Abstract
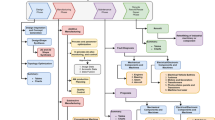
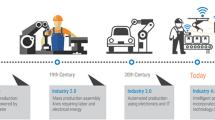
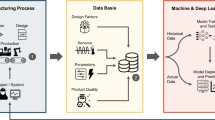
The paradigm shift toward Industry 4.0 is not solely completed by enabling smart machines in a factory but also by facilitating human capability. Refinement of work processes and introduction of new training approaches are necessary to support efficient human skill development. This study proposes a new skill transfer support model in a manufacturing scenario. The proposed model develops two types of deep learning as the backbone: a convolutional neural network (CNN) for action recognition and a faster region-based CNN (R-CNN) for object detection. A case study using toy assembly is conducted utilizing two cameras with different angles to evaluate the performance of the proposed model. The accuracy for CNN and faster R-CNN for the target job reached 94.5% and 99%, respectively. A junior operator can be guided by the proposed model given that flexible assembly tasks have been constructed on the basis of a skill representation. In terms of theoretical contribution, this study integrated two deep learning models that can simultaneously recognize the action and detect the object. The present study facilitates skill transfer in manufacturing systems by adapting or learning new skills for junior operators.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamides, G., Katsanos, C., Constantinou, I., Christou, G., Xenos, M., Hadzilacos, T., et al. (2017). Design and development of a semi-autonomous agricultural vineyard sprayer: Human–robot interaction aspects. Journal of Field Robotics, 34(8), 1407–1426.
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., & Baskurt, A. (2012). Spatio-temporal convolutional sparse auto-Encoder for sequence classification. In BMVC (pp. 1-12).
Backhaus, J., & Reinhart, G. (2017). Digital description of products, processes and resources for task-oriented programming of assembly systems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 28(8), 1787–1800.
Bejnordi, B. E., Zuidhof, G., Balkenhol, M., Hermsen, M., Bult, P., van Ginneken, B., et al. (2017). Context-aware stacked convolutional neural networks for classification of breast carcinomas in whole-slide histopathology images. Journal of Medical Imaging, 4(4), 044504.
Bhandare, A., Bhide, M., Gokhale, P., & Chandavarkar, R. (2016). Applications of convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 7(5), 2206–2215.
Carrio, A., Sampedro, C., Rodriguez-Ramos, A., & Campoy, P. (2017). A review of deep learning methods and applications for unmanned aerial vehicles. Journal of Sensors. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3296874.
Chen, B., Ting, J., Marlin, B., & Freitas, N. (2010). Deep learning of invariant spatio-temporal features from video. In Proceedings of the annual conference of on neural information processing systems (NIPS).
Ciocca, G., Napoletano, P., & Schettini, R. (2018). CNN-based features for retrieval and classification of food images. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 176, 70–77.
Dewa, C. K., & Afiahayati, (2018). Suitable CNN Weight Initialization and Activation Function for Javanese Vowels Classification. Procedia Computer Science, 144, 124–132.
Duan, F., Tan, J. T. C., Tong, J. G., Kato, R., & Arai, T. (2012). Application of the assembly skill transfer system in an actual cellular manufacturing system. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 9(1), 31–41.
Frank, A. G., Dalenogare, L. S., & Ayala, N. F. (2019). Industry 4.0 technologies: Implementation patterns in manufacturing companies. International Journal of Production Economics, 210, 15–26.
Gu, J., Wang, Z., Kuen, J., Ma, L., Shahroudy, A., Shuai, B., et al. (2018). Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognition, 77, 354–377.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 770–778).
Hill, T. (2017). Manufacturing strategy: The strategic management of the manufacturing function. London: Macmillan International Higher Education.
Idrees, H., Zamir, A. R., Jiang, Y. G., Gorban, A., Laptev, I., Sukthankar, R., et al. (2017). The THUMOS challenge on action recognition for videos “in the wild”. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 155, 1–23.
Iwahori, Y., Takada, Y., Shiina, T., Adachi, Y., Bhuyan, M. K., & Kijsirikul, B. (2018). Defect Classification of Electronic Board Using Dense SIFT and CNN. Procedia Computer Science, 126, 1673–1682.
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Spatial transformer networks. In Advances in neural information processing ssystems (pp. 2017–2025).
Jardim-Goncalves, R., Grilo, A., & Popplewell, K. (2016). Novel strategies for global manufacturing systems interoperability. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 27(1), 1–9.
Kiassat, C., & Safaei, N. (2019). Effect of imprecise skill level on workforce rotation in a dynamic market. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 131, 464–476.
Koch, P. J., van Amstel, M. K., Dębska, P., Thormann, M. A., Tetzlaff, A. J., Bøgh, S., et al. (2017). A skill-based robot co-worker for industrial maintenance tasks. Procedia Manufacturing, 11, 83–90.
Landi, C. T., Villani, V., Ferraguti, F., Sabattini, L., Secchi, C., & Fantuzzi, C. (2018). Relieving operators’ workload: Towards affective robotics in industrial scenarios. Mechatronics, 54, 144–154.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436.
Levratti, A., De Vuono, A., Fantuzzi, C., & Secchi, C. (2016, July). TIREBOT: A novel tire workshop assistant robot. In 2016 IEEE international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics (AIM) (pp. 733–738). IEEE.
Lim, C. H., Kim, M. J., Heo, J. Y., & Kim, K. J. (2018). Design of informatics-based services in manufacturing industries: case studies using large vehicle-related databases. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(3), 497–508.
Lin, T.Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., et al. (2014, September). Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 740–755). Cham: Springer.
Liu, M., Ma, J., Lin, L., Ge, M., Wang, Q., & Liu, C. (2017). Intelligent assembly system for mechanical products and key technology based on internet of things. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 28(2), 271–299.
Liu, H., & Wang, L. (2017). Human motion prediction for human–robot collaboration. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 44, 287–294.
Liu, H., & Wang, L. (2018). Gesture recognition for human–robot collaboration: A review. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 68, 355–367.
Microsoft (2019) Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.0312
Oztemel, E., & Gursev, S. (2020). Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31(1), 127–182.
Pei, L., Ye, M., Zhao, X., Dou, Y., & Bao, J. (2016). Action recognition by learning temporal slowness invariant features. The Visual Computer, 32(11), 1395–1404.
Peng, X., Wang, L., Wang, X., & Qiao, Y. (2016). Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: Comprehensive study and good practice. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 150, 109–125.
Peruzzini, M., Grandi, F., & Pellicciari, M. (2020). Exploring the potential of Operator 4.0 interface and monitoring. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 139, 105600.
Qi, T., Xu, Y., Quan, Y., Wang, Y., & Ling, H. (2017). Image-based action recognition using hint-enhanced deep neural networks. Neurocomputing, 267, 475–488.
Rawat, W., & Wang, Z. (2017). Deep convolutional neural networks for image classification: A comprehensive review. Neural computation, 29(9), 2352–2449.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2017). Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (pp. 1137–1149). Los Alamitos, CA: IEEE
Romero, D., Bernus, P., Noran, O., Stahre, J., & Fast-Berglund, Å. (2016, September). The operator 4.0: human cyber-physical systems & adaptive automation towards human-automation symbiosis work systems. In IFIP international conference on advances in production management systems (pp. 677–686). Cham: Springer.
Ruppert, T., Jaskó, S., Holczinger, T., & Abonyi, J. (2018). Enabling technologies for operator 4.0: A survey. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1650.
Shahroudy, A., Ng, T. T., Gong, Y., & Wang, G. (2018). Deep multimodal feature analysis for action recognition in rgb + d videos. IEEE transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(5), 1045–1058.
Shin, S. J., Kim, D. B., Shao, G., Brodsky, A., & Lechevalier, D. (2017). Developing a decision support system for improving sustainability performance of manufacturing processes. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 28(6), 1421–1440.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Sun, Y., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2014). Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1891–1898).
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., et al. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1–9).
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., & Wojna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2818–2826).
Traore, B. B., Kamsu-Foguem, B., & Tangara, F. (2018). Deep convolution neural network for image recognition. Ecological Informatics, 48, 257–268.
van Dael, M., Verboven, P., Dhaene, J., Van Hoorebeke, L., Sijbers, J., & Nicolai, B. (2017). Multisensor X-ray inspection of internal defects in horticultural products. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 128, 33–43.
Vasconez, J. P., Kantor, G. A., & Cheein, F. A. A. (2019). Human–robot interaction in agriculture: A survey and current challenges. Biosystems Engineering, 179, 35–48.
Veeriah, V., Zhuang, N., & Qi, G. J. (2015). Differential recurrent neural networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 4041–4049).
Villani, V., Pini, F., Leali, F., & Secchi, C. (2018). Survey on human–robot collaboration in industrial settings: Safety, intuitive interfaces and applications. Mechatronics, 55, 248–266.
Wang, P., Liu, H., Wang, L., & Gao, R. X. (2018a). Deep learning-based human motion recognition for predictive context-aware human–robot collaboration. CIRP Annals, 67(1), 17–20.
Wang, K. J., Nguyen, P. H., Xue, J., & Wu, S. Y. (2018b). Technology portfolio adoption considering capacity planning under demand and technology uncertainty. Journal of Manufacturing Systems., 47, 1–11.
Wilson, H. J., & Daugherty, P. R. (2018). Collaborative intelligence: Humans and AI are joining forces. Brighton: Harvard Business Review.
Yao, G., Lei, T., & Zhong, J. (2019). A review of convolutional-neural-network-based action recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters, 118, 14–22.
Zeiler, M. D., & Fergus, R. (2014, September). Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 818–833). Cham: Springer.
Zhang, J., Shao, K., & Luo, X. (2018). Small sample image recognition using improved Convolutional Neural Network. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 55, 640–647.
Zhao, Z. Q., Zheng, P., Xu, S. T., & Wu, X. (2019). Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 30(11), 3212–3232.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the comments and suggestions of the editor and the anonymous referees. This work is partially supported by Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the Grant No. MOST 107-2221-E-011-101-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Object and action classes
Appendix: Object and action classes


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, KJ., Rizqi, D.A. & Nguyen, HP. Skill transfer support model based on deep learning. J Intell Manuf 32, 1129–1146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01606-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01606-w