Abstract
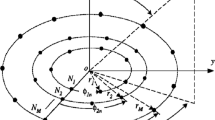
In this paper the maximum sidelobe level (SLL) reductions without and with central element feeding in various designs of three-ring concentric circular antenna arrays (CCAA) are examined using a real-coded Evolutionary Programming (EP) to finally determine the global optimal three-ring CCAA design. Standard real-coded Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and real-coded Particle Swarm Optimization with Constriction Factor and Inertia Weight Approach (PSOCFIWA) are also employed for comparative optimization but both prove to be suboptimal. This paper assumes non-uniform excitation weights and uniform spacing of excitation elements in each three-ring CCAA design. Among the various CCAA designs, the design containing central element and 4, 6 and 8 elements in three successive concentric rings proves to be such global optimal design set with global minimum SLL (−39.66 dB) as determined by Evolutionary Programming.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Stearns and A. Stewart, “An investigation of concentric ring antennas with low sidelobes,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 13 (6), 856–863 (1965).
R. Das, “Concentric ring array,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 14 (3), 398–400 (1966).
N. Goto and D. K. Cheng, “On the synthesis of concentric-ring arrays,” IEEE Proc. 58 (5), 839–840 (1970).
L. Biller and G. Friedman, “Optimization of radiation patterns for an array of concentric ring sources,” IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 21 (1), 57–61 (1973).
M. D. A. Huebner, “Design and optimization of small concentric ring arrays,” Proc. IEEE AP-S Symp., 455–458 (1978).
K.-K. Yan and Y. Lu, “Sidelobe reduction in array-pattern synthesis using genetic algorithm,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 45 (7), 1117–1122 (1997).
M. G. Holtrup, A. Margulnaud and J. Citerns, “Synthesis of electronically steerable antenna arrays with element on concentric rings with reduced sidelobes,” Proc. IEEE AP-S Symp., 800–803 (2001)
M. A. Panduro, A. L. Mendez, R. Dominguez, and G. Romero, “Design of non-uniform circular antenna arrays for side lobe reduction using the method of genetic algorithms,” Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) 60, 713–717 (2006).
M. Shihab, Y. Najjar, N. Dib, and M. Khodier, “Design of non-uniform circular antenna arrays using particle swarm optimization,” J. Electr. Eng. 59 (4), 216–220 (2008).
K. R. Mahmoud, M. I. Eladawy, R. Bansal, S. H. Zainud-Deen, and S. M. M. Ibrahem, “Analysis of uniform circular arrays for adaptive beamforming applications using particle swarm optimization algorithm,” Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 18 (1), 42–52 (2008).
R. Fallahi and M. Roshandel, “Effect of mutual coupling and configuration of concentric circular array antenna on the signal-to-interference performance in CDMA systems,” Prog. Electromagn. Res. PIER 76, 427–447 (2007).
R. L. Haupt, “Optimized element spacing for low sidelobe concentric ring arrays,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56 (1), 266–268 (2008).
M. Dessouky, H. Sharshar, and Y. Albagory, “Efficient sidelobe reduction technique for small-sized concentric circular arrays,” Prog. Electromagn. Res. PIER 65, 187–200 (2006).
J. Kennedy and R. C. Eberhard, “Particle swarm optimization,” Proc. of IEEE Int’l Conf. on Neural Networks, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1942-1948 (1995).
R. C. Eberhart and Y. Shi, “Particle swarm optimization: developments, applications and resources, evolutionary computation,” Proc. 2001 Congr. Evol. Comput. 1, 81–86 (2001).
S. L. Ho, S. Yang, Guangzheng Ni, W. C. Lo Edward, and H. C. Wong, “A particle swarm optimization-based method for multiobjective design optimizations,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 41 (5), 1756–1759 (2005).
D. Mandal, S. P. Ghoshal, and A. K. Bhattacharjee, “Comparative optimal designs of non-uniformly excited concentric circular antenna array using evolutionary optimization techniques,” IEEE 2nd Int. Conf. Emerg. Trends Eng. Technol. ICETET’09, 619–624 (2009).
A. K. Swain and A. S. Morris, “A Novel Hybrid Evolutionary Programming Method for Function Optimization, Evolutionary Computation, 2000,” Proceedings of the 2000 Congress on 1, 699–705 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, D., Ghoshal, S.P. & Bhattacharjee, A.K. Design of Concentric Circular Antenna Array with Central Element Feeding Using Particle Swarm Optimization with Constriction Factor and Inertia Weight Approach and Evolutionary Programing Technique. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 31, 667–680 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-010-9629-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-010-9629-9