Abstract
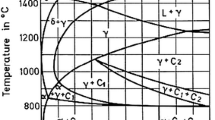
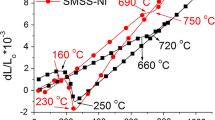
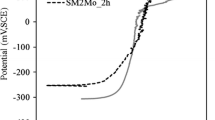
Supermartensitic steels are a new class of martensitic stainless steels developed to obtain higher corrosion resistance and better toughness through the reduction of carbon content, and addition of Ni and Mo. They were developed to more critical applications or to improve the performance obtained with conventional grades AISI 410, 420, and 431. In this study, the influences of the tempering parameters on the microstructure, mechanical properties (hardness and toughness), and sensitization of a Ti-alloyed supermartensitc stainless steel were investigated. The material showed temper embrittlement in the 400–600 °C range, as detected by low temperature (−46 °C) impact tests. The degree of sensitization measured by double loop reactivation potentiodynamic tests increased continuously with the increase of tempering temperature above 400 °C. Healing due to Cr diffusion at high tempering temperatures was not observed. Double tempered specimens showed high amounts (>20%) of reverse austenite but their toughness were similar to specimens single tempered at 625 and 650 °C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olden V, Thaulow C, Johnsen R (2008) Mater Des 29:1934
Kondo K, Ueda M, Oawa K, Amaya H, Hirata H, Takabe H (1999) In: Supermartensitic stainless steels ‘99’, Belgium, p 11
Rodrigues CAD, di Lorenzo PL, Sokolowski A, Barbosa CA, Tremiliosi-Filho G, Rollo JMAD (2006) In: 17th Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia e Ciência dos Materiais, Foz do Iguaçu, p 2695
Rodrigues CAD, Lorenzo PLD, Sokolowski A, Barbosa CA, Rollo JMAD (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 460–461:149
Pickering FB (1978) Physical metallurgy and the design of steels. Applied Science Publishers Ltd, London
ASM (1994) ASM speciality handbook. ASM International, Materials Park
Čihal V, Štefec R (2001) Electrochim Acta 46:3867
Folkhard E (1984) Welding metallurgy of stainless steels. Springer-Verlag/Wien, New York
SM A (1987) ASM metals handbook, vol 12, Fractography. ASM International, Materials Park
API Recommended Practice 571 (2003) Damage mechanisms affecting fixed equipment in the refining industry, Section 4: general damage mechanisms—all industries. Americam Petroleum Institute, Washington DC
Prohaska M, Kanduth H, Mori G, Grill R, Tischler G (2010) Corros Sci 52(5):1582
Lopez N, Cid M, Puiggali M, Azkarate I, Pelayo A (1997) Mater Sci Eng A 229(1–2):123
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Reading
Leffer B (2010) Stainless steels and their properties. Available in https://doi.org/www.outokumpu.com/files/Group/HR/Documents/STAINLESS20.pdf. Accessed 27 Nov 2010
Tavares SSM, da Silva FJ, Scandian C, da Silva GF, Abreu HFG (2010) Corros Sci 52(11):3835
Carrouge D (2011) software MAP_STEEL_AC1TEMP, Phase transformation group, University of Cambridge, Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy. https://doi.org/www.msm.cam.ac.uk/map/steel/programs/ac1new.html. Accessed 4 Apr 2011
Gesnouin C, Hazarabedian A, Bruzzoni P, Ovejero-Garcia J, Bilmes P, Llorente C (2004) Corros Sci 46:1633
Bilmes PD, Solari M, Lorente CL (2001) Mater Charact 46:285
Nakagawa N, Miyazaki T (1999) J Mater Sci 34:3901. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004626907367
Moura V, Kina AY, Tavares SSM, Lima LD, Mainier FB (2008) J Mater Sci 43:536. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1785-5
Kina AY, Tavares SSM, Souza JA, Abreu HFG (2008) J Mater Process Technol 199:391
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge the Brazilian research agencies (CAPES, FAPERJ and CNPq) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, G.F., Tavares, S.S.M., Pardal, J.M. et al. Influence of heat treatments on toughness and sensitization of a Ti-alloyed supermartensitic stainless steel. J Mater Sci 46, 7737–7744 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5753-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5753-8