Abstract
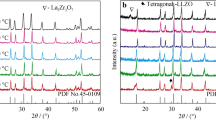
Al-substituted Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZ:Al) was synthesized via conventional solid state reaction. Different dwell times at sintering temperature of 1200 °C led to a varying Li content in LLZ:Al which significantly affected the Li-ion conductivity. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction were used to characterize the sintered pellets which showed a maximum total ionic conductivity of ~3 × 10−4 S cm−1 at room temperature although the samples were composed of cubic and tetragonal LLZ:Al, with the tetragonal phase as its major phase. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy revealed that the Li content steadily decreased from 7.5 to 6.5 Li per formula unit with increasing sintering time. The highest conductivity was observed from the sample with the lowest Li concentration at 6.5 per formula unit. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed the formation of large grains, about 500 μm in diameter, which additionally could be the reason for achieving high total Li-ion conductivity. Electrochemical tests showed that mixed phase LLZ:Al is stable against metallic Li up to 8 V.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Kamaya, K. Homma, Y. Yamakawa, M. Hirayama, R. Kanno, M. Yonemura, T. Kamiyama, Y. Kato, S. Hama, K. Kawamoto, A. Mitsui, Nat. Mater. 10, 682 (2011)
F. Mizuno, A. Hayashi, K. Tadanaga, M. Tatsumisako, Adv. Mater. 17, 918 (2005)
H.-J. Deiseroth, S.-T. Kong, H. Eckert, J. Vannahme, C. Reiner, T. Zaiß, M. Schlosser, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 755 (2008)
R. Prasada Rao, S. Adams, Phys. Status Solidi A 208, 1804 (2011)
P. Birke, F. Salam, S. Dӧring, W. Weppner, Solid State Ionics 118, 149 (1999)
X.M. Wu, X.H. Li, S.W. Wang, Z. Wang, Y.H. Zhang, M.F. Xu, Z.Q. He, Thin Solid Films 425, 103 (2003)
S. Hasegawa, N. Imanishi, T. Zhang, J. Xie, A. Hirano, Y. Takeda, O. Yamamoto, J. Power Sources 189, 371 (2009)
Y. Shimonishi, T. Zhang, P. Johnson, N. Imanishi, A. Hirano, Y. Takeda, O. Yamamoto, N. Sammes, J. Power Sources 195, 6187 (2010)
F. Ding, W. Xu, Y. Shao, X. Chen, Z. Wang, F. Gao, X. Liu, J.-G. Zhang, J. Power Sources 195, 6187 (2010)
V. Thangadurai, H. Kaack, W.J.F. Weppner, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86, 437 (2003)
J. Percival, E. Kendrick, P.R. Slater, Solid State Ionics 179, 1666 (2008)
Y.X. Gao, X.P. Wang, W.G. Wang, Z. Zhuang, D.M. Zhang, Q.F. Fang, Solid State Ionics 181, 1415 (2010)
H. Buschmann, J. Dӧlle, S. Berendts, A. Kuhn, P. Bottke, M. Wilkening, P. Heitjans, A. Senyshyn, H. Ehrenberg, A. Lotnyk, V. Duppel, L. Kienle, J. Janek, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 19378 (2011)
J. Awaka, N. Kijima, H. Hayakawa, J. Akimoto, J. Solid State Chem. 182, 2046 (2009)
J. Awaka, A. Takashima, K. Kataoka, N. Kijima, Y. Idemoto, J. Akimoto, Chem. Lett. 40, 60 (2011)
M. Xu, M.S. Park, J.M. Lee, T.Y. Kim, Y.S. Park, E. Ma, Phys. Rev. B 85, 052301 (2012)
E.J. Cussen, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 5167 (2010)
A. Logeat, T. Kohler, U. Eisele, B. Stiaszny, A. Harzer, M. Tovar, A. Senyshyn, H. Ehrenberg, B. Kozinsky, Solid State Ionics 206, 33 (2012)
S. Adams, R.P. Rao, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 1426 (2012)
Y. Li, J.-T. Han, C.-A. Wang, S.C. Vogel, H. Xie, M. Xu, J.B. Goodenough, J. Power Sources 209, 278 (2012)
I. Kokal, M. Somer, P.H.L. Notton, H.T. Hintzen, Solid State Ionics 185, 42 (2011)
E.A. Il’ina, O.L. Andreev, B.D. Antonov, N.N. Batalov, J. Power Sources 201, 169 (2012)
J. Wolfenstine, E. Rangasamy, J.L. Allen, J. Sakamoto, J. Power Sources 208, 193 (2012)
N. Bernstein, M.D. Johannes, K. Hoang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 205702 (2012)
E. Rangasamy, J. Wolfenstine, J. Sakamoto, Solid State Ionics 206, 28 (2012)
F. Tietz, T. Wegener, M.-T. Gerhards, M. Giarola, G. Mariotto, Solid State Ionics 230, 77 (2013)
A.C. Larson, R.B. Von Dreele, General Structure Analysis System (GSAS), Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR 86–748 (2004)
C.A. Geiger, E. Alekseev, B. Lazic, M. Fisch, T. Armbruster, R. Langner, M. Fechtelkord, N. Kim, T. Pettke, W. Weppner, Inorg. Chem. 50, 1089 (2011)
Y. Li, J.-T. Han, C.-A. Wang, H. Xie, J.B. Goodenough, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 15357 (2012)
H. Xie, J.A. Alonso, Y. Li, M.T. Fernandez-Díaz, J.B. Goodenough, Chem. Mater. 23, 3587 (2011)
A. Kuhn, M. Wilkening, L. Robben, J.-Y. Choi, F. Tietz, P. Heitjans, Z. Phys. Chem 226, 525 (2012)
S. Kumazaki, Y. Iriyama, K. Kim, R. Murugan, K. Tanabe, K. Yamamoto, T. Hirayama, Z. Ogumi, Electrochem. Commun. 13, 509 (2011)
Acknowledgments
Financial support by the Helmholtz Gemeinschaft Deutscher Forschungszentren e.V. in the frame of the granted projects “Elektrochemische Speicher im System – Zuverlässigkeit und Integration“and “Helmholtz-Initiative für Mobile / Stationäre Energiespeichersysteme“, is gratefully acknowledged. ICP-OES measurements were carried out at the Central Institute for Engineering, Electronics and Analytics (ZEA-3) at Forschungszentrum Jülich and are also gratefully acknowledged. Cathode material LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 was sponsored by Hirose tech CO., Ltd., Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, CL., Dashjav, E., Hammer, EM. et al. High conductivity of mixed phase Al-substituted Li7La3Zr2O12 . J Electroceram 35, 25–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-015-9988-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-015-9988-7