Abstract
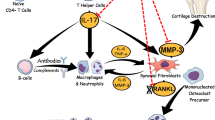
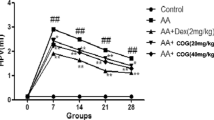
Osteoclasts, bone-resorbing somatic cells, are directly responsible for bone destruction during rheumatoid arthritis. Complete Freund adjuvant (CFA) is a widely used animal model using rodents for studying rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which effectively manifests serious cartilage destruction and progressive bone erosion, affecting synovial joints and serious joint dysfunction. It was considered that joint injury in RA is induced through systemic inflammation pathway. Umbelliferone (UF), a coumarin derivative of Agele marmilosa, possesses anti-inflammatory activity. In the current study, we scrutinize the effect of umbelliferone on CFA-induced arthritis model and explore the possible mechanism on bone destruction. Intradermal administration of CFA (0.05 mL) was to induce RA manifestations in the experimental rats and the same oral administration of UF was received. The anti-arthritic activity of UF was determined by its inhibitory activity on various biochemical markers, viz., pro-inflammatory, inflammatory, antioxidant enzymes, and hematological parameters elevated during RA condition. We also estimated the mRNA expression of osteoclast parameters. Obtained result disclosed significant reduction in the paw edema and increment of the body weight after UF administration. UF reduce the inflammatory mediatory such as COX-2, PGE2, NF-kB, and VEGF; pro-inflammatory cytokines include TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 significantly. Moreover, UF treatment significantly reduced the osteoclast number via modulating the RANKL/RANK/OPG ratio. Furthermore, administration of umbelliferone significantly (P < 0.001) suppressed the NF-κB and VEGF. Collectively, our results indicated the novel role of umbelliferone in osteoclastogenesis and proved that umbelliferone is a modern therapeutic tool as a natural agent for treating arthritis and other autoimmune disorders with bone degradation.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data/material is available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Mbiantcha, Marius, Jabeen Almas, Simjee U. Shabana, Dastagir Nida, and Faheem Aisha. 2017. Anti-arthritic property of crude extracts of Piptadeniastrum africanum (Mimosaceae) in complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1623-5.
Pan, Jun, Rilong Jin, Miaoda Shen, Ronghuan Wu, and Xu. Sanzhong. 2018. Acamprosate protects against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via blocking the ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation 41: 1194–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0766-y.
Kamel, Kamel M., Amany M. Gad, Suzan M. Mansour, Marwa M. Safar, and Hala M. Fawzy. 2018. Novel anti-arthritic mechanisms of Polydatin in complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: involvement of IL-6, STAT-3, IL-17, and NF-кB. Inflammation. 41: 1974–1986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0841-4.
Komatsu, Noriko, and Hiroshi Takayanagi. 2012. Autoimmune arthritis. The interface between the immune system and joints. Advances in Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394299-9.00002-3.
Komatsu, Noriko, and Hiroshi Takayanagi. 2012. Inflammation and bone destruction in arthritis: Synergistic activity of immune and mesenchymal cells in joints. Frontiers in Immunology 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00077.
Chen, Xiao Wu, and Shu Feng Zhou. 2015. Inflammation, cytokines, the IL-17/IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB axis, and tumorigenesis. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S86396.
Cai, Li, Chun mei Li, Wen jian Tang, Ming ming Liu, Wei na Chen, Yuan ye Qiu, and Rong Li. 2018. Therapeutic effect of penta-acetyl geniposide on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats: involvement of inducing synovial apoptosis and inhibiting NF-κB signal pathway. Inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0861-0.
Cao, Chang Chun, Xiao Qiang Ding, Ou Zhou Lou, Chun Feng Liu, Li Peng, Lei Wang, and Chun Fang Zhu. 2004. In vivo transfection of NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides attenuate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney International 65: 834–845. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00463.x.
Xu, Haiyan, Li Cai, Lili Zhang, Guojue Wang, Rongli Xie, Yongshuai Jiang, Yuanyang Yuan, and Hong Nie. 2018. Paeoniflorin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing nuclear factor-κB signalling pathway in osteoclast differentiation. Immunology 154: 593–603. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12907.
Schett, Georg. 2007. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoclasts. Arthritis Research and Therapy 9: 203. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2110.
Kim, Ji Min, and Ho Youn Kim. 2010. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of the Korean Medical Association. 53: 853. https://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2010.53.10.853.
Suzuki, Y., Y. Tsutsumi, M. Nakagawa, H. Suzuki, K. Matsushita, M. Beppu, H. Aoki, Y. Ichikawa, and Y. Mizushima. 2001. Osteoclast-like cells in an in vitro model of bone destruction by rheumatoid synovium. Rheumatology 40: 673–682. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/40.6.673.
Gravallese, E.M. 2002. Bone destruction in arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 61. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.61.suppl_2.ii84.
Shigeyama, Yukio, Thomas Pap, Peter Kunzler, Beat R. Simmen, Renate E. Gay, and Steffen Gay. 2000. Expression of osteoclast differentiation factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 2523–2530. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200011)43:11<2523::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-Z.
Romas, Evan, Natalie A. Sims, Daphne K. Hards, Mandy Lindsay, Julian W.M. Quinn, Peter F.J. Ryan, Colin R. Dunstan, T. John Martin, and Matthew T. Gillespie. 2002. Osteoprotegerin reduces osteoclast numbers and prevents bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis. American Journal of Pathology 161: 1419–1427. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64417-3.
Kumar, Vikas, F.A. Al-Abbasi, Danish Ahmed, Amita Verma, Mohd Mujeeb, and Firoz Anwar. 2015. Paederia foetida Linn. inhibits adjuvant induced arthritis by suppression of PGE 2 and COX-2 expression via nuclear factor-κB. Food & Function. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo00178a.
Kumar, Vikas, F.A. Al-Abbasi, Amita Verma, Mohd Mujeeb, and Firoz Anwar. 2015. Umbelliferone β-d-galactopyranoside exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by attenuating COX-1 and COX-2. Toxicology Research 4: 1072–1084. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tx00095e.
Ramesh, Balakrishnan, Periyasamy Viswanathan, and Kodukkur Viswanathan Pugalendi. 2007. Protective effect of Umbelliferone on membranous fatty acid composition in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. European Journal of Pharmacology 566: 231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.03.045.
Chandramohan, Ramasamy, and Leelavinothan Pari. 2014. Protective effect of umbelliferone on high-fructose diet-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress in rats. Biomedicine and Aging Pathology. 4: 23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomag.2013.12.003.
Kumar, Vikas, F.A. Al-Abbasi, Danish Ahmed, Amita Verma, Mohd Mujeeb, and Firoz Anwar. 2015. Paederia foetida Linn. inhibits adjuvant induced arthritis by suppression of PGE2 and COX-2 expression via nuclear factor-κB. Food & Function 6: 1652–1666. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5fo00178a.
Foyet, Harquin Simplice, David Emery Tsala, Zogo Essono Zogo, Azanfack Name Carine, Lissia Toussoumna Heroyne, and Eyong Kenneth Oben. 2015. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of a methanol extract from Vitellaria paradoxa stem bark. Pharmacognosy Research 7: 367–377. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.159569.
Vijayalaxmi, A., Vasudha Bakshi, Begum Nazia, V. Kowmudi, Kumar-Y Naveen, and Yogesh Reddy. 2015. Anti-arthritic and anti inflammatory activity of beta caryophyllene against Freund’s complete adjuvant induced arthritis in Wistar rats. Journal of Bone Research and Reports. https://doi.org/10.4172/2469-6684.10009.
Talaat, Roba M., Amira S. Abo-El-Atta, Sabah M. Farou, and Karima I. El-Dosoky. 2014. Therapeutic effect of dimethyl dimethoxy biphenyl dicarboxylate on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 21: 846–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-1746-1.
Kumar, Vikas, Prakash Chandra Bhatt, Mahfoozur Rahman, Dinesh Kumar Patel, Nikunj Sethi, Atul Kumar, Nikhil Kumar Sachan, et al. 2016. Melastoma malabathricum Linn attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced chronic inflammation in Wistar rats via inflammation response. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1470-9.
Liu, Jia Yu, Ya Ling Hou, Rong Cao, Hong Xia Qiu, Guo Hua Cheng, Tu Ran, Li Wang, Jun Li Zhang, and Dan Liu. 2017. Protodioscin ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and histology outcome in complete Freund’s adjuvant induced arthritis rats. Apoptosis. 22: 1454–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1420-0.
Vysakh, A., M. Ratheesh, T.P. Rajmohanan, C. Pramod, S. Premlal, B. Girish Kumar, and P.I. Sibi. 2014. Polyphenolics isolated from virgin coconut oil inhibits adjuvant induced arthritis in rats through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action. International Immunopharmacology 20: 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.026.
Wang, Tingyu, Han Qiao, Zanjing Zhai, Jun Zhang, Tu Jinwen, Xinyi Zheng, Niandong Qian, Hong Zhou, Eryi Lu, and Tingting Tang. 2019. Plumbagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by regulating Treg/Th17 cell imbalances and suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Frontiers in Immunology 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.03102.
Singh, Rajbir, Bikram Singh, Sukhpreet Singh, Neeraj Kumar, Subodh Kumar, and Saroj Arora. 2010. Umbelliferone - an antioxidant isolated from Acacia nilotica (L.) Willd. Ex. Del. Food Chemistry 120: 825–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.022.
Feng, Zhi tao, Tong Yang, Xiao qiang Hou, Han yu Wu, Jia teng Feng, Bing jin Ou, San jin Cai, Juan Li, and Zhi gang Mei. 2019. Sinomenine mitigates collagen-induced arthritis mice by inhibiting angiogenesis. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108759.
McInnes, Iain B., Christopher D. Buckley, and John D. Isaacs. 2016. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis-shaping the immunological landscape. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 12: 63–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2015.171.
Zhou, Liang, Ivaylo I. Ivanov, Rosanne Spolski, Roy Min, Kevin Shenderov, Takeshi Egawa, David E. Levy, Warren J. Leonard, and Dan R. Littman. 2007. IL-6 programs TH-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nature Immunology 8: 967–974. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1488.
Cho, Mi-La, Jung-Won Kang, Young-Mee Moon, Hyo-Jung Nam, Joo-Yeon Jhun, Seong-Beom Heo, Hyun-Tak Jin, So-Youn Min, Ji-Hyeon Ju, Kyung-Su Park, Young-Gyu Cho, Chong-Hyeon Yoon, Sung-Hwan Park, Young-Chul Sung, and Ho-Youn Kim. 2006. STAT3 and NF-κB signal pathway is required for IL-23-mediated IL-17 production in spontaneous arthritis animal model IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. The Journal of Immunology 176: 5652–5661. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.9.5652.
Paleolog, E.M. 1996. Angiogenesis: a critical process in the pathogenesis of RA--a role for VEGF? British Journal of Rheumatology 35: 917–919. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.917.
Paleolog, Ewa M., and Jadwiga M. Miotla. 1998. Angiogenesis in arthritis: Role in disease pathogenesis and as a potential therapeutic target. Angiogenesis. 2: 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009229508096.
Gul, Anum, Bimal Kunwar, Maryam Mazhar, Shaheen Faizi, Dania Ahmed, Muhammad Raza Shah, and Shabana U. Simjee. 2018. Rutin and rutin-conjugated gold nanoparticles ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in rats through inhibition of NF-κB and iNOS activation. International Immunopharmacology 59: 310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.017.
Kim, Jung Ha, and Nacksung Kim. 2016. Signaling pathways in osteoclast differentiation. Chonnam Medical Journal 52: 12–17. https://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2016.52.1.12.
Takayanagi, Hiroshi, Sunhwa Kim, Koichi Matsuo, Hiroshi Suzuki, Tomohiko Suzuki, Kojiro Sato, Taeko Yokochi, Hiromi Oda, Kozo Nakamura, Nobutaka Ida, Erwin F. Wagner, and Tadatsugu Taniguchi. 2002. RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-β. Nature. 416: 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1038/416744a.
Takayanagi, Hiroshi, Sunhwa Kim, and Tadatsugu Taniguchi. 2002. Signaling crosstalk between RANKL and interferons in osteoclast differentiation. Arthritis Research 4: S227. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar581.
Gabay, Cem. 2006. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Research & Therapy 8: S3. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1917.
Loi, Florence, Luis A. Córdova, Jukka Pajarinen, Tzu hua Lin, Zhenyu Yao, and Stuart B. Goodman. 2016. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone. 86: 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.02.020.
Firestein, Gary S. 2003. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423: 356–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01661.
Isomäki, Pia. 2012. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Scientific Basis of Healthcare: Arthritis. https://doi.org/10.2165/00002512-199812050-00004.
Straus, Daniel S. 2013. TNFα and IL-17 cooperatively stimulate glucose metabolism and growth factor production in human colorectal cancer cells. Molecular Cancer 12: 78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-78.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledged the Department of Orthopedics Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, 230601, for guidance and support.
Funding
This study was self-funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GW, WN, and QW designed the experimental study; YH, SG, and YZ estimation and interpretation the biochemical data. HL supervised all the experimental protocol and interpreted the data. All the authors equally contributed in manuscript editing. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The whole experimental protocol was approved from the Institutional Animal Use and Care Committee and all institutional procedures and protocols (NIH guidelines) regarding the animal handling and care were followed.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable (N/A).
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Nie, W., Wang, Q. et al. Umbelliferone Ameliorates Complete Freund Adjuvant–Induced Arthritis via Reduction of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Osteoclast Differentiation. Inflammation 44, 1315–1329 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01418-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01418-x