Abstract
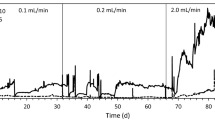
This paper describes a study of continuous decomposition characteristics of ammonia to nitrogen in a multi-cell-stacked electrolyzer with an anion exchange membrane. The pH change of ammonia solution in both the anodic and cathodic chambers of a divided cell due to the water splitting reactions was studied together with the electrolytic decomposition of ammonia. The electrolytic decomposition efficiency of ammonia was considerably affected by the pH change of ammonia solution caused by the water splitting reactions. In the anodic chamber with the ammonia solution, the water splitting reaction which produced protons occurred at a pH of less than 8, and in the cathodic chamber, that producing hydroxyl ions occurred at a pH of more than 11. By using the characteristics of the electrolytic water splitting reactions in a divided cell, a continuous electrolyzer with a self-pH-adjustment function was devised, wherein a portion of the ammonia solution from a pH-adjustment reservoir was circulated through the cathodic chambers of the electrolyzer. This enhanced the pH of the ammonia solution being fed from a pH-adjustment reservoir into the anodic chambers of the electrolyzer, which caused a higher ammonia decomposition yield. Based on this electrolyzer, a salt-free ammonia decomposition process was suggested. In this process, ammonia in the solution was continuously and effectively decomposed into environmentally harmless nitrogen gas.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng C., Sugiura N., Shimada S., Maekawa T. (2003) . J. Hazard. Mater. B103:65
Bae S.K., Park S.C. (1984) . J. Kor. Soc. Environ. Eng. 6:44
Lin S.H., Wu C.L. (1996) . Water Res. 30:715
Bouwer E.J., Crowe P.B. (1988) . J.AWWA. 80:82
Kim K.W., Kim Y.J., Kim I.T., Park G.I., Lee I.H. (2005) . Electrochim. Acta 50:4356
Kim K.W., Kim Y.J., Kim I.T., Park G.I., Lee I.H. (2004) . Kor. Chem. Eng. Res. 42:524
Kim K.W., Kim Y.J., Kim I.T., Park G.I., Lee I.H. (2005) . Kor. Chem. Eng. Res. 43:9
Kim K.W., Kim Y.J., Kim I.T., Park G.I., Lee I.H. (2006) . Water Res. 40:1431
E.P.Bonnin, E.J.Cellar and G.G. Botte, in Proceeding of 206th Meeting of Electrochemical Society, Honolulu, Hawaii, U.S.A., October 3–8 (2004)
Lopez de Mishima B.A., Lescano D., Holgado M.T., Mishima H.T. (1997) . Electrochim. Acta 43:395
Gootzen J.F.E., Wonders A.H., Visscher W., Santen R.A.V. (1997) . Electrochim. Acta 43:1851
Kim K.W., Lee E.H., Kim J.S., Shin K.H., Chung B.I. (2002) . Electrochim. Acta 47:2525
Marincic L., Leitz F.B. (1978) . J. Appl. Electrochem. 8:333
Sasaki K., Hisatomi Y. (1970) . J. Electrochem. Soc. 117:758
Oswin H.G., Salomon M. (1963) . Can. J. Chem. 41:1686
de Vooys A.C.A., Koper M.T.M., van Santen R.A., van Veen J.A.R. (2001) . J. Electroanal. Chem. 506:127
Trasatti S. (1984) . Electrochim. Acta 29:1503
F. Vitse and G.G. Botte, in Proceeding of 206th Meeting of Electrochemical Society, Honolulu, Hawaii, U.S.A., October 3–8 (2004)
Kim K.W., Lee E.H., Kim J.S., Shin K.H., Chung B.I. (2002) . J. Electrochem. Soc. 149:D187
Bryabt E.A., Fulton G.P., Budd G.C. (1992) Disinfection Alternatives for Safe Drinking Water. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
G. C. White, Handbook of Chlorination and Alternative Disinfectants (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1999)
Kim K.W., Lee E.H., Kim J.S., Shin K.H., Kim K.H. (2001) . Electrochim. Acta 46:915
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KW., Kim, IT., Park, GI. et al. Electrolytic decomposition of ammonia to nitrogen in a multi-cell-stacked electrolyzer with a self-pH-adjustment function. J Appl Electrochem 36, 1415–1426 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9234-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9234-8