences Journal, 17(1), 133–139.
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, R. G. (1982). Nitrogen total. In: A. L. Page, R. H. Millar, D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Method of soil analysis american society of agronomy (pp. 575–624). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Chaudhari, P. S., & Bhattacharjee, G. (2002). Capacity of various experimental diets to support biomass and reproduction of Perionyx excavatus. Bioresource Technology, 82, 147–150.
Chauhan, H. K. (2013) Effect of different combinations of animal dung and agro wastes on the reproduction and development of earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ph.D. Thesis. Deen Dayal Upadhyay, Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, U.P. India.
Chauhan, H. K., & Singh, K. (2012). Effect of binary combinations of buffalo, cow and goat dung with different agro wastes on reproduction and development of earthworm Eisenia foetida. World Journal of Zoology, 7(1), 23–29. doi:10.5829/idosi.wjz.2012.7.1.56439.
Chauhan, H. K., & Singh, K. (2013) Effect of tertiary combinations of animal dung on the growth and development of earthworm Eisenia fetida during organic wastes management. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 2, p. 11. http://www.ijrowa.com/content/2/1/11.
Chauhan, H. K., & Singh, K. (2014) Potency of vermiwash with Azadirachta indica A. Juss on yield of gram (Cicer arietinum) and infestation of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). American–Eurasian the Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 6(4), pp. 87–93, ISSN 2079-2050. doi:10.5829/idosi.aejts.2014.6.4.85165.
Dash, M. C., & Senapati, B. K. (1986) Vermitechnology: An option for organic waste management in India. In: M. C. Dash, et al. (Eds.), Natn sem org waste utiliz vermicomp. In: Proceedings, Part B. Sambapur Univ, Jyoti Vihar, Orissa, India, pp. 157–172.
Deka, H., & Deka, S., Baruah, C. K. (2013) Vermicomposting of water hyacinth Eichhornia Crassipes (Mart. Solms) employing indigenous earthworm species. International conference on chemical, agricultural and medical sciences (CAMS-2013). 29–30 Dec 2013 Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia).
Edwards, C. A., & Lofty, J. R. (1972). Biology of earthworms. London: Chapman and Hall.
Elvira, C., Goicoechea, M., Sampdro, L., Mato, S., & Nogalas, R. (1996). Bioconversion of solid paper pulp mill sludge by earthworm. Bioresource Technology, 75, 173–177.
Elvira, C. A., Sampedro, L., Benitez, E., & Nogales, R. (1998). Vermicomposting of sludges from paper mill and dairy industries with Eisenia andrei: A pilot-scale study. Bioresource Technology, 63, 205–211.
Garg, V. K., Chand, S., Chhillar, A., & Yadav, V. K. (2005). Growth and reproduction of Eisenia fetida in various animal wastes during vermicomposting. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 3(2), 51–59.
Garg, V. K., & Gupta, R. (2011). Effect of temperature variations on vermicomposting of household solid waste and fecundity of Eisenia fetida. Bioremediation Journal, 15(3), 165–172.
Garg, V. K., & Kaushik, P. (2003). Vermicomposting of solid textile will sludge and cow dung with the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Bioresource Technology, 90, 311–316.
Garg, V. K., Suthar, S., & Yadav, A. (2011). Management of food industry waste employing vermicompost technology. Bioresource Technology,. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.116.
Garg, V. K., Yadav, Y. K., Sheoran, A., Chand, S., & Kaushik, P. (2006). Live stock excreta management through vermicomposting using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environmentalist, 26, 269–276.
Gunadi, B., & Edwards, C. A. (2003). The Effect of multiple application of different organic wastes on the growth, fecundity and survival of Eisenia foetida (Savigny) (Lumbricidae). Pedobiologia, 47(4), 321–330.
Gupta, P. K. (2005). Vermicomposting for sustainable agriculture (pp. 11–14). Jodhpur: Bharat Printing Press.
Gupta, R., & Garg, V. K. (2007). Stabilization of primary sludge during vermicomposting. Journal of Hazardous Materials,. doi:10.1016/j.hazmat.09.055.
Haimi, J., & Hutha, V. (1986). Capacity of various organic residue to support adequate earthworm biomass in vermicomposting. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2, 23–27.
Hand, P., Hayes, W. A., Satchell, J. E., & Frankland, J. C. (1988). The vermicomposting of cow slurry. In C. A. Edwards & E. F. Neuhauser (Eds.), Earthworms in waste and environmental management (pp. 49–63). The Hague: SPB Academic Publishing.
Hartenstein, R., Neuhauser, E. F., & Kaplan, D. L. (1979). Reproductive potential of the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Oecologia, 43(3), 329–340.
Heartenstien, R., & Heartenstien, F. (1981). Physico-chemical changes affected inactivated sludge by the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Journal of Environmental Quality, 10, 377–382.
Ismail, S. A. (1997). Vermicology: The biology of earthworms. Hyderabad: Orient Longman Press.
Kale, R. D. (1998). Earthworm nature’s gift for utilization of organic wastes. In C. A. Edwards (Ed.), Earthworms ecology. Soil and waste conversion society (pp. 335–373). New York: Ankeny Lowa St. Lucie Press.
Kale, R. D., Bano, K., & Krishnamoorthy, R. V. (1982). Potential of Perionyx excavates for utilizing organic wastes. Pedobiologia, 23, 419–425.
Kaviraj, & Sharma, S. (2003). Municipal solid waste management through vermicomposting employing exotic and local species of earthworms. Bioresource Technology, 90, 169–173.
Khwairakpam, M., & Bhargava, R. (2009). Bioconversion of filter mud using vermicomposting employing two exotic and one local earthworm species. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5846–5852.
Lee, K. E. (1992). Some trends opportunities earthworm research or Darwin children. The future of our discipline. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 24, 1765–1771.
Mansell, G. P., Syres, J. K., & Gregg, P. E. (1981). Plant availability of phosphorus in dead herbage ingested by surface casting earthworm. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 13, 163–167.
Mishra, K., Singh, K., & Tripathi, C. P. M. (2014). Management of municipal solid wastes and production of liquid biofertilizer through vermic-activity of epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 3, 56. doi:10.1007/s40093-014-0056-0.
Nath, G., Singh, K., & Singh, D. K. (2009). Chemical analysis of vermicomposts vermiwash of different combinations of animal, agro and kitchen wastes. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(4), 3672–3676.
Ndegwa, P. M., Thompson, S. A., & Das, K. C. (2000). Effects of stocking density and feeding rate on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresource Technology, 71, 5–12.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total carbon and organic carbon matter. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Method of Soil Analysis (pp. 539–579). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Orozco, F. H., Cegarra, J., Trujillo, L. M., & Roig, A. (1996). Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia fetida: Effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 22, 162–166.
Payal, G., Gupta, A., & Satya, S. (2006). Vermicomposting of different types of wastes using Eisenia fetida a comparative study. Bioresource Technology, 97, 391–395.
Satchell, J. E., & Martin, K. (1984). Phosphate activity in earthworm faeces. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 16, 191–194.
Senesi, N. (1989). Composted materials as organic fertilizers. Science of the Total Environment, 81(82), 521–524.
Suthar, S. (2007). Nutrients changes and biodynamic of earthworms Perionnyx excavates during recycling of some agricultural wastes. BioresourceTechnology,. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.06.01.
Suthar, S., Singh, S., & Dhawan, S. (2008). Earthworm as bioindicators of metals (Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, Pb and Cd) in soils: Is metal bioaccumulation affected by their ecological categories. Ecological Engineering, 32, 99–107.
Tripathi, G., & Bharadwaj, P. (2004). Comparative studies on biomass production, life cycles and efficiency of Eisenia fetida (Savigny) and Lampito mauritii (Kinberg). Bioresource Technology, 92, 275–283.
Viel, M., Sayag, D., & Andre, L. (1987). Optimization of agricultural, industrial waste management through in–vessel composting. In: M. de Bertoldi (Ed.), Compost: Production, quality and use (pp. 230−237). Elseiver Applied Science, Essex.
Wong, J. M. C., Fang, M., Li, G. X., & Wong, W. H. (1997). Feasibility of using coal ash residue as co-composting materials for sewage sludge. Environmental Technology, 18, 563–568.
Yadav, A., Gupta, R., & Garg, V. K. (2013) Organic manure production from cow dung and biogas plant slurry by vermicomposting under field conditions. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 2, p. 21. http://www.ijrowa.com/content/2/1/21.
Yadav, K. D., Tare, V., & Ahammed, M. M. (2010). Vermicomposting of source-separated human faeces for nutrient recycling. Waste Management, 30(1), 50–56.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Dr. V. K. Garg, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, Hisar, Haryana, India, for active support in this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nath, S., Singh, K. Analysis of different nutrient status of liquid bio-fertilizer of different combinations of buffalo dung with gram bran and water hyacinth through vermicomposting by Eisenia fetida . Environ Dev Sustain 18, 645–656 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9666-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-015-9666-6