Abstract
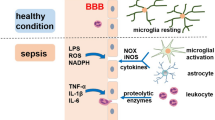
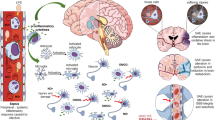
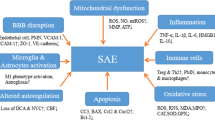
Sepsis is a life-threatening clinical condition caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is a common but poorly understood neurological complication of sepsis, which is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. SAE clinical presentation may range from mild confusion and delirium to severe cognitive impairment and deep coma. Important mechanisms associated with SAE include excessive microglial activation, impaired endothelial barrier function, and blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction. Endotoxemia and pro-inflammatory cytokines produced systemically during sepsis lead to microglial and brain endothelial cell activation, tight junction downregulation, and increased leukocyte recruitment. The resulting neuroinflammation and BBB dysfunction exacerbate SAE pathology and aggravate sepsis-induced brain dysfunction. In this mini-review, recent literature surrounding some of the mediators of BBB dysfunction during sepsis is summarized. Modulation of microglial activation, endothelial cell dysfunction, and the consequent prevention of BBB permeability represent relevant therapeutic targets that may significantly impact SAE outcomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, N.J., L. Ronnback, and E. Hansson. 2006. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 7: 41–53.
Cao, C., M. Yu, and Y. Chai. 2019. Pathological alteration and therapeutic implications of sepsis-induced immune cell apoptosis. Cell Death & Disease 10: 782.
Chen, B., Q. Cheng, K. Yang, and P.D. Lyden. 2010. Thrombin mediates severe neurovascular injury during ischemia. Stroke 41: 2348–2352.
Daneman, R., and A. Prat. 2015. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 7: a020412.
Delano, M.J., and P.A. Ward. 2016. The immune system’s role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunological Reviews 274: 330–353.
Doll, D.N., H. Hu, J. Sun, S.E. Lewis, J.W. Simpkins, and X. Ren. 2015. Mitochondrial crisis in cerebrovascular endothelial cells opens the blood-brain barrier. Stroke 46: 1681–1689.
Eidelman, L.A., D. Putterman, C. Putterman, and C.L. Sprung. 1996. The spectrum of septic encephalopathy. Definitions, etiologies, and mortalities. JAMA 275: 470–473.
Erickson, M.A., and W.A. Banks. 2018. Neuroimmune axes of the blood-brain barriers and blood-brain interfaces: bases for physiological regulation, disease states, and pharmacological interventions. Pharmacological Reviews 70: 278–314.
Erikson, K., H. Tuominen, M. Vakkala, J.H. Liisanantti, T. Karttunen, H. Syrjala, and T.I. Ala-Kokko. 2020. Brain tight junction protein expression in sepsis in an autopsy series. Critical Care 24: 385.
Evans, T. 2018. Diagnosis and management of sepsis. Clinical Medicine (London, England) 18: 146–149.
Furie, B., and B.C. Furie. 2005. Thrombus formation in vivo. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 115: 3355–3362.
Gavins, F. N., E.L. Hughes, N.A.P.S. Buss, P.M. Holloway, S.J. Getting, and J.C. Buckingham. 2012. Leukocyte recruitment in the brain in sepsis: involvement of the annexin 1-FPR2/ALX anti-inflammatory system. The FASEB Journal 26: 4977–4989.
Gofton, T.E., and G.B. Young. 2012. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Nature Reviews. Neurology 8: 557–566.
Gray, M.T., and J.M. Woulfe. 2015. Striatal blood-brain barrier permeability in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 35: 747–750.
Grin’kina, N.M., E.E. Karnabi, D. Damania, S. Wadgaonkar, I.A. Muslimov, and R. Wadgaonkar. 2012. Sphingosine kinase 1 deficiency exacerbates LPS-induced neuroinflammation. PLoS One 7: e36475.
Haileselassie, B., A.U. Joshi, P.S. Minhas, R. Mukherjee, K.I. Andreasson, and D. Mochly-Rosen. 2020. Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy. Journal of Neuroinflammation 17: 36.
Handa, O., J. Stephen, and G. Cepinskas. 2008. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide in activation and dysfunction of cerebrovascular endothelial cells during early onsets of sepsis. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology 295: H1712–H1719.
Harada, K., S. Ohira, K. Isse, S. Ozaki, Y. Zen, Y. Sato, and Y. Nakanuma. 2003. Lipopolysaccharide activates nuclear factor-kappaB through toll-like receptors and related molecules in cultured biliary epithelial cells. Laboratory Investigation 83: 1657–1667.
Haruwaka, K., A. Ikegami, Y. Tachibana, N. Ohno, H. Konishi, A. Hashimoto, M. Matsumoto, D. Kato, R. Ono, H. Kiyama, A.J. Moorhouse, J. Nabekura, and H. Wake. 2019. Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation. Nature Communications 10: 5816.
Heming, N., A. Mazeraud, F. Verdonk, F.A. Bozza, F. Chretien, and T. Sharshar. 2017. Neuroanatomy of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Critical Care 21: 65.
Hernandes, M.S., B. Lassegue, and K.K. Griendling. 2017. Polymerase delta-interacting protein 2: a multifunctional protein. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 69: 335–342.
Hotchkiss, R.S., G. Monneret, and D. Payen. 2013. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nature Reviews. Immunology 13: 862–874.
Iskander, K.N., M.F. Osuchowski, D.J. Stearns-Kurosawa, S. Kurosawa, D. Stepien, C. Valentine, and D.G. Remick. 2013. Sepsis: multiple abnormalities, heterogeneous responses, and evolving understanding. Physiological Reviews 93: 1247–1288.
Jarvis, G.E., B.T. Atkinson, J. Frampton, and S.P. Watson. 2003. Thrombin-induced conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin results in rapid platelet trapping which is not dependent on platelet activation or GPIb. British Journal of Pharmacology 138: 574–583.
Joseph, L.C., M.V. Reyes, K.R. Lakkadi, B.H. Gowen, G. Hasko, K. Drosatos, and J.P. Morrow. 2020. PKCdelta causes sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology 318: H778–H786.
Kang, C.I., J.H. Song, D.R. Chung, K.R. Peck, K.S. Ko, J.S. Yeom, H.K. Ki, J.S. Son, S.S. Lee, Y.S. Kim, S.I. Jung, S.W. Kim, H.H. Chang, S.Y. Ryu, K.T. Kwon, H. Lee, C. Moon, and Korean Network for Study of Infectious D. 2011. Risk factors and pathogenic significance of severe sepsis and septic shock in 2286 patients with gram-negative bacteremia. The Journal of Infection 62: 26–33.
Kikuchi, D.S., A.C.P. Campos, H. Qu, S.J. Forrester, R.L. Pagano, B. Lassegue, R.T. Sadikot, K.K. Griendling, and M.S. Hernandes. 2019. Poldip2 mediates blood-brain barrier disruption in a model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Journal of Neuroinflammation 16: 241.
Leligdowicz, A., and M.A. Matthay. 2019. Heterogeneity in sepsis: new biological evidence with clinical applications. Critical Care 23: 80.
Lin, C.C., H.L. Hsieh, R.H. Shih, P.L. Chi, S.E. Cheng, and C.M. Yang. 2013. Up-regulation of COX-2/PGE2 by endothelin-1 via MAPK-dependent NF-kappaB pathway in mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Communication and Signaling: CCS 11: 8.
Lundblad, R.L., and G.C. White 2nd. 2005. The interaction of thrombin with blood platelets. Platelets 16: 373–385.
Mazeraud, A., C. Righy, E. Bouchereau, S. Benghanem, F.A. Bozza, and T. Sharshar. 2020. Septic-associated encephalopathy: a comprehensive review. Neurotherapeutics 17: 392–403.
Michels, M., L.G. Danieslki, A. Vieira, D. Florentino, D. Dall’Igna, L. Galant, B. Sonai, F. Vuolo, F. Mina, B. Pescador, D. Dominguini, T. Barichello, J. Quevedo, F. Dal-Pizzol, and F. Petronilho. 2015. CD40-CD40 ligand pathway is a major component of acute neuroinflammation and contributes to long-term cognitive dysfunction after sepsis. Molecular Medicine 21: 219–226.
Nwafor, D.C., A.L. Brichacek, A.S. Mohammad, J. Griffith, B.P. Lucke-Wold, S.A. Benkovic, W.J. Geldenhuys, P.R. Lockman, and C.M. Brown. 2019. Targeting the blood-brain barrier to prevent sepsis-associated cognitive impairment. Journal of Central Nervous System Disease 11: 1179573519840652.
Okada, T., T. Kajimoto, S. Jahangeer, and S. Nakamura. 2009. Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling in central nervous system. Cellular Signalling 21: 7–13.
Paredes, F., K. Sheldon, B. Lassegue, H.C. Williams, E.A. Faidley, G.A. Benavides, G. Torres, F. Sanhueza-Olivares, S.M. Yeligar, K.K. Griendling, V. Darley-Usmar, and Martin A. San. 2018. Poldip2 is an oxygen-sensitive protein that controls PDH and alphaKGDH lipoylation and activation to support metabolic adaptation in hypoxia and cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 115: 1789–1794.
Piccinini, M., F. Scandroglio, S. Prioni, B. Buccinna, N. Loberto, M. Aureli, V. Chigorno, E. Lupino, G. DeMarco, A. Lomartire, M.T. Rinaudo, S. Sonnino, and A. Prinetti. 2010. Deregulated sphingolipid metabolism and membrane organization in neurodegenerative disorders. Molecular Neurobiology 41: 314–340.
Qi, X., N. Qvit, Y.C. Su, and D. Mochly-Rosen. 2013. A novel Drp1 inhibitor diminishes aberrant mitochondrial fission and neurotoxicity. Journal of Cell Science 126: 789–802.
Rabuel, C., and A. Mebazaa. 2006. Septic shock: a heart story since the 1960s. Intensive Care Medicine 32: 799–807.
Ren, C., R.Q. Yao, H. Zhang, Y.W. Feng, and Y.M. Yao. 2020. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a vicious cycle of immunosuppression. Journal of Neuroinflammation 17: 14.
Rubenfeld, G.D., E. Caldwell, E. Peabody, J. Weaver, D.P. Martin, M. Neff, E.J. Stern, and L.D. Hudson. 2005. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. The New England Journal of Medicine 353: 1685–1693.
Rudd, K.E., S.C. Johnson, K.M. Agesa, K.A. Shackelford, D. Tsoi, D.R. Kievlan, D.V. Colombara, K.S. Ikuta, N. Kissoon, S. Finfer, C. Fleischmann-Struzek, F.R. Machado, K.K. Reinhart, K. Rowan, C.W. Seymour, R.S. Watson, T.E. West, F. Marinho, S.I. Hay, R. Lozano, A.D. Lopez, D.C. Angus, C.J.L. Murray, and M. Naghavi. 2020. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 395: 200–211.
Sakr, Y., U. Jaschinski, X. Wittebole, T. Szakmany, J. Lipman, S.A. Namendys-Silva, I. Martin-Loeches, M. Leone, M.N. Lupu, J.L. Vincent, and Investigators I. 2018. Sepsis in intensive care unit patients: worldwide data from the Intensive Care over Nations audit. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 5: ofy313.
Scicluna, B.P., L.A. van Vught, A.H. Zwinderman, M.A. Wiewel, E.E. Davenport, K.L. Burnham, P. Nurnberg, M.J. Schultz, J. Horn, O.L. Cremer, M.J. Bonten, C.J. Hinds, H.R. Wong, J.C. Knight, T. van der Poll, and consortium M. 2017. Classification of patients with sepsis according to blood genomic endotype: a prospective cohort study. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 5: 816–826.
Semmler, A., C.N. Widmann, T. Okulla, H. Urbach, M. Kaiser, G. Widman, F. Mormann, J. Weide, K. Fliessbach, A. Hoeft, F. Jessen, C. Putensen, and M.T. Heneka. 2013. Persistent cognitive impairment, hippocampal atrophy and EEG changes in sepsis survivors. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 84: 62–69.
Singer, M., C.S. Deutschman, C.W. Seymour, M. Shankar-Hari, D. Annane, M. Bauer, R. Bellomo, G.R. Bernard, J.D. Chiche, C.M. Coopersmith, R.S. Hotchkiss, M.M. Levy, J.C. Marshall, G.S. Martin, S.M. Opal, G.D. Rubenfeld, T. van der Poll, J.L. Vincent, and D.C. Angus. 2016. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315: 801–810.
Sonneville, R., F. Verdonk, C. Rauturier, I.F. Klein, M. Wolff, D. Annane, F. Chretien, and T. Sharshar. 2013. Understanding brain dysfunction in sepsis. Annals of Intensive Care 3: 15.
Sweeney, M.D., A.P. Sagare, and B.V. Zlokovic. 2018. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nature Reviews. Neurology 14: 133–150.
Tang, Y., F. Soroush, S. Sun, E. Liverani, J.C. Langston, Q. Yang, L.E. Kilpatrick, and M.F. Kiani. 2018. Protein kinase C-delta inhibition protects blood-brain barrier from sepsis-induced vascular damage. Journal of Neuroinflammation 15: 309.
Towner, R.A., D. Saunders, N. Smith, W. Towler, M. Cruz, S. Do, J.E. Maher, K. Whitaker, M. Lerner, and K.A. Morton. 2018. Assessing long-term neuroinflammatory responses to encephalopathy using MRI approaches in a rat endotoxemia model. Geroscience 40: 49–60.
van der Poll, T., F.L. van de Veerdonk, B.P. Scicluna, and M.G. Netea. 2017. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews. Immunology 17: 407–420.
van Gool, W.A., D. van de Beek, and P. Eikelenboom. 2010. Systemic infection and delirium: when cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet 375: 773–775.
Vutukuri, R., R. Brunkhorst, R.I. Kestner, L. Hansen, N.F. Bouzas, J. Pfeilschifter, K. Devraj, and W. Pfeilschifter. 2018. Alteration of sphingolipid metabolism as a putative mechanism underlying LPS-induced BBB disruption. Journal of Neurochemistry 144: 172–185.
Wang, H., L.J. Hong, J.Y. Huang, Q. Jiang, R.R. Tao, C. Tan, N.N. Lu, C.K. Wang, M.M. Ahmed, Y.M. Lu, Z.R. Liu, W.X. Shi, E.Y. Lai, C.S. Wilcox, and F. Han. 2015. P2RX7 sensitizes Mac-1/ICAM-1-dependent leukocyte-endothelial adhesion and promotes neurovascular injury during septic encephalopathy. Cell Research 25: 674–690.
Weigel, C., S.S. Huttner, K. Ludwig, N. Krieg, S. Hofmann, N.H. Schroder, L. Robbe, S. Kluge, A. Nierhaus, M.S. Winkler, I. Rubio, J. von Maltzahn, S. Spiegel, and M.H. Graler. 2020. S1P lyase inhibition protects against sepsis by promoting disease tolerance via the S1P/S1PR3 axis. EBioMedicine 58: 102898.
Wiltshire, R., V. Nelson, D.T. Kho, C.E. Angel, S.J. O’Carroll, and E.S. Graham. 2016. Regulation of human cerebro-microvascular endothelial baso-lateral adhesion and barrier function by S1P through dual involvement of S1P1 and S1P2 receptors. Scientific Reports 6: 19814.
Winkler, M.S., A. Nierhaus, M. Holzmann, E. Mudersbach, A. Bauer, L. Robbe, C. Zahrte, M. Geffken, S. Peine, E. Schwedhelm, G. Daum, S. Kluge, and C. Zoellner. 2015. Decreased serum concentrations of sphingosine-1-phosphate in sepsis. Critical Care 19: 372.
Zhou, H., G. Andonegui, C.H. Wong, and P. Kubes. 2009. Role of endothelial TLR4 for neutrophil recruitment into central nervous system microvessels in systemic inflammation. Journal of Immunology 183: 5244–5250.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Kathy Griendling for her help with proofreading the manuscript. Figures were created with Biorender.com.
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Funding
M.S. Hernandes was supported by NIH HL095070, NIH HL152167, and Emory University Research Committee 00097383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QG drafted the manuscript. QG and MSH edited and revised the manuscript. QG and MSH approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Hernandes, M.S. Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Inflammation 44, 2143–2150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01501-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01501-3