Abstract
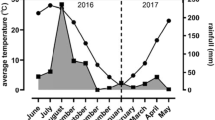
We observed a group of capped langurs for 12 mo in the Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary, Arunachal Pradesh, India. We recorded the time of feeding on different food plant species, food categories, and the feeding heights of monkeys in trees. Capped langurs spent 68% of their feeding time on leaves, 16% on flowers, and 16% on fruits. Feeding on leaves was consistently high (p < 0.01) during the year, with the highest feeding in May (85%) and the lowest in January (47%). The seasonal difference in feeding on leaves is significant (p < 0.05): it was higher in summer and during monsoon. The feeding time on flowers was maximal (35%) in March and that on fruits and seeds was minimal (38%) in January. Langurs ate 52 plant species throughout the year. The largest number of plants (6) were species of Moraceae, and langurs spent more feeding time (20%) on them alone. The number of plants eaten per month varied significantly (p < 0.05). Langurs ate Gmelina arborea, Albizzia lucida, Ficus glomereta, and Makania micrantha throughout the year. They spent 44% of their feeding time in terminal canopies and their average feeding height was 30–35 m. This is the first study to examine the feeding ecology of capped langurs and provides baseline data for the species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsan, M. F. (1994). Feeding ecology of the primates of Bangladesh. In B. Thierry, J. R. Anderson, J. J. Roeder, & N. Herrenschmidt (Eds.) Current Primatology, Vol. 1: Ecology and Evolution. Strasbourg: Université Louis Pasteur.
Altmann, J. (1974). Observational study of behaviour: Sampling methods. Behaviour, 49, 227–267.
Badham, M. A. (1967). A note on breeding the spectacled leaf monkey Presbytis obscura at Twycross Zoo. International Yearbook, 7, 89.
Bartlett, T. Q. (1999). Feeding and Ranging Behaviour of the White-Headed Gibbon (Hylobates lar) in Khai Yai National Park, Thailand. Ph.D. thesis, Washington University, pp. 1–192.
Biswas, J., Medhi, R., & Mohnot, S. M. (1996). Behavior and ecology of introduced pair of golden langur to Umananda river island, Assam. IPS/ASP Congress Abstracts. Madison, WI, 041.
Champion, H. G., & Seth, S. K. (1968). A Revised Survey of Forest Types of India. New Delhi: Government of India.
Choudhury, A. (1989). Ecology of the capped langur (Presbytis pileatus) in Assam, India. Folia Primatologica, 52, 88–92.
Davies, A. G. (1984). An Ecological Study of the Red Leaf Monkey (Presbytis rubicunda) in the Dipterocarp Forest of Sabah, Northern Borneo. Ph. D. thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge.
Gupta, A. K. (1998). Habitat use by capped langur (Trachypithecus pileatus) in Tripura, northeast India. (abstract) XVII Congress of the International Primatological Society. University of Antananrivo, Madagascar.
Gupta, A. K., & Chivers, D. J. (2000). Feeding ecology and conservation of the golden langur Trachypithecus geei Khajuria in Tripura, Northeast India. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 97, 349–362.
Gupta, A. K., & Kumar, A. (1994). Feeding ecology and conservation of the Phayre's leaf monkey Presbytis phayrei in northeast India. Biological Conservation, 69, 301–306.
Khan, M. A. R., & Ahsan, M. F. (1986). The status of the primates in Bangladesh and a description of their forest habitats. Primate Conservation, 7, 102–108.
Krishnamani, R. (1994). Diet composition of the bonnet macaque (Macaca radiata) in a tropical dry evergreen forest of southern India. Tropical Biodiversity, 2, 285–302.
Kumar, A., & Solanki, G. S. (2004). A rare feeding observation on water lilies (Nymphaea alba) by the capped langur, Trachypithecus pileatus. Folia Primatologica, 75, 157–159.
Mitchell, A. H. (1994). Ecology of Hose’s Langur, Presbytis hosei, in Mixed Logged and Unlogged Dipterocarp Forest of Northeast Borneo. Ph.D. thesis, Yale University, New Haven.
Newton, P. N. (1992). Feeding and ranging patterns of forest hanuman langurs (Presbytis entellus). International Journal of Primatology, 13, 245–285.
Oates, F. G. (1988). The diet of the olive Colobus monkey Procolobus verus, in Sierra Leone. International Journal of Primatology, 9, 457–478.
Oates, J. F., Waterman, P. G., & Choo, G. M. (1980). Food selection by the South Indian leaf monkey, Presbytis johnii in relation to leaf chemistry. Oecologia, 45, 45–56.
Roonwal, M. L., & Mohnot, S. M. (1977). Primates of South Asia: Ecology, Sociobiology, and Behavior. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Simpson, G. G., Roe, A., & Lewontin, R. C. (1960). Quantitative Zoology. New York: Harcourt, Brace and Company.
Smith, R. L., & Smith, T. M. (2000). Elements of Ecology. San Francisco: Benjamin/Cummings.
Solanki, G. S. (2005). Habitat evaluation and ecological studies on some wildlife species in Pakhui wildlife Sanctuary, Arunachal Pradesh, India. Final Technical Project Report, Submitted to Ministry of Environment & Forest, Government of India.
Solanki, G. S., Kumar, A., & Sharma, B. K. (2007). Reproductive strategies in Trachypithecus pileatus in India. International Journal of Primatology, 28(5), 1075–1083.
Srivastava, A. (1999). Primates of Northeast India p. 207. Bikaner, Rajasthan, India: Megadiversity Press.
Stanford, C. B. (1991). The diet of the capped langur (Presbytis pileata) in a moist deciduous forest in Bangladesh. International Journal of Primatology, 12, 199–216.
Stanford, C. B. (1992). Comparative ecology of the capped langur Presbytis pileata Blyth in two forest types in Bangladesh. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 89, 187–193.
Struhsaker, T. T. (1975). The Red Colobus Monkeys. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sunderraj, W., & Johnsingh. A. J. T. (1993). Impact of flash flood on the gallery forest and arboreal mammals of river Servalar, Mundanthurai Plateau, south India. Research Report, Wildlife Institute of India, 19 pp.
Waterman, P. G., Ross, J. A. M., Bennett, E. L., & Davies, A. G. (1988). A comparison of the floristic and leaf chemistry of the tree flora in two Malaysian rain forests and influence of leaf chemistry on populations of colobine monkeys in the old world. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 34, 1–32.
Zhang, Y.-Z., Wang, S., & Quan, G.-Q. (1981). On the geographical distribution of primates in China. Journal of Human Evolution, 10, 215–226.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Ministry of Environment & Forest, Government of India for providing financial support. We also thank the Principal Chief Conservator of Forest, Government of Arunachal Pradesh, for necessary permission and facilities to work in the Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary and also the officials of the sanctuary for logistic support during the study. We thank the director, North Eastern Regional Institute of Science & Technology and the Head, Department of Forestry for providing all the facilities required for the study. We thank both reviewers for critical evaluation and constructive suggestions for improving the manuscript, and Dr. S. D. Baral, Department of English, Mizoram University for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solanki, G.S., Kumar, A. & Sharma, B.K. Feeding Ecology of Trachypithecus pileatus in India. Int J Primatol 29, 173–182 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-008-9234-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-008-9234-0