Abstract
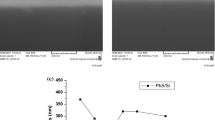
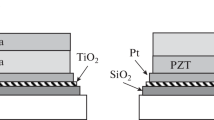
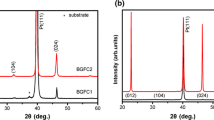
In this investigation, PZT films were sputter-deposited on Si/SiO2/Ti/Pt substrates using a dual-target system. The dual targets Pb/PZT(PbZr0.54Ti0.46O3) and PbO/PZT(PbZr0.54Ti0.46O3) were used to reveal the effects of various lead compensation source materials on the microstructure and ferroelectric properties of the films. The structures of the films were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The chemical binding state was determined using X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS). Ferroelectric polarizability was measured using a Radiant Technology RT66A tester. The influence of deposition temperatures on the microstructure and ferroelectric properties of the films was studied. Perovskite PZT films were successfully deposited using the Pb/PZT and the PbO/PZT dual target sputtering systems at a substrate temperature of between 500 and 580∘C. Structural change was elucidated as a function of deposition temperatures and the lead sources were correlated with the ferroelectric properties of the film. The ferroelectric characteristics of the PZT films deposited using the PbO/PZT dual target were better than those of films deposited using the Pb/PZT dual target, because the former films had a higher bonding energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Sayer and K. Sreenivas, Science, 247, 1056 (1990).
T. Shiosak, Ultrason. Symp. Proc., IEEE, 537(1990).
N. Wakiya, K. Kuroyanagi, Y. Xuan, K. Shinozaki, and N. Mizutani, Thin Solid Films, 372, 156 (2000).
J.N. Kim, K.S. Shin, D.H. Kim, B.O. Park, N.K. Kim, and S.H. Cho, Applied Surface Science, 206(1–4), 119 (2003).
M. Cerqueira, R.S. Nasar, E.R. Leite, E. Longo, and J.A. Varela, Ceram. Int., 26(3), 231 (2000).
M.G. Kang, K.T. Kim, and C.I. Kim, Thin Solid Films, 398–399, 448 (2001).
O. Sugiyami, Y. Kondo, H. Suzuki, and S. Kaneko, J. Sol-Gel Soc. Technol., 26, 749 (2003).
C.R. Cho, Cryst. Res. Technol., 35(1), 77 (2000).
N. Ozer and T. Sands, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 19(1–3), 157 (2000).
C.R. Cho, L.F. Francis, and D.L. Polla, Mater. Lett., 38(2), 125 (1999).
S.A. Impey, Z. Huang, and A. Patel, J. Appl. Phys., 83(4), 2202 (1998).
R. Bruchhaus, Ferroelectrics, 133(1–4), 73 (1992).
N.J. Wu, A. Ignatiev, A.W. Mesarwi, H. Lin, K. Xan, and H.D. Shih, Mater. Chem. Phys., 32, 5019 (1993).
A.R. Zomorrodian, A. Messarwi, N.J. Wu, and A. Ignatiev, Appl. Surf. Sci., 90, 343 (1995).
P. Verardi, F. Craciun, L. Mirenghi, M. Dinescu, and V. Sandu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 138–139, 552 (1999).
A.R. Zomorrodian, A.M.A., and N.J. Wu, Ceram. Int., 25(2), 137 (1999).
H. Kidoh, T. Ogawa, H. Yashima, A. Morimoto, and T. Shimizu, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Pt.1, 31, 2965 (1992).
S. Takatani, H. Keiko, K.A. Keiko, and K. Torii, J. Appl. Phys., 85(11), 7784 (1999).
C.W. Chung, Y.H. Byun, and H.I. Kim, Microelectron. Eng., 63(4), 353 (2002).
W.Y. Choi and H.G. Kim, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 138(1A), 122 (1999).
W.Y. Choi, J.H. Ahn, and W.J. Lee, Mater. Lett., 37(3), 119 (1998).
K. Iijima, I. Ueda, and K. Kugimiya, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Pt.1, 30(9B), 2149 (1991).
T. Hase and T. Shiosaki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Pt.1, 30(9B), 2159 (1991).
S. Yamauchi and M. Yoshimaru, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 35, 1553 (1996).
L.N. Chapin and S.A. Myers, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 243, 153 (1992).
M.D. Keijser and D.J.M. Dormans, MRS Bull, 21, 37 (1996).
C.K. Kwok and S.B. Desu, Ceram. Trans., 25, 85 (1992).
T.S. Kim, D.J. Kim, J.K. Lee, and H.J. Jung, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A15(6), 2831 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, W.L., He, J.L. Influence of the Lead Source Materials on the Microstructure and Ferroelectric Properties of PZT Films Sputter-Deposited Using Lead and Lead Oxide. J Electroceram 13, 35–39 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5072-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5072-5