Abstract
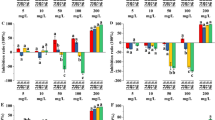
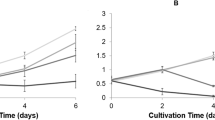
Cyanobacterial contamination of water has been a serious problem in recent years. Thus, the effective control of undesired cyanobacteria has become an urgent issue. We studied therefore the effects of ρ-coumaric acid and vanillic acid on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa and the allelopathic mechanisms. The results showed that the growth of toxic M. aeruginosa was significantly inhibited by ρ-coumaric acid and vanillic acid, with an EC50 of 0.26 ± 0.07 and 0.34 ± 0.05 mmol L−1, respectively. Our data also demonstrated that both ρ-coumaric acid and vanillic acid triggered the generation of superoxide anion radicals (O2 •−). The O2 •− might induce a lipid peroxidation which may change cell membrane penetrability, thereby leading to the eventual death of M. aeruginosa. Our current studies further provide evidence that some phenolic acids such as ρ-coumaric acid and vanillic acid may be a potential effective solution for aquatic management.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum U (1996) Allelopathic interactions involving phenolic acids. J Nemat 28:259–267
Cavas L, Yurdakoc K, Yokes B (2005) Antioxidant status of Lobiger serradifalci and Oxynoe olivacea (Opisthobranchia, Mollusca). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 314:227–235
Chen CZ, Cooper SL (2002) Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes. Biomaterials 23:3359–3368
Denyer SP, Stewart GSAB (1998) Mechanisms of action of disinfectants. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 41:261–268
Djurdjevic L, Dinic A, Pavlovic P, Mitrovic M, Karadzic B, Tesevic V (2004) Allelopathic potential of Allium ursinum L. Biochem Syst Ecol 32:533–544
Einhellig FA (1995) Mechanism of action of allelochemicals in allelopathy. In: In Inderjit K, Dakshini MM, Einhellig FA (eds) Allelopathy: organisms, processes, and applications. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 96–116
Gross EM, Meyer H, Schilling G (1996) Release and ecological impact of algicidal hydrolysable polyphenols in Myriophyllum spicatum. Phytochemistry 41(1):133–138
Gross EM, Erhard D, Ivanyi E (2003) Allelopathic activity of Ceratophyllum demersum L. and Najas marina ssp. intermedia (Wolfgang) Casper. Hydrobiologia 15:583–589
He CQ, Ye JX (1999) Inhibitory effects of Acorus tatarinowii on algae growth. Acta Ecologica Sinica 19(5):754–758 in Chinese with English abstract
Inderjit J, Streibig C, Olofsdotter M (2002) Joint action of phenolicacid mixtures and its significance in allelopathy research. Physiol Plantarum 11(4):422–4287
Liu H, Xie P, Zhou J, Liu XJ, Tang HJ (2003) Studies on photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll a derivatives of lake Donghu by using HPLC. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 27(1):1–6 in Chinese with English abstract
Millie DF, Fahnenstiel GL, Carrick HJ, Lohrenz SE, Schofield O (2002) Phytoplankton pigments in coastal Lake Michigan: distributions during the spring isothermal period and relation with episodic sediment resuspension. J Phycol 38:639–648
Nakai S, Hosomi M, Okada M, Murakami A (1996) Control of algal growth by macrophytes and macrophyte extracted bioactive compounds. Water Sci Technol 34(7–8):227–235
Nakai S, Inoue Y, Hosomi M, Murakami A (2001) Algal growth inhibition effects and inducement modes by plant-producing phenols. Water Res 35:1855–1859
Park MH, Han MS, Ahn CY, Kim HS, Yoon BD, Oh HM (2006) Growth inhibition of bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by rice straw extract. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:307–312
Rassoulzadegan M, Akyurtlakli N (2002) An investigation on the toxic effects of Malathion (organophosphate insecticide) on the Daphnia magna Straus, 1820 (Crustacea, Cladocera). Turk J Zoolog 26:349–355
Rice EL (1984) Allelopathy, 2nd edn. Academic, Orlando, pp 1–2
Sun XX, Choi JK, Kim EK (2004) A preliminary study on the mechanism of harmful algal bloom mitigation by use of sophorolipid treatment. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 304:35–49
Van ED, Wouter J, Van DB (2002) Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquat Bot 72:261–274
Vardi A, Schatz D, Beeri K, Motro U, Sukenik A, Levine A, Kaplan A (2002) Dinoflagellate–cyanobacterium communication may determine the composition of phytoplankton assemblage in a mesotrophic lake. Curr Biol 12:1767–1772
Xian QM, Chen HD, Zou HX, Yin DQ (2006) Allelopathic activity of volatile substance from submerged macrophytes on Microcystin aeruginosa. Acta Ecologica Sinica 26(11):3549–3554
Xiao HS, He WJ, Fu WQ, Chao HY, Fan ZN (1999) A spectrophotometer method testing oxygen radicals. Prog Biochem Biophys 26(2):180–182 in Chinese with English abstract
Yagi K (1994) Lipid peroxides in hepatic, gastrointestinal and pancreatic diseases. In: Armstrong D (ed) Free radicals in diagnostic medicine. Plenum, New York, pp 1–15
Zhang TT, Chen CP, He M, Wu AP, Nie LW (2007a) Allelopathic effects of several higher aquatic plants on algae. J Biol 24(4):16–20 in Chinese with English abstract
Zhang TT, Wu AP, He M, Nie LW (2007b) The allelopathic inhibition and allelopathic mechanism of phenolic acids on algae in water bloom. China Environ Sci 27(4):472–476 in Chinese with English abstract
Zhang TT, He M, Wu AP, Nie LW (2008) Allelopathic inhibition of ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid on Microcystis aeruginosa Kuetz with no toxicological effects on Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 28(9):1887–1893 in Chinese with English abstract
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30870429) and the Provincial Key Laboratory of Biotic Environment and Ecological Safety in Anhui.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, TT., Zheng, CY., Hu, W. et al. The allelopathy and allelopathic mechanism of phenolic acids on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa . J Appl Phycol 22, 71–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9429-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9429-6