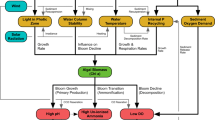
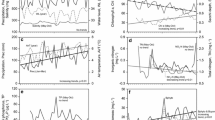
Abstract
Water-level fluctuations (WLF) in lakes and rivers, especially their extent, frequency and duration, are dominant forces controlling the functioning of these ecosystems. In particular, WLF play an important role in the lake’s littoral and aquatic–terrestrial interface processes. WLF may take place on different spatial and temporal scales under natural conditions but water levels have been artificially modified in regulated lakes, and their impacts are expected to be enhanced within the actual global change scenarios with forthcoming management problems. This article presents an overview on the literature published on this important topic since 1991 by using journals indexed in the ISI Web of Knowledge. The overall objective was to examine temporal and spatial trends in publications on WLF, the specific aspect of WLF concerned and their main effects. Throughout the article we have used case studies to illustrate different effects of WLF on the variety of lake habitats and indicators that have been studied. Overall, the number of papers published on the subject since the 1990s has risen steadily, when less than ten papers were published each year; until 2006 and peaking in 2005. The greatest number of papers on WLF has been carried out in Europe and North America (c. 73%). These data also showed that the effects of WLF have not been studied equally for different groups of organisms. There is a greater interest on macrophytes, which are the most studied group of organisms (18.4% of the papers). Nearly 7% of the papers deal with algae, and zooplankton and invertebrates account for a 7% followed by fish. WLF effects on ecosystems are very complex, and the biological effects in lakes are greatest in shallow water and littoral areas, where even small changes in water levels can result in the conversion of large areas of a standing-water environment in air exposed habitats. Finally, these data might serve to highlight knowledge gaps still existing on this topic and, in particular, some of the approaches that can potentially contribute to solve several of these lacunae are explored.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angeli, N. & M. Cantonati, 2005. Depth-distribution of surface sediment diatoms in Lake Tovel, Italy. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung Limnologie 29: 539–544.
Auer, M. T., R. P. Canale, H. C. Grunler & Y. Matsuoka, 1982. Ecological studies and mathematical modeling of Cladophora in Lake Huron: I. Program description and field monitoring of growth dynamics. Journal of Great Lakes Research 8: 73–83.
Battarbee, R. W., 1999. The importance of palaeolimnology to lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 395(396): 149–159.
Bedford, K. W., 1992. The physical effects of the Great-Lakes on tributaries and wetlands—a summary. Journal of Great Lakes Research 18: 571–589.
Beklioglu, M., G. Altinayar & C. O. Tan, 2006. Water level control over submerged macrophyte development in five shallow lakes of Mediterranean Turkey. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 166: 535–556.
Beklioglu, M., S. Romo, I. Kagalou, X. Quintana & E. Becares, 2007. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 584: 317–326.
Blindow, I., G. Andersson, A. Hargeby & S. Johansson, 1993. Long-term pattern of alternative stable states in two shallow eutrophic lakes. Freshwater Biology 30: 159–167.
Bowers, R. & F. A. De Szalay, 2004. Effects of hydrology on unionids (Unionidae) and zebra mussels (Dreissenidae) in a Lake Erie coastal wetland. American Midland Naturalist 151: 286–300.
Bowers, R. & F. A. De Szalay, 2005. Effects of water level fluctuations on zebra mussel distribution in a Lake Erie coastal wetland. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 20: 85–92.
Brown, E. A., C. H. Wu, D. M. Mickelson & T. B. Edil, 2005. Factors controlling rates of bluff recession at two sites on Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31: 306–321.
Busch, W. D. N. & S. J. Lary, 1996. Assessment of habitat impairments impacting the aquatic resources of Lake Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 53(Suppl. 1): 113–120.
Cantonati, M. & N. Angeli, 2003. New findings on the ecology and ultrastructure of Cymbella ancyli Cleve. Diatom Research 18: 377–384.
Cantonati, M., S. Scola, N. Angeli, G. Guella & R. Frassanito, 2008 Environmental controls of epilithic diatom depth-distribution in an oligotrophic lake characterised by marked water-level fluctuations. European Journal of Phycology (in press).
Casanova, M. T. & M. A. Brock, 2000. How do depth, duration and frequency of flooding influence the establishment of wetland plant communities? Plant Ecology 147: 237–250.
Chow-Fraser, P., 2005. Ecosystem response to changes in water level of Lake Ontario marshes: lessons from the restoration of Cootes Paradise Marsh. Hydrobiologia 539: 189–204.
Coops, H., M. Beklioglu & T. L. Crisman, 2003. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506: 23–27.
Coops, H. & K. E. Havens, 2005. Role of water-level fluctuations in lakes and wetlands—introduction. Hydrobiologia 539: 169–169.
Coops, H. & S. H. Hosper, 2002. Water-level management as a tool for the restoration of shallow lakes in the Netherlands. Lake and Reservoir Management 18: 293–298.
Crowder, A. A., J. P. Smol, R. Dalrymple, R. Gilbert, A. Mathers & J. Price, 1996. Rates of natural and anthropogenic change in shoreline habitats in the Kingston Basin, Lake Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 53: 121–135.
Dearing, J. A., 1997. Sedimentary indicators of lake-level changes in the humid temperate zone: a critical review. Journal of Paleolimnology 18: 1–14.
De Domitrovic, Y. Z., 2003. Effect of fluctuations in water level on phytoplankton development in three lakes of the Parana river floodplain (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 510: 175–193.
De Emiliani, M. O. G., 1997. Effects of water level fluctuations on phytoplankton in a river-floodplain lake system (Parana River, Argentina). Hydrobiologia 357: 1–15.
Desgranges, J. L., J. Ingram, B. Drolet, J. Morin, C. Savage & D. Borcard, 2006. Modelling wetland bird response to water level changes in the Lake Ontario-St. Lawrence River hydrosystem. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 113: 329–365.
Dienst, M., K. Schmieder & W. Ostendorp, 2004. Effects of water level variations on the dynamics of the reed belts of Lake Constance. Limnologica 34: 29–36.
Dinka, M., E. Agoston-Szabo, A. Berczik & G. Kutrucz, 2004. Influence of water level fluctuation on the spatial dynamic of the water chemistry at Lake Ferto/Neusiedler See. Limnologica 34: 48–56.
Engel, S. & S. A. Nichols, 1994. Aquatic macrophyte growth in a turbid windswept lake. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 9: 97–109.
Euliss, N. H., J. W. Labaugh, L. H. Fredrickson, D. M. Mushet, M. R. K. Laubhan, G. A. Swanson, T. C. Winter, D. O. Rosenberry & R. D. Nelson, 2004. The wetland continuum: a conceptual framework for interpreting biological studies. Wetlands 24: 448–458.
Ferreira, L. V., 1997. Effects of the duration of flooding on species richness and floristic composition in three hectares in the Jau National Park in floodplain forests in central Amazonia. Biodiversity and Conservation 6: 1353–1363.
Fischer, P. & U. Ohl, 2005. Effects of water-level fluctuations on the littoral benthic fish community in lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Behavioral Ecology 16: 741–746.
Furey, P. C., R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2004. Water level drawdown affects physical and biogeochemical properties of littoral sediments of a reservoir and a natural lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 20: 280–295.
Gafny, S., A. Gasith & M. Goren, 1992. Effect of water level fluctuation on shore spawning of Mirogrex terraesanctae (Steinitz), (Cyprinidae) in Lake Kinneret, Israel. Journal of Fish Biology 41: 863–871.
Gophen, M., 2000. Lake kinneret (Israel) ecosystem: long-term instability or resiliency? Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 123: 323–335.
Håkanson, L., 1977. Influence of wind, fetch, and water depth on distribution of sediments in lake Vanern, Sweden. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 14: 397–412.
Hake, M., T. Dahlgren, M. Ahlund, P. Lindberg & M. O. G. Eriksson, 2005. The impact of water level fluctuation on the breeding success of the Black-throated Diver Gavia arctica in south-west Sweden. Ornis Fennica 82: 1–12.
Hambright, K. D., W. Eckert, P. R. Leavitt & C. L. Schelske, 2004. Effects of historical lake level and land use on sediment and phosphorus accumulation rates in Lake Kinneret. Environmental Science and Technology 38: 6460–6467.
Hamilton, W. S., 1987. Defending our lakes shores. Civil Engineering 57: 75–77.
Hannon, G. E. & M. J. Gaillard, 1997. The plant-macrofossil record of past lake-level changes. Journal of Paleolimnology 18: 15–28.
Hawes, I. & R. Smith, 1993. The effect of localised nutrient enrichment on the shallow, epilithic periphyton of oligotrophic Lake Taupo, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 27: 365–372.
Hellsten, S., M. Marttunen, R. Palomaeki, J. Riihimaeki & E. Alasaarela, 1996. Towards an ecologically based regulation practice in Finnish hydroelectric lakes. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management 12: 535–545.
Hoyer, M. V., C. A. Horsburgh, D. E. Canfield Jr & R. W. Bachmann, 2005. Lake level and trophic state variables among a population of shallow Florida lakes and within individual lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 2760–2769.
Hudon, C., 1997. Impact of water level fluctuations on St. Lawrence River aquatic vegetation. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 54: 2853–2865.
Hudon, C., P. Gagnon, J. P. Amyot, G. Létourneau, M. Jean, C. Plante, D. Rioux & M. Deschênes, 2005. Historical changes in herbaceous wetland distribution induced by hydrological conditions in Lake Saint-Pierre (St. Lawrence River, Quebec, Canada). Hydrobiologia 539: 205–224.
Imamoto, H., K. Horiya, M. Yamasaki & I. Washitani, 2007. An experimental system to study ecophysiological responses of submerged macrophytes to temperature and light. Ecological Research 22: 172–176.
Jean, M. & A. Bouchard, 1991. Temporal changes in wetland landscapes of a section of the St. Lawrence River, Canada. Environmental Management 15: 241–250.
Kangur, K., T. Mols, A. Milius & R. Laugaste, 2003. Phytoplankton response to changed nutrient level in Lake Peipsi (Estonia) in 1992–2001. Hydrobiologia 506: 265–272.
Kilincaslan, T., 2000. The rising water level in Lake Van: environmental features of the Van basin which increase the destructive effect of the disaster. Water Science and Technology 42: 173–177.
Leslie, A. J., T. L. Crisman, J. P. Prenger & K. C. Ewel, 1997. Benthic macroinvertebrates of small Florida pondcypress swamps and the influence of dry periods. Wetlands 17: 447–455.
Loiselle, S. A., L. Bracchini, A. Cozar, A. M. Dattilo & C. Rossi, 2005. Extensive spatial analysis of the light environment in a subtropical shallow lake, Laguna Ibera, Argentina. Hydrobiologia 534: 181–191.
Mageed, A. A. A. & M. T. Heikal, 2006. Factors affecting seasonal patterns in epilimnion zooplankton community in one of the largest man-made lakes in Africa (Lake Nasser, Egypt). Limnologica 36: 91–97.
Magnuson, J. J., K. E. Webster, R. A. Assel, C. J. Bowser, P. J. Dillon, J. G. Eaton, H. E. Evans, E. J. Fee, R. I. Hall, L. R. Mortsch, D. W. Schindler & F. H. Quinn, 1997. Potential effects of climate changes on aquatic systems: Laurentian Great Lakes and Precambrian Shield region. Hydrological Processes 11: 825–871.
Mcgowan, S., P. R. Leavitt & R. I. Hall, 2005. A whole-lake experiment to determine the effects of winter droughts on shallow lakes. Ecosystems 8: 694–708.
Meyer, J. L., M. J. Sale, P. J. Mulholland & P. N. Leroy, 1999. Impacts of climate change on aquatic ecosystem functioning and health. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 35: 1373–1386.
Morin, J. & M. Leclerc, 1998. From pristine to present state: hydrology evolution of Lake Saint-Francois, St. Lawrence River. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 25: 864–879.
Mortsch, L. D., 1998. Assessing the impact of climate change on the Great Lakes shoreline wetlands. Climatic Change 40: 391–416.
Murphy, K. J., 2002. Plant communities and plant diversity in softwater lakes of northern Europe. Aquatic Botany 73: 287–324.
Nishihiro, J., S. Araki, N. Fujiwara & I. Washitani, 2004a. Germination characteristics of lakeshore plants under an artificially stabilized water regime. Aquatic Botany 79: 333–343.
Nishihiro, J., S. Miyawaki, N. Fujiwara & I. Washitani, 2004b. Regeneration failure of lakeshore plants under an artificially altered water regime. Ecological Research 19: 613–623.
Noges, T., 2004. Reflection of the changes of the North Atlantic Oscillation Index and the Gulf Stream Position Index in the hydrology and phytoplankton of Vortsjarv, a large, shallow lake in Estonia. Boreal Environment Research 9: 401–407.
Noges, P. & R. Laugaste, 1998. Seasonal and long-term changes in phytoplankton of Lake Vortsjarv. Limnologica 28: 21–28.
Nowlin, W. H., J. M. Davies, R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2004. Effects of water level fluctuation and short-term climate variation on thermal and stratification regimes of a British Columbia Reservoir and Lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 20: 91–109.
Ortega-Mayagoitia, E., X. Armengol & C. Rojo, 2000. Structure and dynamics of zooplankton in a semi-arid wetland, the National Park Las Tablas de Daimiel (Spain). Wetlands 20: 629–638.
Paillisson, J. M. & L. Marion, 2006. Can small water level fluctuations affect the biomass of Nymphaea alba in large lakes? Aquatic Botany 84: 259–266.
Poff, N. L. & J. D. Allan, et al., 1997. The natural flow regime: a paradigm for river conservation and restoration. BioScience 47(11): 769–784.
Punning, J. M. & A. Leeben, 2003. A comparison of sediment and monitoring data: implications for paleomonitoring a small lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 89: 1–13.
Punning, J. M. & L. Puusepp, 2007. Diatom assemblages in sediments of Lake Juusa, Southern Estonia with an assessment of their habitat. Hydrobiologia 586: 27–41.
Rhodes, S. L. & K. B. Wiley, 1993. Great Lakes toxic sediments and climate change. Implications for environmental remediation. Global Environmental Change 3: 292–305.
Riis, T. & I. Hawes, 2002. Relationships between water level fluctuations and vegetation diversity in shallow water of New Zealand lakes. Aquatic Botany 74: 133–148.
Riis, T. & I. Hawes, 2003. Effect of wave exposure on vegetation abundance, richness and depth distribution of shallow water plants in a New Zealand lake. Freshwater Biology 48: 75–87.
Rossa, D. C. & C. C. Bonecker, 2003. Abundance of planktonic and non-planktonic rotifers in lagoons of the Upper Parana River floodplain. Amazoniana-Limnologia Et Oecologia Regionalis Systemae Fluminis Amazonas 17: 567–581.
Rowe, D., E. Graynoth, G. James, M. Taylor & L. Hawke, 2003. Influence of turbidity and fluctuating water levels on the abundance and depth distribution of small, benthic fish in New Zealand alpine lakes. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 12: 216–227.
Scheffer, M. & E. H. Van Nes, 2007. Shallow lakes theory revisited: various alternative regimes driven by climate, nutrients, depth and lake size. Hydrobiologia 584: 455–466.
Scheifhacken, N., C. Fiek & K. O. Rothhaupt, 2007. Complex spatial and temporal patterns of littoral benthic communities interacting with water level fluctuations and wind exposure in the littoral zone of a large lake. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 169: 115–129.
Schindler, D. E. & M. D. Scheuerell, 2002. Habitat coupling in lake ecosystems. Oikos 98: 177–189.
Schmieder, K., 2004. European lake shores in danger—concepts for a sustainable development. Limnologica 34(1–2): 3–14.
Smol, J., 2002. Pollution of lakes and rivers: a paleoenvironmental perspective. New York, Oxford University Press.
Song, K. Y., K. D. Zoh & H. Kang, 2007. Release of phosphate in a wetland by changes in hydrological regime. Science of the Total Environment 380: 13–18.
Sorensen, J. A., L. W. Kallemeyn & M. Sydor, 2005. Relationship between mercury accumulation in young-of-the-year yellow perch and water-level fluctuations. Environmental Science and Technology 39: 9237–9243.
Stockner, J., A. Langston, D. Sebastian & G. Wilson, 2005. The limnology of Williston Reservoir: British Columbia’s largest lacustrine ecosystem. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada 40: 28–50.
Urbanc-Bercic, O. & A. Gaberscik, 2004. The relationship of the processes in the rhizosphere of common reed Phragmites australis, (Cav.) TRIN. ex STEUDEL to water fluctuation. International Review of Hydrobiology 89: 500–507.
Van Der Valk, A. G., 2005. Water-level fluctuations in North American prairie wetlands. Hydrobiologia 539: 171–188.
Van Geest, G. J., H. Coops, R. M. M. Roijackers, A. D. Buijse & M. Scheffer, 2005a. Succession of aquatic vegetation driven by reduced water-level fluctuations in floodplain lakes. Journal of Applied Ecology 42: 251–260.
Van Geest, G. J., F. Roozen, H. Coops, R. M. M. Roijackers, A. D. Buijse, E. Peeters & M. Scheffer, 2003. Vegetation abundance in lowland flood plan lakes determined by surface area, age and connectivity. Freshwater Biology 48: 440–454.
Van Geest, G. J., H. Wolters, F. C. J. M. Roozen, H. Coops, R. M. M. Roijackers, A. D. Buijse & M. Scheffer, 2005b. Water-level fluctuations affect macrophyte richness in floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia 539: 239–248.
Wagner, T. & C. M. Falter, 2002. Response of an aquatic macrophyte community to fluctuating water levels in an oligotrophic lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 18: 52–65.
Wallsten, M. & P. Forsgren, 1989. The effects of increased water level on aquatic macrophytes. Journal of Aquatic Plant Management 27: 32–37.
Wilcox, D. A. & J. E. Meeker, 1991. Disturbance effects on aquatic vegetation in regulated and unregulated lakes in Northern Minnesota. Canadian Journal of Botany-Revue Canadienne De Botanique 69: 1542–1551.
Wilcox, D. A., & J. E. Meeker, 1992. Implications for faunal habitat related to altered macrophyte structure in regulated lakes in Northern Minnesota. Wetlands 12(3): 192–203.
Wilcox, D. & T. Whillans, 1999. Techniques for restoration of disturbed coastal wetlands of the Great Lakes. Wetlands 19: 835–857.
Yang, J.-R. & H. C. Duthie, 1995. Regression and weighted averaging models relating surficial sedimentary diatom assemblages to water depth in Lake Ontario. Journal of Great Lakes Research 21: 84–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: K. M. Wantzen, K.-O. Rothhaupt, M. Mörtl, M. Cantonati, L. G.-Tóth & P. Fischer
Ecological Effects of Water-Level Fluctuations in Lakes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leira, M., Cantonati, M. Effects of water-level fluctuations on lakes: an annotated bibliography. Hydrobiologia 613, 171–184 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9465-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9465-2