Abstract
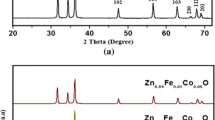
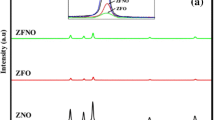
Zn1−x Fe x S (x = 0.00, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.12, and 0.15) samples have been synthesized by the chemical co-precipitation method, using ZnCl2 and Na2S as starting materials, FeCl3 as a dopant and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as capping agent. Investigations of the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of the prepared samples have been carried out. The results of X-ray diffraction (XRD), selected area electron diffraction of TEM images, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy have shown that Fe ions are incorporated into the lattice of ZnS crystallites as substitutional impurity at Zn sites in the structure without disturbing the original ZnS wurtzite structure. The average crystallite size from the XRD data and transmission electron microscopy has been found to be in the range of 4–10 nm. Magnetization behavior (i.e., M–H Characteristics) shows the evolution of ferromagnetic behavior with Fe incorporation. It has been found that there is an optimum iron ion concentration for observing the maximum magnetization. The optimum iron ion concentration has been found to be, x = 0.08 in the synthesized samples of Zn1−x Fe x S. The observed magnetization behavior has been understood as ferromagnetic behavior of Fe ions. The decrease of ferromagnetism for the higher Fe ion concentration has been discussed as a result of Fe–Fe interaction in close proximity to result antiferromagnetism for decreasing the magnetization.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy DA, Murali G, Vijaylakshmi RP, Reddy BK (2011) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in EDTA capped Cr-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 105:119–124
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2012) Doping effects of Co2+ ions on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron Eng 89:129–132
Srivastava N, Srivastava PC (2010) Synthesis and characterization of (single- and poly-) crystalline NiO nanorods by a simple chemical route. Phys E 42:2225–2230
Jayakumar OD, Gopalakrishnan IK, Kulshrestha SK (2006) On the room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn doped ZnO. Phys B 381:194–198
Zhao RB, Hou DL, Guo JM, Zhen CM, Tang GD (2010) Room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped ZnO powders. J Supercond Nov Magn 23:1261–1265
Qi J, Gao D, Zhang L, Yang Y (2010) Room-temperature ferromagnetism of the amorphous Cu-doped ZnO thin films. Appl Surf Sci 256:2507–2508
Limaye MV, Singh SB, Das R, Poddar P, Kulkarni SK (2011) Room temperature ferromagnetism in undoped and Fe doped ZnO nanorods: microwave-assisted synthesis. J Solid State Chem 184:391–400
Chen JJ, Yu MH, Zhou WL, Sun K, Wang LM (2005) Room-temperature ferromagnetic Co-doped ZnO nanoneedle array prepared by pulse laser deposition. Appl Phys Lett 87:173119
Duan LB, Zhao XR, Liu JM, Wang T, Rao GH (2010) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in lightly Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 99:679–683
Reddy DA, Murali G, Poornaprakash B, Vijaylakshmi RP, Reddy BK (2012) Effect of annealing temperature on optical and magnetic properties of Cr doped ZnS nanoparticles. Solid State Commun 152:596–602
Reddy DA, Murali G, Poornaprakash B, Vijaylakshmi RP, Reddy BK (2012) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn0.97−x Cu x Cr0.03S nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 258:5206–5211
Li Y, Cao C, Chen Z (2011) Magnetic and optical properties of Fe doped ZnS nanoparticles synthesized by microemulsion method. Chem Phys Lett 517:55–58
Ragam M, Kalaiselvan G, Arumugam S, Shankar N, Ramachandran K (2012) Room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn x Zn1−x S (x = 0.00−0.07) nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 541:222–226
Zeng X, Zang J, Huang F (2012) Optical and magnetic properties of Cr-doped ZnS nanocrystallites. J Appl Phys 111:123525
Peng D, Min LF, Cang ZC, Wu ZW, Huan Z, Gang CL, Gui ZL (2010) Structure, room-temperature magnetic and optical properties of Mn-doped TiO2 nano powders prepared by the sol–gel process. Chin Phys B 19:118102
Hou DL, Zhao RB, Meng HJ, Jia LY, Ye XJ, Zhou HJ, Li XL (2008) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Cu-doped TiO2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 516:3223–3226
Shutthanandan V, Thevuthasan S, Droubay T, Heald SM, Engelhard MH, McCready DE, Chambers SA, Nachimuthu P, Mun BS (2006) Synthesis of room-temperature ferromagnetic Cr-doped TiO2 (1 1 0) rutile single crystals using ion implantation. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 242:198–200
Cho JH, Hwang TJ, Joh YG, Kim EC, Kim DH, Lee KJ, Park HW, Ri HC, Kim JP, Cho CR (2006) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in highly-resistive Ni doped TiO2. Appl Phys Lett 88:092505
Ahmed SA (2010) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Mn doped SnO2 powders. Solid State Commun 150:2190–2193
Coey JMD, Douvalis AP, Fitzgerald CB, Venkatesan M (2004) Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl Phys Lett 84:1332–1334
Hong NH, Sakai J, Prellier W, Hassini A (2005) Transparent Cr-doped SnO2 thin films: ferromagnetism beyond room temperature with a giant magnetic moment. J Phys Condens Matter 17:1697–1702
Hong NH, Ruyter A, Prellier W, Sakai J, Huong NT (2005) Magnetism in Ni-doped SnO2 thin films. J Phys Condens Matter 17:6533–6568
Ivanov VA, Krstajic PM, Peeters FM, Fleurov V, Kikoin K (2003) On the nature of ferromagnetism in dilute magnetic semiconductors: GaAs:Mn and GaP:Mn. J Magn Magn Mater 258:237–240
Zhang J, Li XZ, Xu B, Sellmyer DJ (2005) Influence of nitrogen growth pressure on the ferromagnetic properties of Cr-doped AlN thin films. Appl Phys Lett 86:212504
Ji XH, Lau SP, Yu SF, Yang HY, Herng TS, Chen JS (2007) Ferromagnetic Cu-doped AlN nanorods. Nanotechnology 18:105601
Yang SL, Gao RS, Niu PL, Yu RH (2009) Room-temperature ferromagnetic behavior of cobalt-doped AlN nanorod arrays. Appl Phys A 96:769–774
Li H, Bao HQ, Song B, Wang WJ, Chen XL, He LJ, Yuan WX (2008) Ferromagnetic properties of Mn-doped AlN. Phys B 403:4096–4099
Li H, Song B, Bao HQ, Wang G, Wang WJ, Chen XL (2009) Ferromagnetism of Mn-doped GaN polycrystalline powders. J Magn Magn Mater 321:222–225
Suemasu T, Yamaguchi K, Tomioka H, Hasegawa F (2003) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Cr-doped GaN films grown by MOMBE on GaAs(111)A substrates. Phys Stat Sol C7:2860–2863
Tao ZK, Zang R, Cui XG, Xiu XQ, Zhang GY, Xie ZL, Gu SL, Shi Y, Zheng YD (2008) Optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped GaN diluted magnetic semiconductors prepared by MOCVD method. Chin Phys Lett 25:1476–1478
Fang X, Zhai T, Gautam UK, Li L, Wu L, Bando Y, Golberg D (2011) ZnS nanostructures: from synthesis to applications. Prog Mater Sci 56:175–287
Patel PC, Srivastava N, Srivastava PC (2013) Synthesis of wurtzite ZnS nanocrystals at low temperature. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 24:4098–4104. doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1367-z
Chawla AK, Singhal S, Nagar S, Gupta HO, Chandra R (2010) Study of composition dependent structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Cu-doped Zn1−x Cd x S nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 108:123519
Cheng W, Ma X (2009) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO. J Phys Conf Ser 152:012039
Hu YM, Li SS, Chia CH (2011) Correlation between saturation magnetization and surface morphological features in Zn1−x Cr x O thin films. Appl Phys Lett 98:052503
Wang YX, Liu H, Li ZO, Zhang XX, Zheng RK, Ringer SK (2006) Role of structural defects on ferromagnetism in amorphous Cr-doped TiO2 films. Appl Phys Lett 89:042511
Li L, Liu H, Luo X, Zhang X, Wang W, Cheng Y, Song Q (2008) Ferromagnetism in polycrystalline Cr-doped ZnO films: experiment and theory. Solid State Commun 146:420–424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, P.C., Srivastava, P.C. Fe doping in ZnS for realizing nanocrystalline-diluted magnetic semiconductor phase. J Mater Sci 49, 6012–6019 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8321-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8321-1