Abstract
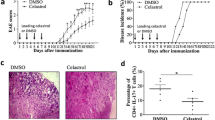
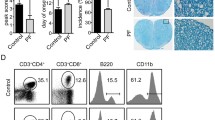
Human inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), is a demyelinating disease of central nervous system (CNS). The experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is the most commonly used as experimental model because of its key pathological features’ approximation of MS. The interaction between complex elements in immune system and in the CNS determines the MS pathogenesis. However, there is no cure for MS and the treatment for MS still encounters great challenges. Thus, finding a more effective disease-modifying treatment is imminent. In the present study, we investigated whether 9,10-Anhydrodehydroartemisin (ADART), a compound derived from artemisinin, could decrease demyelination in EAE and the underlying mechanisms. In established EAE mice, 100 mg/kg 9,10-Anhydrodehydroartemisinin (ADART) effectively reduced CNS and peripheral immune system infiltration inflammatory cells including CD4+ IFN-γ+ Th1 cells and CD4+ IL-17A+ Th17 cells. Correspondingly, the serum level of IFN-γ and IL-17A was also reduced. In vitro, ADART almost completely inhibited Th17 differentiation, and partially inhibited Th1 differentiation in 10 μM. This research revealed that ADART could be a great promising avenue among current therapies for MS.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
References
Gauthier, S.A., B.I. Glanz, M. Mandel, and H.L. Weiner. 2006. A model for the comprehensive investigation of a chronic autoimmune disease: The multiple sclerosis CLIMB study. Autoimmunity Reviews 5: 532–536.
Legroux, L., and N. Arbour. 2015. Multiple sclerosis and T lymphocytes: An entangled story. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology 10: 528–546.
Fletcher, J.M., S.J. Lalor, C.M. Sweeney, N. Tubridy, and K.H. Mills. 2010. T cells in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 162: 1–11.
McGinley, A.M., S.C. Edwards, M. Raverdeau, and K.H.G. Mills. 2018. Th17 cells, gamma delta T cells and their interplay in EAE and multiple sclerosis. Journal of Autoimmunity 87: 97–108.
Ho, P.R., H. Koendgen, N. Campbell, B. Haddock, S. Richman, and I. Chang. 2017. Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with multiple sclerosis: A retrospective analysis of data from four clinical studies. Lancet Neurology 16: 925–933.
Bloomgren, G., S. Richman, C. Hotermans, M. Subramanyam, S. Goelz, A. Natarajan, S. Lee, T. Plavina, J.V. Scanlon, A. Sandrock, and C. Bozic. 2012. Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. The New England Journal of Medicine 366: 1870–1880.
Khakzad, M.R., A. Ganji, V. Ariabod, and I. Farahani. 2017. Artemisinin therapeutic efficacy in the experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology 39: 348–353.
Wang, J.X., W. Tang, R. Zhou, J. Wan, L.P. Shi, Y. Zhang, Y.F. Yang, Y. Li, and J.P. Zuo. 2008. The new water-soluble artemisinin derivative SM905 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by suppression of inflammatory and Th17 responses. British Journal of Pharmacology 153: 1303–1310.
Yang, Z., J. Ding, C. Yang, Y. Gao, X. Li, X. Chen, Y. Peng, J. Fang, and S. Xiao. 2012. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of artesunate in experimental colitis. Current Medicinal Chemistry 19: 4541–4551.
Jin, O., H. Zhang, Z. Gu, S. Zhao, T. Xu, K. Zhou, B. Jiang, J. Wang, X. Zeng, and L. Sun. 2009. A pilot study of the therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of artesunate in the MRL/lpr murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 6: 461–467.
Hou, L., K.E. Block, and H. Huang. 2014. Artesunate abolishes germinal center B cells and inhibits autoimmune arthritis. PLoS One 9: e104762.
Liu, X., J. Cao, G. Huang, Q. Zhao, and J. Shen. 2019. Biological activities of artemisinin derivatives beyond malaria. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 19: 205–222.
Toovey, S., and A. Jamieson. 2004. Audiometric changes associated with the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria with co-artemether. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 98: 261–267 discussion 268-9.
Rappocciolo, E. 2004. Antimicrobial peptides as carriers of drugs. Drug Discovery Today 9: 470.
Wang, X., W. Zhai, J. Zhu, W. Zhao, X. Zou, S. Qu, S. Wang, Z. He, Z. Li, L. Wang, B. Sun, and H. Li. 2019. Treatment of the bone marrow stromal stem cell supernatant by nasal administration-a new approach to EAE therapy. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 10: 325.
Chung, C.Y., and F. Liao. 2016. CXCR3 signaling in glial cells ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by restraining the generation of a pro-Th17 cytokine milieu and reducing CNS-infiltrating Th17 cells. Journal of Neuroinflammation 13: 76.
Kaskow B.J., and Baecher-A.C. 2018. Effector T cells in multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 8: a029025.
Souza, P.S., E.D. Goncalves, G.S. Pedroso, H.R. Farias, S.C. Junqueira, R. Marcon, et al. 2017. Physical exercise attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting peripheral immune response and blood-brain barrier disruption. Molecular Neurobiology 54: 4723–4737.
McFarland, H.F., and R. Martin. 2007. Multiple sclerosis: A complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nature Immunology 8: 913–919.
Van Kaer, L., J.L. Postoak, C. Wang, G. Yang, and L. Wu. 2019. Innate, innate-like and adaptive lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of MS and EAE. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 16: 531–539.
Goverman, J. 2009. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nature Reviews. Immunology 9: 393–407.
Aranami, T., and T. Yamamura. 2008. Th17 Cells and autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE/MS). Allergology International 57: 115–120.
Kroenke, M.A., T.J. Carlson, A.V. Andjelkovic, and B.M. Segal. 2008. IL-12- and IL-23-modulated T cells induce distinct types of EAE based on histology, CNS chemokine profile, and response to cytokine inhibition. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205: 1535–1541.
Zheng, H., H. Zhang, F. Liu, Y. Qi, and H. Jiang. 2014. T cell-depleted splenocytes from mice pre-immunized with neuroantigen in incomplete Freund's adjuvant involved in protection from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunology Letters 157: 38–44.
Lee, H.G., L.K. Kim, and J.M. Choi. 2020. NFAT-specific inhibition by dNP2-VIVIT ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulation of Th1 and Th17. Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development 16: 32–41.
Quan, M.Y., X.J. Song, H.J. Liu, X.H. Deng, H.Q. Hou, L.P. Chen, T.Z. Ma, X. Han, X.X. He, Z. Jia, and L. Guo. 2019. Amlexanox attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting dendritic cell maturation and reprogramming effector and regulatory T cell responses. Journal of Neuroinflammation 16: 52.
Novikova, N.S., A.S. Diatlova, K.Z. Derevtsova, E.A. Korneva, T.V. Viktorovna, Y. Ostrinki, L. Abraham, S. Quinn, Y. Segal, L.P. Churilov, M. Blank, Y. Shoenfeld, R. Aharoni, and H. Amital. 2019. Tuftsin-phosphorylcholine attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Neuroimmunology 337: 577070.
Wang, J.X., W. Tang, L.P. Shi, J. Wan, R. Zhou, J. Ni, Y.F. Fu, Y.F. Yang, Y. Li, and J.P. Zuo. 2007. Investigation of the immunosuppressive activity of artemether on T-cell activation and proliferation. British Journal of Pharmacology 150: 652–661.
Thome, R., A.C. de Carvalho, T. Alves da Costa, L.L. Ishikawa, T.F. Fraga-Silva, A. Sartori, et al. 2016. Artesunate ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting leukocyte migration to the central nervous system. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 22: 707–714.
Li, X., T.T. Li, X.H. Zhang, L.F. Hou, X.Q. Yang, F.H. Zhu, W. Tang, and J.P. Zuo. 2013. Artemisinin analogue SM934 ameliorates murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through enhancing the expansion and functions of regulatory T cell. PLoS One 8: e74108.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070768, 31871404, 31900658), the Special Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences for strategic pilot technology (XDA12040327), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (Grant No. 2017SHZDZX01), and the State Key Laboratory of Drug Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Design and experimentation: J.L., W.Z., X.J., L.X., Z.L., Q.Z., and Y.Z.; supervision: C.D. and J.S.; and manuscript writing: W.Z. and C.D.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All experiment procedures were approved and carried out in accordance with the Tongji University Animal Care Committee guidelines.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J., Zhuang, W., Zhang, Y. et al. 9,10-Anhydrodehydroartemisinin Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation. Inflammation 44, 1793–1802 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01456-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01456-5