Abstract
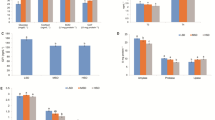
Amino acids (AA) regulate key metabolic pathways, including some immune responses. Therefore, this study aimed to assess whether an increased availability of dietary AA can mitigate the expected increase in plasma cortisol and metabolites levels due to high stocking density and its subsequent immunosuppression. Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) were maintained at low stocking density (LSD; 3.5 kg m−2) or high stocking density (HSD; 12 kg m−2) for 18 days. Additionally, both treatments were fed a control or a high protein (HP) diet (LSD, LSD HP, HSD and HSD HP). The HP diet slightly increased the levels of digestible indispensable AA, together with tyrosine and cysteine. HSD was effective in inducing a chronic stress response after 18 days of treatment since fish held at HSD presented higher plasma cortisol, glucose and lactate levels. Moreover, this increase in stress indicators translated in a decrease in plasma lysozyme, alternative complement pathway (ACP) and peroxidase activities, suggesting some degree of immunosuppression. Interestingly, while plasma glucose and lactate levels in HSD HP specimens decreased to similar values than LSD fish, plasma lysozyme, ACP and peroxidase activities increased, with even higher values than LSD groups for ACP activity. It is suggested that the HP diet may be used as functional feed since it may represent a metabolic advantage during stressful events and may counteract immunosuppression in sole.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aragão C, Corte-Real J, Costas B, Dinis MT, Conceição LEC (2008) Stress response and changes in amino acid requirements in Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis Kaup 1758. Amino Acids 34:143–148
Aragão C, Costas B, Vargas-Chacoff L, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Dinis MT, Mancera JM, Conceição LEC (2010) Changes in plasma amino acid levels in a euryhaline fish exposed to different environmental salinities. Amino Acids 38:311–317
Arends RJ, Mancera JM, Muñoz JL, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Flik G (1999) The stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) to air exposure and confinement. J Endocr 163:149–157
Caipang CMA, Berg I, Brinchmann MF, Kiron V (2009) Short-term crowding stress in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. modulates the humoral immune response. Aquaculture 295:110–115
Cerezuela R, Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2009) Effects of dietary vitamin D3 administration on innate immune parameters of seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:243–248
Cohen SA, Meys M, Tarvin TL (1989) The pico-tag method—a manual of advanced techniques for amino acids analysis. Waters, Division of Milipore, Bedford
Conceição LEC, Aragão C, Dias J, Costas B, Terova G, Martins C, Tort L (2012) Dietary nitrogen and fish welfare. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:119–141
Conde-Sieira M, Aguilar AJ, López-Patiño MA, Míguez JM, Soengas JL (2010) Stress alters food intake and glucosensing response in hypothalamus, hindbrain, liver, and Brockmann bodies of rainbow trout. Physiol Behav 101:483–493
Costas B, Aragão C, Mancera JM, Dinis MT, Conceição LEC (2008) High stocking density induces crowding stress and affects amino acid metabolism in Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis (Kaup 1858) juveniles. Aquac Res 39:1–9
Costas B, Conceição LEC, Aragão C, Martos JA, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Mancera JM, Afonso A (2011a) Physiological responses of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) after stress challenge: effects on non-specific immune parameters, plasma free amino acids and energy metabolism. Aquaculture 316:68–76
Costas B, Conceição LEC, Dias J, Novoa B, Figueras A, Afonso A (2011b) Dietary arginine and repeated handling increase disease resistance and modulate innate immune mechanisms of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858). Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:838–847
Costas B, Aragão C, Soengas JL, Míguez JM, Rema P, Dias J, Afonso A, Conceição LEC (2012a) Effects of dietary amino acids and repeated handling on stress response and brain monoaminergic neurotransmitters in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) juveniles. Comp Biochem Physiol A 161:18–26
Costas B, Rêgo PCNP, Simões I, Marques JF, Castro-Cunha M, Afonso A (2012b) Cellular and humoral immune responses of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) following challenge with two Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida strains from different geographical origins. J Fish Dis (in press). doi:10.1111/jfd12033
Cuesta A, Laiz-Carrión R, Martín del Río MP, Meseguer J, Mancera JM, Esteban MA (2005) Salinity influences the humoral immune parameters of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:255–261
Demers NE, Bayne CJ (1997) The immediate effects of stress on hormones and plasma lysozyme in rainbow trout. Dev Comp Immunol 21:363–373
Dhabhar FS (2009) A hassle a day may keep the pathogens away: the fight-or-flight stress response and the augmentation of immune function. Integr Comp Biol 49:215–236
Dias J, Yúfera M, Valente LMP, Rema P (2010) Feed transit and apparent protein, phosphorus and energy digestibility of practical feed ingredients by Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquaculture 302:94–99
Dinis MT, Ribeiro L, Soares F, Sarasquete C (1999) A review on the cultivation potential of Solea senegalensis in Portugal and Spain. Aquaculture 176:27–38
Ellis AE (1999) Immunity to bacteria in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:291–308
Fast MD, Hosoya S, Johnson SC, Afonso LOB (2008) Cortisol response and immune-related effects of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus) subjected to short- and long-term stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 24:194–204
Gatlin DM, Barrows FT, Brown P, Dabrowski K, Gaylord TG, Hardy RW, Herman E, Hu G, Krogdahl Å, Nelson R, Overturf K, Rust M, Sealey W, Skonberg D, Souza EJ, Stone D, Wilson R, Wurtele E (2007) Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: a review. Aquac Res 38:551–579
Herrera M, Vargas-Chacoff L, Hachero I, Ruíz-Jarabo I, Rodiles A, Navas JI, Mancera JM (2009) Physiological responses of juvenile wedge sole Dicologoglossa cuneata (Moreau) to high stocking density. Aquac Res 40:790–797
Höglund E, Sorensen C, Bakke MJ, Nilsson GE, Øverli Ø (2007) Attenuation of stress-induced anorexia in brown trout (Salmo trutta) by pre-treatment with dietary l-tryptophan. Br J Nutr 97:786–789
Holland MCH, Lambris JD (2002) The complement system in teleosts. Fish Shellfish Immunol 12:399–420
Hseu JR, Lu FI, Su HM, Wang LS, Tsai CL, Hwang PP (2003) Effect of exogenous tryptophan on cannibalism, survival and growth in juvenile grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 218:251–263
Imsland AK, Foss A, Conceição LEC, Dinis MT, Delbare D, Schram E, Kamstra A, Rema P, White P (2003) A review of the culture potential of Solea solea and Solea senegalensis. Rev Fish Biol Fish 13:379–407
Kaushik SJ (1998) Whole body amino acid composition of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and turbot (Psetta maxima) with an estimation of their IAA requirement profiles. Aquat Living Resour 11:355–358
Lepage O, Tottmar O, Winberg S (2002) Time-course of the effect of dietary l-tryptophan on plasma cortisol levels in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Exp Biol 206:3679–3687
Lepage O, Vílchez IM, Pottinger TG, Winberg S (2003) Elevated dietary intake of l-tryptophan counteracts the stress-induced elevation of plasma cortisol in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 205:3589–3599
Li P, Yin Y-L, Li D, Kim SW, Wu G (2007) Amino acids and immune function. Br J Nutr 98:237–252
Li P, Mai K, Trushenski J, Wu G (2009) New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds. Amino Acids 37:43–53
Ma X, Lin Y, Jiang Z, Zheng C, Zhou G, Yu D, Cao T, Wang J, Chen F (2010) Dietary arginine supplementation enhances antioxidative capacity and improves meat quality of finishing pigs. Amino Acids 38:95–102
Mauri I, Romero A, Acerete L, MacKenzie S, Roher N, Callol A, Cano I, Alvarez MC, Tort L (2011) Changes in complement responses in Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) under crowding stress, plus viral and bacterial challenges. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:182–188
Melchior D, Seve B, Le Floc’h N (2004) Chronic lung inflammation affects plasma amino acid concentrations in pigs. J Anim Sci 82:1091–1099
Milligan CL (1997) The role of cortisol in amino acid mobilization and metabolism following exhaustive exercise in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Fish Physiol Biochem 16:119–128
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Montero D, Izquierdo MS, Tort L, Robaina L, Vergara JM (1999) High stocking density produces crowding stress altering some physiological and biochemical parameters in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata L, juveniles. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:53–60
Murray CK, Fletcher TC (1976) The immunohistochemical localization of lysozyme in plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.) tissues. J Fish Biol 9:329–334
Neumann NF, Fagan D, Belosevic M (1995) Macrophage activating factor(s) secreted by mitogen stimulated goldfish kidney leucocytes synergize with bacterial lipopolysaccharide to induce nitric oxide production in teleost macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol 19:473–482
NRC (1993) Nutrient requirements of fish. National Academy Press, Washington
Perianayagam MC, Oxenkrug GF, Jaber BL (2005) Immune-modulating effects of melatonin, N-acetylserotonin, and N-acetyldopomine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1053:386–393
Pinto W, Aragão C, Soares F, Dinis MT, Conceição LEC (2007) Growth, stress response and free amino acid levels in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup 1858) chronically exposed to exogenous ammonia. Aquac Res 38:1198–1204
Pottinger TG (2008) The stress response in fish-mechanisms, effects and measurement. In: Branson EJ (ed) Fish welfare. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 32–48
Prunet P, Øverli Ø, Douxfils J, Bernardini G, Kestemont P, Baron D (2012) Fish welfare and genomics. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:43–60
Quade MJ, Roth JA (1997) A rapid, direct assay to measure degranulation of bovine neutrophil primary granules. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 58:239–248
Rotllant J, Pavlidis M, Kentouri M, Abad ME, Tort L (1997) Non-specific immune responses in the red porgy, Pagrus pagrus after crowding stress. Aquaculture 156:279–290
Rotllant J, Ruane NM, Dinis MT, Canário AVM, Power DM (2006) Intra-adrenal interactions in fish: catecholamine stimulated cortisol release in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A 143:375–381
Saeij JPJ, Verburg-van Kemenade LBM, van Muiswinkel WB, Wiegertjes GF (2003) Daily hangling stress reduces resistance of carp to Trypanoplasma borreli: in vitro modulatory effects of cortisol on leukocyte function and apoptosis. Dev Comp Immunol 27:233–245
Salas-Leiton E, Anguis V, Martín-Antonio B, Crespo D, Planas JV, Infante C, Cañavate JP, Manchado M (2010) Effects of stocking density and feed ration on growth and gene expression in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis): potential effects on the immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:296–302
Segner H, Sundh H, Buchmann K, Douxfils J, Sundell KS, Mathieu C, Ruane N, Jutfelt F, Toften H, Vaughan L (2012) Health of farmed fish: its relation to fish welfare and its utility as welfare indicator. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:85–105
Stolte EH, Nabuurs SB, Bury NR, Sturm A, Flik G, Savelkoul HFJ, Verburg-van Kemenade BML (2008) Stress and innate immunity in carp: corticosteroid receptors and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Mol Immunol 46:70–79
Suenaga R, Tomonaga S, Yamane H, Kurauchi I, Tsuneyoshi Y, Sato H, Denbow DM, Furuse M (2008) Intracerebroventricular injection of l-arginine induces sedative and hypnotic effects under an acute stress in neonatal chicks. Amino Acids 35:139–146
Sunyer JO, Tort L (1995) Natural hemolitic and bactericidal activities of seabream Sparus aurata serum are affected by the alternative complement pathway. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 45:333–345
Tafalla C, Novoa B (2000) Requirements for nitric oxide production by turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) head kidney macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol 24:623–631
Tort L (2011) Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1366–1375
Verburg-van Kemenade LBM, Stolte EH, Metz JR, Chadzinska M (2009) Neuroendocrine-immune interactions in teleost fish. In: Bernier NJ, Van Der Kraak G, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol 28. Academic Press Inc., San Diego, pp 313–364
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 7:591–625
Weyts FAA, Cohen N, Flik G, Verburg-van Kemenade BML (1999) Interactions between the immune system and the hypothalamo-pituitary-interrenal axis in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:1–20
Wilson RP (2002) Amino acids and proteins. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition. Elsevier Science, San Diego, pp 144–179
Yao K, Guan S, Li T, Huang R, Wu G, Ruan Z, Yin Y (2011) Dietary l-arginine supplementation enhances intestinal development and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in weanling piglets. Br J Nutr 105:703–709
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by project STRESSAA-POCTI/CVT/49324/2002 (FCT, Portugal and FEDER). Benjamín Costas and Cláudia Aragão were supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal (SFRH/BD/38697/2007 and SFRH/BPD/37197/2007, respectively).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costas, B., Aragão, C., Dias, J. et al. Interactive effects of a high-quality protein diet and high stocking density on the stress response and some innate immune parameters of Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis . Fish Physiol Biochem 39, 1141–1151 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9770-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9770-1