Abstract
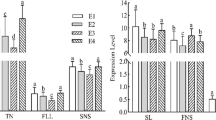
Phenotypic diversity was assessed for quantitative and qualitative traits in a salt-tolerant subset of the international safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) germplasm collection originating from 11 countries in three regions (Central Asia, Southwest Asia and Africa) of the Middle East. Phenotypically, the germplasm, among and within regions, was highly variable, especially for rosette- and yield-related traits. Frequency of desirable variants of seven agronomically important traits ranged from 14% for long rosette period to 50% for no or few spines. Level of population differentiation was high for number of capitula per plant (30%), whereas most traits partitioned their diversity (82–87%) within populations. Region-specific nonrandom associations among sets of qualitative traits and the existence of broad morphological and phenotypic diversity in this germplasm were supported by the large number of log-linear models needed to describe qualitative trait associations, the high number of principal components needed to account for total variability, and the low discriminatory power of phenotypic traits among germplasm from regions and countries in the Middle East. These results suggest that adaptation of the species to the wide spatial and temporal variation in the Middle East resulted in a multitude of ecotypes and in enormous amount of local variation. A multivariate selection criterion for high biological and seed yield, long rosette period and no or few spines identified five accessions from Southwest Asia that can be introduced into subsistence farming systems as a multipurpose crop under saline agriculture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Abebe A. Bjornstad (1996) ArticleTitleGenetic diversity in Ethiopian barley in relation to geographical regions, altitude range and agro-ecological zones as an aid to germplasm collection and conservation strategy Hereditas 124 17–29
A. Agresti (1990) Categorical Data Analysis Wiley International New York, USA 558
N. Alemayehu H. Becker (2002) ArticleTitleGenotypic diversity and patterns of variation in a germplasm material of Ethiopian mustard (Brassica carinata A. Braun) Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 49 573–582 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021204412404
A. Ashri (1971) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the world collection of safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. I. Reaction to several diseases and associations with morphological characters in Israel Crop Sci. 11 253–257
K. Assefa S. Ketama H. Tefera H.T. Nguyen A. Blum M. Ayele G. Bai B. Simane T. Kefyalew (1999) ArticleTitleDiversity among germplasm lines of the Ethiopian cereal tef [Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter] Euphytica 106 87–97 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003582431039
A. Bagheri B. Yazdi-Samadi M. Taeb M.R. Ahmadi (2001) ArticleTitleA study of genetic diversity in landrace populations of safflower in Iran Iran. J. Agric. Sci. 32 447–456
V.L. Bradley R.L. Guenthner R.C. Johnson R.M. Hannan (1999) Evaluation of safflower germplasm for ornamental use J. Janick (Eds) Perspectives on New Crops and New Uses ASHS Press Alexandria, VA, USA 433–435
Chaudhry A.H. 1986. Evaluation and culture of sunflower and safflower in dobari lands of Sind. First Annual Report. PL480 Program of USDA, Project No. PK-ARS-226, Grant No. FG.PA 395, 25 p.
B. Chowdhury A.B. Mandal S.P. Banerjee (1999) ArticleTitleAssessment of variability and cause and effect relationships in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Ann. Agric. Res. 20 278–281
J. Harlan (1992) Crops and Man EditionNumber2 ASA, CSSA, Inc. Madison, WI, USA 284
S. Hernandez-Verdugo R. Luna-Reyes K. Oyama (2001) ArticleTitleGenetic structure and differentiation of wild and domesticated populations of Capsicum annuuum (Solanaceae) from Mexico Plant Syst. Evol. 226 129–142
Johnson R., Ghorpade P. and Bradley V. 2001. Evaluation of the USDA core safflower collection for seven quantitative traits. International Safflower Conference, July 23, 2001.
R.H. Kavani P.T. Shukla R.B. Madariya (2000) ArticleTitleAnalysis of variability for seed yield and related characters in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Madras Agric. J. 87 449–452
Khan M.A., von Witzke-Ebrecht S., Maass B.L. and Becker H.C. 2003. Evaluation of a worldwide collection of safflower for morphological diversity and fatty acid composition. Deutscher Tropentag, October 8–10, 2003, Gőttingen, Technological and Institutional Innovations for Sustainable Rural Development.
P.F. Knowles (1969) ArticleTitleCenters of plant diversity and conservation of crop germplasm: Safflower Econ. Bot. 23 324–329
P.F. Knowles (1989) Safflower G. Rebbelen R.K. Downey A. Ashri (Eds) Oil Crops of the World McGraw-Hill New York, USA 363–374
Knowles P.F. and Ashri A. 1995. Safflower Carthamus tinctorius (Compositae). In: Smartt J. and Simmonds N.W. (eds), Evolution of Crop Plants, 2nd edn., Longman Scientific and Technical, pp. 47–50.
A. Kotecha (1979) ArticleTitleInheritance and association of six traits in safflower Crop Sci. 19 523–527
G. Ladizinsky (1998) Plant Evolution Under Domestication Kluwer Dordrecht 254
P.S. Lahane A.M. Mukewar J.S. Zope H.V. Kalpande V.V. Kalpande (1999) ArticleTitleGenetic variability for different traits in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) J. Soil Crops 9 130–132
D. Li H.H. Mündel (1996) Safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. Promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops, 7 Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, Gatersleben, Germany/International Plant Genetic Resources Institute Rome, Italy 83
D. Li M. Zhou R. Rao (Eds) (1993) Characterization and Evaluation of Safflower Germplasm Geological Publishing House Beijing, China 260
InstitutionalAuthorNameNational Plant Germplasm System (NPGS) (2000) Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) Database Management Unit (DBMU), NPGS, USDA Beltsville, Maryland
M.Z. Patel M.V. Reddy B.S. Rana B.J. Reddy (1989) ArticleTitleGenetic divergence in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 49 113–117
V.D. Patel V.S. Reddy Y.S. Nerkar (1994) ArticleTitleEfficiency of early generation selections for yield and related characters in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Theor. Appl. Genet. 89 293–296
G.B. Polignano E. Elba P. Uggenti G. Scippa (1999) ArticleTitleGeographical patterns of variation in Bari faba bean germplasm collection Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 46 183–192 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008667532542
M.A. Rabbani A. Iwabuchi Y. Murakami T. Suzuki K. Takayanagi (1998) ArticleTitlePhenotypic variation and the relationships among mustard (Brassica juncea L.) germplasm from Pakistan Euphytica 101 357–366 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1018305201279
Rohlf F.J. 2000. NTSYSpc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.1 User guide 38p. Exeter Software.
N. Senapati K.M. Samal I.C. Mohanta A. Dhal (1999) ArticleTitlePerformance, variability and character association in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Indian J. Agric. Res. 33 254–258
StatSoft Inc. 2001. STATISTICA (data analysis software systems), version 6, www.statsoft.com.
J. Uher (1997) Safflower in European agriculture A. Corleto H.-H. Mündel (Eds) Safflower: A Multipurpose Species with Unexploited Potential and World Adaptability. Proceedings of the Fourth International Safflower Conference Bari, Italy
H.D. Upadhyaya (2003) ArticleTitleGeographical patterns of variation for morphological and agronomic characteristics in the chickpea germplasm collection Euphytica 132 343–352 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025078703640
A.L. Urie (1986) ArticleTitleInheritance of partial hull in safflower Crop Sci. 26 493–498
K. Brocke Particlevom A. Christnck E. Weltzien R.T. Presterl H.H. Geiger (2003) ArticleTitleFarmers’ seed systems and management practices determine pearl millet genetic diversity patterns in semiarid regions of India Crop Sci. 43 1680–1689
F.C. Yeh R.-C. Yang T.B.J. Boyle Z.-H. Ye J.X. Mao (2000) POPGENE, the User-Friendly Shareware for Population Genetic Analysis Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Center, University of Alberta Canada
J.H. Zar (1996) Biostatistical Analysis EditionNumber3 Prentice Hall NJ, USA 662
Q. Zhang R.W. Allard (1986) ArticleTitleSampling variance of the genetic diversity index J. Hered. 77 54–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaradat, A.A., Shahid, M. Patterns of Phenotypic Variation in a Germplasm Collection of Carthamus tinctorius L. from the Middle East. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53, 225–244 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-6150-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-6150-9