Abstract
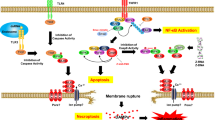
Inflammation is a complex biological process which alters the normal physiological function of the immune system resulting in an abnormal microenvironment that leads to several clinical complications. The process of inflammation is mediated through various intracellular signaling factors inside the cells. Apoptosis signal–regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is an inflammation-derived kinase that controls the activation of other family of kinases such as p38 mitogen–activated protein kinases (p38 MAPKs), which mediates various the inflammatory processes. In this study, we cultured THP-1 macrophage cells to undergo inflammatory proliferation with LPS (1 μg/ml) and TNFα (10 ng/ml) stimulation. Initial in silico analysis was utilized to predict novel microRNAs (miRNAs) that target ASK1 signaling and its expression levels in LPS and TNFα stimulated THP-1 cells were estimated. Among the miRNAs, miR-532-3p showcased the highest binding affinity towards ASK1 kinase. We witnessed that transient transfection of miR-532-3p diminished the levels of ASK1 and downstream phosphorylation/translocation of p38 MAPK. Furthermore, direct targeting of ASK1 resulted in regulation of uncontrolled release of cytokines (TNFα, IL-6, and IL-23) and chemokines (GM-CSF and MIP-2α). Overall, we suggest that miR-532-3p attenuates the pro-inflammatory nature of macrophages by targeting ASK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and can be used as a molecular intervention for treating inflammatory diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orecchioni, M., Y. Ghosheh, A.B. Pramod, and K. Ley. 2019. Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS-) vs. alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol 10: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084.
Pellicciotta, M., R. Rigoni, E.L. Falcone, S.M. Holland, A. Villa, and B. Cassani. 2019. The microbiome and immunodeficiencies: lessons from rare diseases. J Autoimmun 98: 132–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2019.01.008.
Lu, S.H., Hsia, Y.J., Shih, K.C., Chou, T.C., 2019. Fucoidan prevents RANKL-stimulated osteoclastogenesis and LPS-induced inflammatory bone loss via regulation of Akt/GSK3beta/PTEN/NFATc1 signaling pathway and calcineurin activity. Mar. drugs 17. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060345.
Wade, S.M., M. Trenkmann, T. McGarry, M. Canavan, V. Marzaioli, S.C. Wade, D.J. Veale, and U. Fearon. 2019. Altered expression of microRNA-23a in psoriatic arthritis modulates synovial fibroblast pro-inflammatory mechanisms via phosphodiesterase 4B. J Autoimmun 96: 86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.08.008.
Zhang, C.-H., J.-Q. Sheng, S. Sarsaiya, F.-X. Shu, T.-T. Liu, X.-Y. Tu, G.-Q. Ma, G.-L. Xu, H.-X. Zheng, and L.-F. Zhou. 2019. The anti-diabetic activities, gut microbiota composition, the anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellaria-coptis herb couple against insulin resistance-model of diabetes involving the Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 237: 202–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.02.040.
Zhou, D., C. Huang, Z. Lin, S. Zhan, L. Kong, C. Fang, and J. Li. 2014. Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal 26: 192–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.004.
Gao, C.-H., H.-L. Dong, L. Tai, and X.-M. Gao. 2018. Lactoferrin-containing immunocomplexes drive the conversion of human macrophages from M2- into M1-like phenotype. Front Immunol 9: 37. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00037.
Babazada, H., F. Yamashita, and M. Hashida. 2014. Suppression of experimental arthritis with self-assembling glycol-split heparin nanoparticles via inhibition of TLR4-NF-kappaB signaling. J Control Release 194: 295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.015.
Burbano, C., J. Villar-Vesga, G. Vasquez, C. Munoz-Vahos, M. Rojas, and D. Castano. 2019. Proinflammatory differentiation of macrophages through microparticles that form immune complexes leads to T- and B-cell activation in systemic autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 10: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02058.
Han, H.-S., Shin, J.-S., Lee, S.-B., Park, J.C., Lee, K.-T., 2018. Cirsimarin, a flavone glucoside from the aerial part of Cirsium japonicum var. ussuriense (Regel) Kitam. ex Ohwi, suppresses the JAK/STAT and IRF-3 signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Chem Biol Interact 293, 38–47. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.07.024.
Sindhu, S., S. Kochumon, S. Shenouda, A. Wilson, F. Al-Mulla, and R. Ahmad. 2019. The cooperative induction of CCL4 in human monocytic cells by TNF-alpha and palmitate requires MyD88 and involves MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184658.
Philippe, L., G. Alsaleh, A. Pichot, E. Ostermann, G. Zuber, B. Frisch, J. Sibilia, S. Pfeffer, S. Bahram, D. Wachsmann, and P. Georgel. 2013. MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 72: 1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201654.
Chen, S., Y. Zuo, L. Huang, P. Sherchan, Jian Zhang, Z. Yu, J. Peng, Junyi Zhang, L. Zhao, D. Doycheva, F. Liu, J.H. Zhang, Y. Xia, and J. Tang. 2019. The MC4 receptor agonist RO27-3225 inhibits NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis via the ASK1/JNK/p38 MAPK pathway in a mouse model of intracerebral haemorrhage. Br J Pharmacol 176: 1341–1356. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14639.
Ahmad, R., N. Akhter, A. Al-Roub, S. Kochumon, A. Wilson, R. Thomas, S. Ali, J. Tuomilehto, and S. Sindhu. 2019. MIP-1alpha induction by palmitate in the human monocytic cells implicates TLR4 signaling mechanism. Cell Physiol Biochem 52: 212–224. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000015.
Lee, J., J.W. Choi, J.K. Sohng, R.P. Pandey, and Y. Il Park. 2016. The immunostimulating activity of quercetin 3-O-xyloside in murine macrophages via activation of the ASK1/MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 31: 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.12.008.
Wang, J., Y. Zhuo, L. Yin, H. Wang, Y. Jiang, X. Liu, M. Zhang, F. Du, S. Xia, and Q. Shao. 2016. Doxycycline protects thymic epithelial cells from mitomycin C-mediated apoptosis in vitro via Trx2-NF-kappaB-Bcl-2/Bax Axis. Cell Physiol Biochem 38: 449–460. https://doi.org/10.1159/000438642.
Colamatteo, A., T. Micillo, S. Bruzzaniti, C. Fusco, S. Garavelli, V. De Rosa, M. Galgani, M.I. Spagnuolo, F. Di Rella, A.A. Puca, P. de Candia, and G. Matarese. 2019. Metabolism and autoimmune responses: the microRNA connection. Front Immunol 10: 1969. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01969.
Saul, M.J., A.C. Emmerich, D. Steinhilber, and B. Suess. 2019. Regulation of eicosanoid pathways by microRNAs. Front Pharmacol 10: 824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00824.
Larabi, A., N. Barnich, and H.T.T. Nguyen. 2019. New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD. Autophagy 16: 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1635384.
Shapouri-Moghaddam, A., S. Mohammadian, H. Vazini, M. Taghadosi, S.-A. Esmaeili, F. Mardani, B. Seifi, A. Mohammadi, J.T. Afshari, and A. Sahebkar. 2018. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol 233: 6425–6440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26429.
Tili, E., J.-J. Michaille, A. Cimino, S. Costinean, C.D. Dumitru, B. Adair, M. Fabbri, H. Alder, C.G. Liu, G.A. Calin, and C.M. Croce. 2007. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 179: 5082–5089. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5082.
Das, A., K. Ganesh, S. Khanna, C.K. Sen, and S. Roy. 2014. Engulfment of apoptotic cells by macrophages: a role of microRNA-21 in the resolution of wound inflammation. J Immunol 192: 1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1300613.
Fu, L., P. Zhu, S. Qi, C. Li, and K. Zhao. 2018. MicroRNA-92a antagonism attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury in mice through suppressing the PTEN/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 107: 703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.040.
Tang, B., X. Li, Y. Ren, J. Wang, D. Xu, Y. Hang, T. Zhou, F. Li, and L. Wang. 2017. MicroRNA−29a regulates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in murine macrophages through the Akt1/ NF-kappaB pathway. Exp Cell Res 360: 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.08.013.
Gao, W., and H. Yang. 2019. MicroRNA1243p attenuates severe community acquired pneumonia progression in macrophages by targeting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6. Int J Mol Med 43: 1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.4011.
Jiang, P., R. Liu, Y. Zheng, X. Liu, L. Chang, S. Xiong, and Y. Chu. 2012. MiR-34a inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through targeting Notch1 in murine macrophages. Exp Cell Res 318: 1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.03.018.
Ma, C., Y. Wang, A. Shen, and W. Cai. 2017. Resveratrol upregulates SOCS1 production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting miR-155. Int J Mol Med 39: 231–237. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2802.
Zhang, L., C. Huang, Y. Guo, X. Gou, M. Hinsdale, P. Lloyd, and L. Liu. 2015. MicroRNA-26b modulates the NF-kappaB pathway in alveolar macrophages by regulating PTEN. J Immunol 195: 5404–5414. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1402933.
Sujitha, S., P. Dinesh, and M. Rasool. 2018. Berberine modulates ASK1 signaling mediated through TLR4/TRAF2 via upregulation of miR-23a. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 359: 34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.09.017.
Agarwal, V., G.W. Bell, J.-W. Nam, and D.P. Bartel. 2015. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005.
Rennie, W., S. Kanoria, C. Liu, C.S. Carmack, J. Lu, and Y. Ding. 2019. Sfold tools for microRNA target prediction. Methods Mol Biol 1970: 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9207-2_3.
Luo, J.-F., X.-Y. Shen, C.K. Lio, Y. Dai, C.-S. Cheng, J.-X. Liu, Y.-D. Yao, Y. Yu, Y. Xie, P. Luo, X.-S. Yao, Z.-Q. Liu, and H. Zhou. 2018. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway by nardochinoid C inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Front Pharmacol 9: 911. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00911.
Wang, Y., Z. Yang, L. Wang, L. Sun, Z. Liu, Q. Li, B. Yao, T. Chen, C. Wang, W. Yang, Q. Liu, and S. Han. 2019a. miR-532-3p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting PTPRT. Biomed Pharmacother 109: 991–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.145.
Yuan, S., Y. Dong, L. Peng, M. Yang, L. Niu, Z. Liu, and J. Xie. 2019. Tumor-associated macrophages affect the biological behavior of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 18: 1840–1846. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10483.
Wang, Z., K. Maruyama, Y. Sakisaka, S. Suzuki, H. Tada, M. Suto, M. Saito, S. Yamada, and E. Nemoto. 2019b. Cyclic stretch force induces periodontal ligament cells to secrete exosomes that suppress IL-1beta production through the inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in macrophages. Front Immunol 10: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01310.
Ben Mkaddem, S., E. Pedruzzi, C. Werts, N. Coant, M. Bens, F. Cluzeaud, J.M. Goujon, E. Ogier-Denis, and A. Vandewalle. 2010. Heat shock protein gp96 and NAD(P)H oxidase 4 play key roles in Toll-like receptor 4-activated apoptosis during renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Differ 17: 1474–1485. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.26.
Park, H.J., Y.J. Choi, J.H. Lee, and M.J. Nam. 2017. Naringenin causes ASK1-induced apoptosis via reactive oxygen species in human pancreatic cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 99: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.008.
Akhtar, N., A.K. Singh, and S. Ahmed. 2016. MicroRNA-17 suppresses TNF-alpha signaling by interfering with TRAF2 and cIAP2 association in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol 197: 2219–2228. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1600360.
Han, J., F. Wang, Y. Lan, J. Wang, C. Nie, Y. Liang, R. Song, T. Zheng, S. Pan, T. Pei, C. Xie, G. Yang, X. Liu, M. Zhu, Y. Wang, Yao Liu, F. Meng, Y. Cui, B. Zhang, Yufeng Liu, X. Meng, J. Zhang, and L. Liu. 2019. KIFC1 regulated by miR-532-3p promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via gankyrin/AKT signaling. Oncogene 38: 406–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0440-8.
Wang, J.-X., X.-J. Zhang, C. Feng, T. Sun, K. Wang, Y. Wang, L.-Y. Zhou, and P.-F. Li. 2015. MicroRNA-532-3p regulates mitochondrial fission through targeting apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis 6: e1677. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.41.
Esteves, J.V., C.Y. Yonamine, D.C. Pinto-Junior, F. Gerlinger-Romero, F.J. Enguita, and U.F. Machado. 2018. Diabetes modulates microRNAs 29b-3p, 29c-3p, 199a-5p and 532-3p expression in muscle: possible role in GLUT4 and HK2 repression. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9: 536. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00536.
Guo, W., Zhaoyu Chen, Zhian Chen, J. Yu, H. Liu, T. Li, T. Lin, H. Chen, M. Zhao, G. Li, and Y. Hu. 2018. Promotion of cell proliferation through inhibition of cell autophagy signalling pathway by Rab3IP is restrained by microRNA-532-3p in gastric cancer. J Cancer 9: 4363–4373. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.27533.
Gagez, A.-L., I. Duroux-Richard, S. Lepretre, F. Orsini-Piocelle, R. Letestu, S. De Guibert, E. Tuaillon, V. Leblond, O. Khalifa, V. Gouilleux-Gruart, A. Banos, O. Tournilhac, J. Dupuis, C. Jorgensen, G. Cartron, and F. Apparailly. 2017. miR-125b and miR-532-3p predict the efficiency of rituximab-mediated lymphodepletion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. A French Innovative Leukemia Organization study. Haematologica 102: 746–754. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2016.153189.
Funding
Palani Dinesh received funding from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) in the form of Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) [acknowledgment no.: 112290/2K17/1; file no.: 09/844(0059)/2018].
Sali Sujitha received funding from the University Grants Commission (UGC) for Maulana Azad National Fellowship in the form of Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) [file no.: 2017-18/MANF-2017-18-KER-82149].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinesh, P., Kalaiselvan, S., Sujitha, S. et al. MicroRNA-532-3p Regulates Pro-Inflammatory Human THP-1 Macrophages by Targeting ASK1/p38 MAPK Pathway. Inflammation 44, 229–242 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01325-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01325-7