Abstract
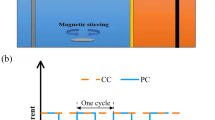
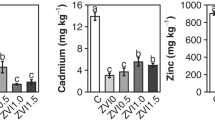
Pulsed electrokinetics studies were carried out to optimize the removal of Zn and Cd from fine-grained soils and to observe the effects of varying the pulse frequency, pulse time ratio (on/off), and DC voltage gradient. Existing forms of heavy metals in the soil matrix were determined using a sequential extraction method. The strongly bound fraction (bound to organic matter and residuals) that is difficult to remove from the soil matrix comprised 74 and 62% of the total Zn and Cd, respectively. In the electrokinetic remediation experiments, MgSO4 was employed to increase the ionic strength of the soil for 2 weeks. Transportation of heavy metals was influenced by the frequency, pulse ratio, and the voltage gradient of the pulsed electric field. Extraction efficiency of Zn and Cd near the anode was correlated positively with the voltage gradient at a given pulse and ratio. A high pulse frequency (1,800 cycles/h) enhanced the removal efficiency of the heavy metals compared to a low pulse frequency (1,200 cycles/h) at a supplied voltage gradient of 1 V/cm. Although pulsed electrokinetics was more effective in extracting and desorbing ions near the anode than conventional electrokinetics, its ability to transport heavy metals from the anode to the cathode was relatively small. Total removals with pulsed electrokinetics were 21–31% for Zn and 18–24% for Cd. In summary, pulsed electrokinetics can enhance removal efficiency of heavy metals and is beneficial with regard to electrical energy consumption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi HD, Park SW, Ryu BG, Cho JM, Kim KJ, Baek K (2009) Environ Eng Res 14(3):153
Jeon CS, Baek K, Park JK, Oh YK, Kim SD (2009) J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):804
Baek K, Kim DH, Park SW, Ryu BG, Bajargal T, Yang JS (2009) J Hazard Mater 161(1):457
Kim DH, Ryu BG, Park SW, Seo CI, Baek K (2009) J Hazard Mater 165:501
Lee CG, Chon HT, Jung MC (2001) Geochem 16:1377
Acar YB, Gale RJ, Alshawabkeh AN, Marks RE, Puppala S, Bricka M, Parker R (1995) J Hazard Mater 40(2):117
Yeung AT, Hsu CN (2005) J Environ Eng-ASCE 131(2):298
Nystrom GM, Ottosen LM, Villumsen A (2004) Eng Geol 77:349
Reddy KR, Danda S, Saichek RE (2004) J Environ Eng-ASCE 130(11):1357
Reddy KR, Saichek RE (2004) J Environ Sci Health A-Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 39(5):1189
Kim DH, Jeon CS, Baek k, Ko SH, Yang JS (2009) J Hazard Mater 161:565
Park SW, Lee JY, Yang JS, Kim KJ, Baek K (2009) J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):1168
Ottosen LM, Hansen HK, Laursen S, Villumsen (1997) Environ Sci Technol 31:1711
Reddy KR, Chinthamreddy S (2003) J Geotech Geoenviron-ASCE 129(3):263
Cho JM, Kim KJ, Chung KY, Hyun S, Baek K (2009) Sep Sci Technol 44(10):2371
Eykholt G, Daniel D (1994) J Geotech Eng 120(5):797
Acar YB, Alshawabkeh AN (1993) Environ Sci Technol 27(13):2638
Reddy KR, Xu CY, Chinthamreddy S (2001) J Hazard Mater 84(2–3):279
Ryu BG, Park SW, Baek K, Yang JS (2009) Sep Sci Technol 44(10):2421
Rojo A, Hansen HK, Ottosen LM (2006) Miner Eng 19:500
Zhou DM, Deng CF, Cang L, Alshawabkeh AN (2005) Chemosphere 61(4):519
Zhou DM, Deng CF, Cang L (2004) Chemosphere 56(3):265
Pazos M, Sanroman MA, Cameselle C (2005) Chemosphere 62:817
Hansen HK, Rojo A (2007) Electrochim Acta 52(10):3399
Kornilovich B, Mishchuk N, Abbruzzese K, Pshinko G, Klishchenko R (2005) Colloid Surface A-Physicochem Eng Asp 265(1–3):114
Tessier A, Campbell P, Bisson M (1979) Anal Chem 51(7):844
Mitchell JK (1993) Fundamentals of soil behavior, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Environmental Technology and Industry through GAIA project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, BG., Yang, JS., Kim, DH. et al. Pulsed electrokinetic removal of Cd and Zn from fine-grained soil. J Appl Electrochem 40, 1039–1047 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-0046-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-0046-5