Abstract
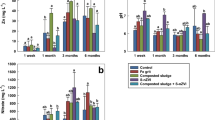
The most common drinking water clarification technology worldwide is based on precipitation using the floccules of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide FeO(OH). The coagulation sludge obtained is usually mixed with biowaste and composted. Inexperienced farmers are interested in these composts, in the expectation that the smallest fractions of the precipitated organic matter together with the colloidal particles of clay captured during the clarification process might increase the level of soil organic matter as well as cation-exchange capacity (CEC) of soil and increase crop yields. Nevertheless, those who have used these composts observed that plants on treated soil show signs of phosphorus (P) insufficiency, despite having been fertilized appropriately. It has been published recently that the traces of iron (Fe) from the FeO(OH) turn the soil P into Fe phosphates (FeP), which makes P not readily available to agricultural plants. A 6-year field-scale experiment was carried out and was accompanied by robust analyses on soils and yields. It was confirmed that the traces of Fe from the coagulation sludge worsen the availability of soil P to plants. However, for the first time, evidence has been obtained concerning the fact that the Fe also damages the efficiency of P fertilizers applied afterward. A questionnaire was conducted among drinking water treatment plant operators and regulators to identify a reason why similar practices have not been banned yet. The results showed a growing awareness of the issue among experts, but politicians seem to prefer putting off unpopular measures. We recommend abandoning the application of these composts onto arable land and the revitalization of the affected fields using biochar activated by calcium and aluminum phosphates (CaP and AlP) so that the problem is not delayed to such an extent that its solution would become a problem for future generations.

Similar content being viewed by others
5. References
Abu-Bakar, H., Williams, L., & Hallett, S. H. (2021). Quantifying the impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on household water consumption patterns in England. NPJ Clean Water, 4(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00103-8
Andersson, H., Bergström, L., Djodjic, F., Ulén, B., & Kirchmann, H. (2013). Topsoil and subsoil properties influence phosphorus leaching from four agricultural soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(2), 455–463. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2012.0224
Bencsik, A., Tóbiás Kosár, S., Machová, R. (2018). Corporate culture in service companies that support knowledge sharing. Journal of Tourism and Services, 9(16), 7–13. https://doi.org/10.29036/jots.v9i16.41
Blazkova, I., & Dvoulety, O. (2018). Sectoral and firm-level determinants of profitability: A multilevel approach. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 6(2), 32–44. https://doi.org/10.37335/ijek.v6i2.76
Bolisetty, S., Peydayesh, M., & Mezzenga, R. (2019). Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chemical Society Reviews, 48(2), 463–487. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00493E
Brabenec, T., Maroušková, A., Zoubek, T., & Filip, M. (2021). Residues from water precipitation via ferric hydroxide threaten soil fertility. Sustainability, 13(8), 4327. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084327
Bull, R. J., Birnbaum, L., Cantor, K. P., Rose, J. B., Butterworth, B. E., Pegram, R. E. X., & Tuomisto, J. (1995). Water chlorination: Essential process or cancer hazard? Toxicological Sciences, 28(2), 155–166. https://doi.org/10.1006/faat.1995.1156
Busch, D., Kammann, C., Grünhage, L., & Müller, C. (2012). Simple biotoxicity tests for evaluation of carbonaceous soil additives: Establishment and reproducibility of four test procedures. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41(4), 1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0122
Calvo, J. (2018). High-Tech Start-Ups in Japan: Cogent Labs, AI-OCR Solutions for Automated Business Process Outsourcing. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 6(2), 12–31. https://doi.org/10.37335/ijek.v6i2.75
Chen, X. X., Zhang, W., Liang, X. Y., Liu, Y. M., Xu, S. J., Zhao, Q. Y., Du, Y. F., Zhang, L., Chen, X. P., & Zou, C. Q. (2019). Physiological and developmental traits associated with the grain yield of winter wheat as affected by phosphorus fertilizer management. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53000-z
Exley, C. (2017). Aluminum should now be considered a primary etiological factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports, 1(1), 23–25. https://doi.org/10.3233/ADR-170010
Fu, R., Yuan, J. D., Xu, T. T., Xu, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhang, R., Tian, H., & Gao, Y. J. (2021). Effects of phosphorus application rates on spring rape yield and soil phosphorus balance. Ying Yong Sheng tai xue bao = The Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(3), 906–912. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202103.010
Ishikawa, S., Ueda, N., Okumura, Y., Iida, Y., & Baba, K. (2007). Recovery of coagulant from water supply plant sludge and its effect on clarification. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 9(2), 167–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-007-0173-1
Khursheed, A., Mustafa, F., Fatima, M., & Siddique, F. (2018). Entrepreneurial intentions: gem based empirical analysis on the northern Europe and Asian countries. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 6(2), 59–70. https://doi.org/10.2478/IJEK-2018-0014
Kliestik, T., Misankova, M., Valaskova, K., & Svabova, L. (2018). Bankruptcy prevention: New effort to reflect on legal and social changes. Science and Engineering Ethics, 24(2), 791–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-017-9912-4
Kliestik, T., Valaskova, K., Nica, E., Kovacova, M., & Lazaroiu, G. (2020a). Advanced methods of earnings management: monotonic trends and change-points under spotlight in the Visegrad countries. Oeconomia Copernicana, 11(2), 371–400. https://doi.org/10.24136/oc.2020.016
Kliestik, T., Nica, E., Musa, H., Poliak, M., & Mihai, E. A. (2020b). Networked, Smart, and Responsive Devices in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Systems. Economics, Management and Financial Markets, 15(3), 23–29. https://doi.org/10.22381/EMFM15320203
Kopecky, M., Peterka, J., Kolar, L., Konvalina, P., Marousek, J., Vachalova, R., Herout, M., Strunecky, O., Batt, J., & Tran, D. K. (2021). Influence of selected maize cultivation technologies on changes in the labile fraction of soil organic matter sandy-loam cambisol soil structure. Soil and Tillage Research, 207, 104865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104865
Kovacova, M., Kliestik, T., Valaskova, K., Durana, P., & Juhaszova, Z. (2019). Systematic review of variables applied in bankruptcy prediction models of Visegrad group countries. Oeconomia Copernicana, 10(4), 743–772. https://doi.org/10.24136/oc.2019.034
Kubálek, J., Čámská, D., & Strouhal, J. (2017). Personal Bankruptcies from Macroeconomic Perspective. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 5(2), 78–88. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijek-2017-0013
Machová, V., Vrbka, J., (2018). Value generators for businesses in agriculture. The 12th International Days of Statistics and Economics Conference Proceedings. Praha, Czech Republic: Melandrium, 1123–1132, ISBN 978–80–87990–14–8
Mardoyan, A., & Braun, P. (2015). Analysis of Czech Subsidies for Solid Biofuels. International Journal of Green Energy, 12(4), 405–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2013.841163
Maroušek, J., Bartoš, P., Filip, M., Kolář, L., Konvalina, P., Maroušková, A., Moudrý, J., Peterka, J., Šál, J., Šoch, M., Stehel, V., Strunecký, O., Suchý, K., Vochozka, M., Vrbka, J., & Zoubek, T. (2020b). Advances in the agrochemical utilization of fermentation residues reduce the cost of purpose-grown phytomass for biogas production. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1738597
Maroušek, J., Maroušková, A., & Kůs, T. (2020a). Shower cooler reduces pollutants release in production of competitive cement substitute at low cost. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1825560
Marousek, J., Mysková, K., & Zak, J. (2015). Managing environmental innovation: Case study on biorefinery concept. Revista Técnica De La Facultad De Ingeniería Universidad Del Zulia, 38(3), 216–220.
Marousek, J., Stehel, V., Vochozka, M., Kolar, L., Marouskova, A., Strunecky, O., Peterka, J., Kopecky, M., & Shreedhar, S. (2019). Ferrous sludge from water clarification: Changes in waste management practices advisable. Journal of Cleaner Production, 218, 459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.037
Muo, I., & Azeez, A. (2019). Green entrepreneurship: literature review and agenda for future research. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge, 7(2), 17–29. https://doi.org/10.2478/ijek-2019-0007
Peters, E., Kliestik, T., Musa, H., & Durana, P. (2020). Product decision-making information systems, real-time big data analytics, and deep learning-enabled smart process planning in sustainable industry 4.0. Journal of Self-Governance and Management Economics, 8(3), 16–22. https://doi.org/10.22381/JSME8320202
Petruzzelli, D., Volpe, A., Limoni, N., & Passino, R. (2000). Coagulants removal and recovery from water clarifier sludge. Water Research, 34(7), 2177–2182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00357-7
Roccaro, P., Mancini, G., & Vagliasindi, F. G. (2005). Water intended for human consumption—Part I: Compliance with European water quality standards. Desalination, 176(1–3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2004.11.010
Ryltseva, Y. (2021). Express-method of determining the water-yielding capacity of natural water sludge in modern dewatering technologies. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1030(1), 012108. IOP Publishing
Singh, N. B., Nagpal, G., & Agrawal, S. (2018). Water purification by using adsorbents: A review. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 11, 187–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006
Stávková, J., & Maroušek, J. (2021). Novel sorbent shows promising financial results on P recovery from sludge water. Chemosphere, 276, 130097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130097
Tortajada, C., & van Rensburg, P. (2020). Drink more recycled wastewater. Nature, 577(7788), 26–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-03913-6
Valaskova, K., Throne, O., Kral, P., & Michalkova, L. (2020). Deep learning-enabled smart process planning in cyber-physical system-based manufacturing. Journal of Self-Governance and Management Economics, 8(1), 121–127. https://doi.org/10.22381/JSME8120205
Vochozka, M., Rowland, Z., Suler, P., & Marousek, J. (2020). The influence of the international price of oil on the value of the EUR/USD exchange rate. Journal of Competitiveness, 12(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.7441/joc.2020.02.10
Yang, J., Gu, Y., Chen, Z., Song, Y., Sun, F., Liu, J., & Waigi, M. G. (2021). Colonization and performance of a pyrene-degrading bacterium Mycolicibacterium sp. Pyr9 on root surfaces of white clover. Chemosphere, 263, 127918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127918
Zaman, S., Begum, A., Rabbani, K. S., & Bari, L. (2016). Low cost and sustainable surface water purification methods using Moringa seeds and scallop powder followed by bio–sand filtration. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 17(1), 125–137. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2016.111
Zhu, H., Teng, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, L., Ren, W., Luo, Y., & Christie, P. (2021). Changes in clover rhizosphere microbial community and diazotrophs in mercury-contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 767, 145473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maroušek, J., Maroušková, A., Zoubek, T. et al. Economic impacts of soil fertility degradation by traces of iron from drinking water treatment. Environ Dev Sustain 24, 4835–4844 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01636-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01636-1