Abstract
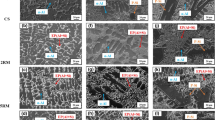
The deformation behavior of spray-formed hypereutectic aluminum–silicon alloys—AlSix (x = 18, 25, and 35 wt%)—has been studied by means of compression test at various temperatures and strain rates. The flow stress of the spray-formed Al–Si alloys increases with decreasing compression temperature and increasing strain rate. Higher silicon content in the alloys also leads to higher flow stress during deformation. The flow curves determined from the compression tests exhibit that the deformation of the materials is controlled by two competing mechanisms: strain hardening, and flow softening. Particle damage during the deformation may have an influence on the flow curves of the alloys with large silicon particles. Based on the flow curves obtained from the compression tests and knowledge of aluminum extrusion, the spray-formed hypereutectic Al–Si alloy billets have been hot extruded into wires with a high area reduction ratio around 189. Since primary silicon particles were greatly refined and uniformly distributed in the spray-formed materials, the heavy deformations of the spray-formed Al–Si alloys containing high amount of silicon were successfully performed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatch JE (1984) Aluminium, properties and physical metallurgy. American Society for Metals, Metals Park
Wu Y, Cassada WA, Lavernia EJ (1995) Metall Mater Trans 26A:1235
Yamauchi I, Ohnaka I, Kawamoto S, Fukusako T (1986) Trans Jpn Inst Met 27:195
Lavernia EJ, Wu Y (1996) Spray atomization and deposition. Wiley, New York
Grant PS (1995) Prog Mater Sci 39:497
Lawley A (2000) In: Bauckhage K, Uhlenwinkel V, Fritsching U (eds) Spray deposition and melt atomization SDMA 2000. University Bremen, Germany, p 3
Leatham AG (1999) Met Powder Rep 54:36
Grant PS (2007) Metall Mater Trans 38A:1520
Chiang CH, Tsao CYA (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 417:90
Chiang CH, Tsao CYA (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 396:263
Ha TK, Park WJ, Ahn S, Chang YW (2002) J Mater Process Technol 130–131:691
Hogg SC, Lambourne A, Ogilvy A, Grant PS (2006) Scr Mater 55:111
Johnston C, Crossley A (2004) MSTNEWS 4:14
Johnson W, Mellor PB (1973) Engineering plasticity. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, London
Dieter GE (1988) Mechanical metallurgy. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Davis JR (1993) ASM specialty handbook, aluminum and aluminum alloys. ASM International, Materials Park
McQueen HJ (1998) J Met 50(6):28
Prasad YVRK, Seshacharyulu T (1998) Int Mater Rev 43(6):243
Xia X, McQueen HJ (1997) Appl Compos Mater 4:333
Xiao BL, Fan JZ, Tian XF, Zhang WY, Shi LK (2005) J Mater Sci 40:5757. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-1292-5
Kouzeli M, Weber L, San Marchi C, Mortensen A (2001) Acta Mater 49:497
Kouzeli M, Weber L, San Marchi C, Mortensen A (2001) Acta Mater 49:3699
San Marchi C, Cao F, Kouzeli M, Mortensen A (2002) Mater Sci Eng A337:202
Tshätsch H (1987) Handbuch Umformtechnik: Arbeitsverfahren, Maschinen, Werkzeuge, Hoppenstedt-Technik-Tab.-Verl., Darmstadt
Cui C, Schulz A, Matthaei-Schulz E, Zoch HW (2009) J Mater Sci 44:4814. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3734-y
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology via the Federation of Industrial Research Associations (Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen “Otto von Guericke” e.V.; AiF) within the program AiF-191ZN at the Foundation Institute for Materials Science (IWT) in Bremen. We also would like to thank our project partners for their beneficial contributions and valuable discussions on this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, C., Schulz, A., Epp, J. et al. Deformation behavior of spray-formed hypereutectic Al–Si alloys. J Mater Sci 45, 2798–2807 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4269-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4269-y