Abstract
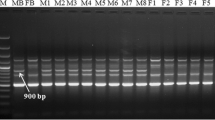
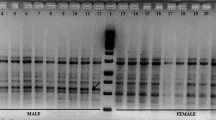
DNA fingerprinting studies have been carried out with the physiologically mature male and female plants of Jojoba using 80 ISSR primers with a view to generate sex-linked markers. After bulk segregant analysis, two unique ISSR markers, viz. ISSR8481500 and VIS111317 have been developed which can be used for determining the sex at the seedling stage. Of the eighty primers tested on the pooled male DNA and pooled female DNA samples, six ISSR primers were found to be associated with sex expression. Of the six, only two primers ISSR848 and VIS11 generated unique male sex specific bands of ~1,500 and ~1,300 bp which were consecutively present in all the male genotypes and absent in all the respective female genotypes. The remaining four primers when tried on individuals of different genotypes were confined to their sex specificity in only two female genotypes and absent in their male counterparts. One of the male-sex specific markers, VIS111317 has also been cloned and sequenced which showed homology with a sex linked gene, DD44 from dioecious Silene species. Furthermore, VIS111317 was converted into a male sex-specific sequence tagged sites (STS) marker of 584 bp. The male specific STS marker thus developed has been verified and validated on 100 populations of male and female individuals from ten different genotypes of Jojoba to endorse the diagnostic reliability of the STS marker. This can gainfully be employed for screening of sex at seedling stage which would be quite helpful for uprooting the undesired plants, thereby, saving resources like labor, water, fertilizers and space for highly desirable female plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal M, Shrivastava N, Padh H (2011) Development of sex-linked AFLP markers in Simmondsia chinensis. Plant Breed 130:114–116
Agrawal V, Sharma K, Gupta S, Kumar R, Prasad M (2007) Identification of sex in Simmondsia chinensis (Jojoba) using RAPD markers. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1:207–210
Aleksandrov OS, Divashuk MG, Karlov GI (2011) Development of a sex-specific molecular marker for Japanese Hop Humulus japonicas Siebold & Zucc. Russ J Genet 47:1016–1020
Alstrom-Rapaport C, Lascoux M, Wang YC, Roberts G, Tuskan GA (1998) Identification of a RAPD marker linked to sex determination in the basket willow (Salix viminalis L.). J Hered 89:44–49
Al-Widyana MI, Al-Muhtaseb MA (2010) Experimental investigation of Jojoba as a renewable energy source. Energy Convers Manag 51:1702–1707
Baratakke RC, Patil CG (2009) Identification of a RAPD marker linked to sex determination in Momordica dioica Roxb. Indian J Genet 69:254–255
Canoira L, Alcantara R, Garcıa-Martınez J, Carrasco J (2006) Biodiesel from Jojoba oil-wax: transesterification with methanol and properties as a fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 30:76–81
Chaves-Bedoya G, Nunenz V (2007) A SCAR marker for the sex types determination in Colombian genotypes of Carica papaya. Euphytica 153:215–220
Da Costa FR, Pereira TNS, Gabriel APC, Pereira MG (2011) ISSR markers for genetic relationships in Caricaceae and sex differentiation in papaya. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 11:352–357
Danilova TV, Karlov GI (2006) Application of inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism for detection of sex-specific molecular markers in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 151:15–21
Dhawan C, Kharb P, Sharma R, Uppal S, Aggarwal RK (2013) Development of male-specific SCAR marker in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Tree Genet Genomes. doi:10.1007/s11295-013-0617-9
Flachowsky H, Schumann E, Webbere WE, Peil A (2001) Application of AFLP for the detection of sex-specific markers in hemp. Plant Breed 120:305–309
Gentry HS (1958) The natural history of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider) and its cultural aspect. Econ Bot 12:261–295
George J, Karun A, Manimekala R, Rajesh MK, Remya P (2007) Identification of RAPD markers linked to sex determination in palmyrah (Borassus flabellifer L.). Curr Sci 93:1075–1077
Gill GP, Harvey CF, Gardner RC, Frasef LG (1998) Development of sex-linked PCR markers for gender identification in Actinidia. Theor Appl Genet 97:439–445
Harsh LN, Tewari JC, Patwal DS, Meena GL (1987) Package and practices for cultivation of Jojoba Simmondsia chinensis in arid zone. Central Arid Zone Research Institute, Jodhpur
Hosseini FS, Hassani HS, Arrin MJ, Baghizadeh A, Mohammadi-Nejab G (2011) Sex determination of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis cv. Arizona) by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) molecular marker. Afr J Biotechnol 10:470–474l
Huzayyin AS, Bawady AH, Rady MA, Dawood A (2004) Experimental evaluation of diesel engine performance and emission using blends of Jojoba oil and diesel fuel. Energy Convers Manag 45:2093–2112
Ii Y, Uragami A, Uno Y, Kanechi M, Inagaki N (2012) RAPD based analysis of differences between male and female genotypes of Asparagus officinalis. Hortic Sci (Prague) 39:33–37
Ince AG, Karaca M (2011) Early determination of sex in Jojoba plant by CAPS assay. J Agric Sci 149:327–336
Ince AG, Karaca M, Onus AN (2010) A reliable gender diagnostic PCR assay for Jojoba [Simmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider]. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57:773–779
Jamsari A, Nitz I, Reamon-Buttner SM, Jung C (2004) BAC derived diagnostic markers for sex determination in Asparagus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1140–1146
Korekar G, Sharma RK, Kumar R, Meenu, Bisht NC, Srivastava RB, Ahuja PS, Stobdan T (2012) Identification and validation of sex-linked SCAR markers in dioecious Hippophae rhamnoides L. (Elaeagnaceae). Biotechnol Lett 34:973–978
Lee CW, Sherman RA (1985) Meiosis in Jojoba, Simmondsia chinensis. Isr J Bot 34:1–6
Li M, Yang H, Li F, Yang F, Yin G, Gan S (2010) A male-specific SCAR marker in Calamus simplicifolius, a dioecious rattan species endemic to China. Mol Breed 25:549–551
Lianjun W, Changbo D, Degao L, Qingchang L (2012) Identification of a male-specific amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) marker in Broussonetia papyrifera. Afr J Biotechol 11:8196–8201
Maki M (2009) Development of SCAR markers for sex determination in the dioecious shrub Acuba japonica (Cornaceae). Genome 52:231–237
Mandolino G, Carboni A, Forapani S, Faeti V, Ranalli P (1999) Identification of DNA markers linked to the male sex in dioecious hemp. Theor Appl Genet 98:86–92
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations (random amplified polymorphic DNA/restriction fragment length polymorphism). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Ming R, Wang J, Moore PH, Paterson AH (2007) Sex chromosomes in flowering plants. Am J Bot 94:141–150
Moore RC, Kozyreva O, Lebel-Hardenack S, Siroky J, Hobza R, Vyskot B, Grant SR (2003) Genetic and functional analysis of DD44, a sex-linked gene from the dioecious plant Silene latifolia, provides clues to early events in sex chromosome evolution. Genetics 163:321–334
Nanda S, Kar B, Nayak S, Jha S, Joshi RK (2013) Development of an ISSR based STS marker for sex identification in pointed gourd (Trichosanthes dioica Roxb.). Sci Hortic 150:11–15
Patil CG, Baratakke RC, Sandigwad AM (2012) Development of a RAPD-based SCAR marker for sex identification in Momordica dioica Roxb. Isr J Plant Sci 60:457–465
Polley A, Seigner E, Ganal MG (1997) Identification of sex in hop (Humulus lupulus) using molecular markers. Genome 40:357–361
Rana S, Shirkot P, Yadav MC (2009) A female sex associated randomly amplified polymorphic DNA marker in dioecious Hippophae salicifolia. Genes Genomes Genomics 3:96–101
Reamon-Buttner SM, Jung C (2000) AFLP-derived STS markers for the identification of sex in Asparagus officinalis L. Theor Appl Genet 100:432–438
Reamon-Buttner SM, Schondelmaier J, Jung C (1998) AFLP markers tightly linked to the sex locus in Asparagus officinalis L. Mol Breed 4:91–98
Reddy MP, Sarla N, Siddiq EA (2002) Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128:9–17
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dymnamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sakamoto KL, Shimomura K, Kamada H, Satoh S (1995) A male-associated DNA sequence in a dioecious plant, Cannabis sativa L. Plant Cell Physiol 36:1549–1554
Sharma K, Agrawal V, Prasad M, Gupta S, Kumar R, Prasad M (2008) ISSR marker-assisted selection of male and female plants in a promising dioecious crop, Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis). Plant Biotechnol Rep 2:239–243
Shevachmana M, Shania A, Garti N (2004) Formation and investigation of microemulsions based on Jojoba oil and nonionic surfactants. J Am Oil Chem Soc 81:1143–1152
Shirkot P, Sharma DR, Mohapatra T (2002) Molecular identification of sex in Actinidia deliciosa var deliciosa by RAPD markers. Sci Hortic 94:33–39
Singh M, Kumar S, Singh AK, Ram D, Kalloo G (2002) Female sex associated RAPD marker in pointed gourd (Trichosanthes dioica Roxb.). Curr Sci 82:131–132
Stobdan T, Angchuk D, Singh SS (2008) Seabuckthorn: an emerging storehouse for researchers in India. Curr Sci 94:1236–1237
Torjek O, Bucherna N, Kiss E, Homoki H (2002) Novel male specific markers (MADC5, MADC6) in hemp. Euphytica 127:209–218
Urasaki N, Tokumoto M, Tarora K, Ban Y, Kayano T, Tanaka H, Oku H, Chinen I, Terauchi R (2002) A male and hermaphrodite specific RAPD marker for papaya (Carica papaya L.). Theor Appl Genet 104:281–285
Wiseman MO, Price RL (1987) Functional properties of protein concentrates from pressed Jojoba meal. Cereal Chem 64:94–97
Xu WJ, Wang BW, Cui KM (2004) RAPD and SCAR markers linked to sex determination in Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Euphytica 136:233–238
Yakubov B, Barazani O, Golan-Goldfish A (2005) Combination of SCAR primers and touchdown PCR for sex determination in Pistacia vera L. Sci Hortic 103:473–478
Yang H, Gan S, Yin G, Hu H (2005) Identification of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers linked to sex determination in Calamus simplicifolius C.F. Wei. J Int Plant Biol 47:1249–1253
Younis RAA, Ismail OM, Soliman SS (2008) Identification of sex-specific DNA markers for datepalm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) using RAPD and ISSR techniques. Res J Agric Biol Sci 4:278–284
Zhou Y, Wang X, Zhang X (2011) Development and application of a SRAP marker for the identification of sex in Buchloe dactyloides. Euphytica 181:261–266
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR) anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Delhi, Government of India for the sanction of a Major research project (SERB/SR/SO/PS/05/2012) to Veena Agrawal and DST young scientist project [SR/FT/LS-109/2008 (G)] to Kuldeep Sharma. Monika Heikrujam is indebted to CSIR, India for the award of CSIR JRF and SRF. We are also thankful to Mr. LR Saini, AJORP, Rajsthan for providing plant materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heikrujam, M., Sharma, K., Kumar, J. et al. Generation and validation of unique male sex-specific sequence tagged sites (STS) marker from diverse genotypes of dioecious Jojoba-Simmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider. Euphytica 199, 363–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1136-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1136-y