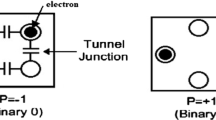
Abstract
Despite many advances in the electronics industry, much effort is being made to improve existing technologies. One of the proposed technologies in this field is the Quantum Cellular Automata (QCA), which provides low power, low area, high density, and high-speed structures. Latches and flip-flops are always the most commonly used circuits in digital design, and designing these structures with greater stability and capability is very important. In this paper, with the use of the appropriate D latch in terms of volume and delay, the edge sensitive D flip-flops in the QCA technology are introduced with the ability of set and reset based on optimized multiplexer design. The simulation results show that the proposed designs are stable and useful structures in terms of area, delay and complexity and are suitable for use in the larger circuits. For example proposed synchronous rising edge D flip-flop with set and reset pins has 74 quantum cells, 2.5 clock cycles delay and 0.09μm2 occupied area.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srivastava S. Probabilistic modeling of quantum-dot cellular automata
Compano, R., Molenkamp, L., Paul, D.J.: Roadmap for Nanoelectronics. European Commission IST Programme, Future and Emerging Technologies (2000)
Lent, C.S., Tougaw, P.D., Porod, W., Bernstein, G.H.: Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology. 4(1), 49–57 (1993 Jan)
Yang, X., Cai, L., Zhao, X.: Low power dual-edge triggered flip-flop structure in quantum dot cellular automata. Electron. Lett. 46(12), 825–826 (2010)
Hashemi, S., Navi, K.: New robust QCA D flip flop and memory structures. Microelectron. J. 43(12), 929–940 (2012)
Vetteth, A., Walus, K., Dimitrov, V.S., Jullien, G.A.: Quantum-dot cellular automata of flip-flops. ATIPS Laboratory. 2500, (2003)
Sardinha, L.H., Silva, D.S., Vieira, M.A., Vieira, L.F., Neto, O.P.: Tcam/cam-qca:(ternary) content addressable memory using quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. J. 46(7), 563–571 (2015)
Abutaleb, M.M.: Robust and efficient quantum-dot cellular automata synchronous counters. Microelectron. J. 61, 6–14 (2017)
Yang, X., Cai, L., Zhao, X., Zhang, N.: Design and simulation of sequential circuits in quantum-dot cellular automata: falling edge-triggered flip-flop and counter study. Microelectron. J. 41(1), 56–63 (2010)
Walus, K., Dysart, T.J., Jullien, G.A., Budiman, R.A.: QCADesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3(1), 26–31 (2004)
Chakrabarty R, Mahato DK, Banerjee A, Choudhuri S, Dey M, Mandal NK. A novel design of flip-flop circuits using quantum dot cellular automata (QCA). InComputing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), 2018 IEEE 8th Annual 2018 Jan 8 (pp. 408–414). IEEE
Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R., Kianpour, M.: A novel QCA implementation of MUX-based universal shift register. J. Comput. Electron. 13(1), 198–210 (2014)
Purkayastha, T., De, D., Chattopadhyay, T.: Universal shift register implementation using quantum dot cellular automata. Ain Shams Engineering Journal. 9 (2016)
Shamsabadi, A.S., Ghahfarokhi, B.S., Zamanifar, K., Movahedinia, N.: Applying inherent capabilities of quantum-dot cellular automata to design: D flip-flop case study. J. Syst. Archit. 55(3), 180–187 (2009)
Zoka, S., Gholami, M.: A novel rising edge triggered resettable D flip-flop using five input majority gate. Microprocess. Microsyst. 61, 327–335 (2018)
Srivastava S, Asthana A, Bhanja S, Sarkar S. QCAPro-an error-power estimation tool for QCA circuit design. InCircuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2011 IEEE International Symposium on 2011 May 15 (pp. 2377–2380). IEEE
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binaei, R., Gholami, M. Design of Multiplexer-Based D Flip-Flop with Set and Reset Ability in Quantum Dot Cellular Automata Nanotechnology. Int J Theor Phys 58, 687–699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3967-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3967-0