Abstract
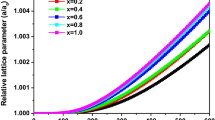
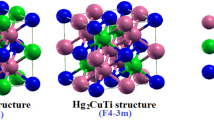
The structural, electronic, optical, and thermodynamic properties of Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N alloys were computed using first-principles calculations. The effects of exchange and correlation have been considered by means of the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) with the Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof parametrization. In addition, the Tran–Blaha-modified Becke–Johnson potential (TB-mBJ) was applied to give a better description of the band-gap energies and optical spectra. The lattice parameters, bulk modulus, and band-gap energy show nonlinear dependence on concentration x. Results for rock-salt Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N alloys show that the band gap undergoes an indirect (\(\Gamma \rightarrow X\))-to-direct (\(\Gamma \rightarrow \Gamma \)) transition at a given yttrium composition, followed by a direct (\(\Gamma \rightarrow \Gamma \))-to-indirect (\(\Gamma \rightarrow X\)) transition in a higher yttrium concentration. For wurtzite Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N alloys, the band gap presents a direct (\(\Gamma \rightarrow \Gamma \))-to-indirect (\(M\rightarrow \Gamma \)) transition at a given yttrium composition, followed by an indirect (\(M\rightarrow \Gamma \))-to-indirect (\(M\rightarrow \Sigma \)) transition in a higher yttrium concentration. The real dielectric function, imaginary dielectric function, refractive index, and extinction coefficient were calculated using the TB-mBJ potential. Using a regular solution model, slightly lower mixing enthalpies for wurtzite Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N alloys were found. The mixing enthalpy for a given concentration differs depending on structures, and on the interaction between atoms of constituents. The effect of temperature on the volume, bulk modulus, Debye temperature, and the heat capacity for Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N alloys was analyzed using the quasi-harmonic Debye model. Results show that the heat capacity is fairly sensitive to composition as temperature increases.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vurgaftman I, Meyer JR, Ram-Mohan LR (2001) Review: Band parameters for IIIV compound semiconductors and their alloys. J Appl Phys 89:5815–5875
Adachi S (2009) Properties of semiconductor alloys: group-IV, IIIV and IIVI semiconductors., Wiley series in materials for electronic and optoelectronic applicationsWiley, West Sussex
Glen A, Slack RA, Tanzilli R, Pohl O, Vandersande JW (1987) The intrinsic thermal conductivity of AIN. J Phys Chem Solids 48:641–647
Virkar AV, Jackson TB, Cutler RA (1989) Thermodynamic and kinetic effects of oxygen removal on the thermal conductivity of aluminum nitride. J Am Ceram Soc 72:2031–2042
Shaffer PTB, Mroz TJ (1991) Aluminum Nitride. Advanced Refractory Technology Inc, Buffalo
Mroz TJ (1992) Annual materials review: aluminum nitride. Am Ceram Soc Bull 71:782–786
Weimer AW, Cochran GA, Eisman GA, Henley JP, Hook BD, Mills LK, Guiton TA, Knudsen AK, Nicholas NR, Volmering JE, Moor WG (1994) Rapid process for manufacturing Aluminum Nitride powder. J Am Ceram Soc 77:3–18
Vollstadt H, Ito E, Akaishi M, Akimoto S, Fukunaga O (1990) High pressure synthesis of rock salt type of AlN. Proc Jpn Acad B 66:7–9
Du L, Edgar JH, Peascoe-Meisner R, Gong Y, Bakalova S, Kuball M (2010) Sublimation crystal growth of yttrium nitride. J Cryst Growth 312:2896–2903
Zoita CN, Braic M, Braic V (2011) Structural, optical and electronic properties of In\(_{1-x}\)Y\(_x\)N thin films. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 6:1877–1886
Henkes AE, Vasquez Y, Schaak RE (2007) Converting metals into phosphides: a general strategy for the synthesis of metal phosphide nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 129:1896–1897
Iga K, Kinoshita S (1996) Process technology for semiconductor lasers. Crystal Growth and Microprocesses, vol 30., Springer Series in Materials ScienceSpringer, Berlin
Quillec M (1996) Materials for optoelectronics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Mishra UK, Singh J (2008) Semiconductor device physics and design. Springer, Netherlands
Guisbiers G, Wautelet M, Buchaillot L (2009) Phase diagrams and optical properties of phosphide, arsenide, and antimonide binary and ternary III-V nanoalloys. Phys Rev B 79:155426(1)–155426(8)
Kuykendall T, Ulrich P, Aloni S, Yang P (2007) Complete composition tunability of InGaN nanowires using a combinatorial approach. Nat Mater 6:951–956
Lu Ch-H, Li Y-Ch, Chen Y-H, Tsai S-Ch, Lai Y-L, Li Y-L, Liu Ch-P (2013) Output power enhancement of InGaN/GaN based green light-emitting diodes with high-density ultra-small In-rich quantum dots. J Alloys Compd 555:250–254
Zhang CS, Yan MF, You Y, Chen HT, Zhang FY, Bai B, Chen L, Long Z, Li RW (2014) Stability and properties of alloyed \(\varepsilon \)-(Fe\(_{1-x}\)M\(_x\))3N nitrides (M = Cr, Ni, Mo, V Co, Nb, Mn, Ti and Cu): A first-principles calculations. J Alloys Compd 615:854–862
Zukauskaite A, Wingqvist G, Palisaitis J, Jensen J, Persson PO, Matloub R, Muralt P, Kim Y, Birch J, Hultman L (2012) Microstructure and dielectric properties of piezoelectric magnetron sputtered w-Sc\(_x\)N thin films. J Appl Phys 111:093527(1)–093527(7)
Ding XZ, Zeng XT (2005) Structural mechanical and tribological properties of CrAlN coatings deposited by reactive unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf Coat Technol 200:1372–1376
Alling B, Marten T, Abrikosov IA, Karimi A (2007) Comparison of thermodynamic properties of cubic Cr\(_{1-x}\)N from first-principles calculations. J Appl Phys 102:044314(1)–044314(8)
Alling B, Ruban AV, Karimi A, Peil OE, Simak SI, Hultman L, Abrikosov IA (2007) Mixing and decomposition thermodynamics of c-Ti\(_{1-x}\)N from first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 75:045123(1)–045123(13)
Mayrhofer PH, Sonnleitner D, Bartosik M, Holec D (2014) Structural and mechanical evolution of reactively and non-reactively sputtered ZrAlN thin films during annealing. Surf Coat Technol 244:52–56
Žukauskaitė A, Tholander CH, Palisaitis J, Persson P, Darakchieva V, Sedrine NB, Tasnádi F, Alling B, Birch J, Hultman L (2012) Y\(_x\)N thin films. J Phys D Appl Phys 45:422001(1)–422001(5)
Sedrine NB, Zukauskaite A, Birch J, Hultman L, Darakchieva V (2013) Bandgap engineering and optical constants of Y\(_x\)N alloys. Jpn J Appl Phys 52:08JM02(1)–08JM02(3)
Hohenberg P, Kohn W (1964) Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys Rev 136:B864–B871
Kohn W, Sham LJ (1965) Self-Consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev 140:A1133–A1138
Zunger A, Wei SH, Ferreira LG, Bernard JE (1990) Special quasirandom structures. Phys Rev Lett 65:353–356
Rashid M, Noor NA, Sabir B, Ali S, Sajjad M, Hussain F, Khan NU, Amin B, Khenata R (2014) Ab-initio study of fundamental properties of ternary ZnO\(_{1-x}\)S\(_x\) alloys by using special quasi-random structures. Comp Mater Sci 91:285–291
Dong L, Alpay SP (2011) Theoretical analysis of the crystal structure, band-gap energy, polarization, and piezoelectric properties of ZnO-BeO solid solutions. Phys Rev B 84:035315(1)–035315(8)
Dong L, Alpay SP (2012) Polarization, piezoelectric properties, and elastic coefficients of In\(_x\)N solid solutions from first principles. J Mater Sci 47:75877593
Vegard L (1921) Die Konstitution der Mischkristalle und die Raumfllung der Atome. Z Phys 5:17–26
Denton AR, Ashcroft NW (1991) Vegards law. Phys Rev A 43:3161–3164
Jobst B, Hommel D, Lunz U, Gerhard T, Landwehr G (1996) \(E_0\) band-gap energy and lattice constant of ternary Zn\(_{1-x}\)Mg\(_x\)Se as functions of composition. Appl Phys Lett 69:97–99
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Madsen GKH, Kvasnicka D, Luitz J (2001) WIEN2k an augmented plane wave plus local orbital program for calculating crystal properties. Vienna University of Technology, Vienna
Perdew JP, Burke K, Emzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Tran F, Blaha P (2009) Accurate band gaps of semiconductors and insulators with a semilocal exchange-correlation potential. Phys Rev Lett 102:226401(1)–226401(4)
Araujo RB, de Almeida JS, Ferreira da Silva A (2013) Electronic properties of III-nitride semiconductors: A first-principles investigation using the Tran-Blaha modified Becke-Johnson potential. J Appl Phys 114:183702(1)–183702(6)
Murnaghan FD (1944) The compressibility of media under extreme pressures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 30(9):244–247
Yu PY, Cardona M (2010) Fundamental of semiconductors: physics and materials properties, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin
Otero-de-la-Roza A, Luaña V (2011) Gibbs2: A new version of the quasi-harmonic model code. I. Robust treatment of the static data. Comput Phys Commun 182:1708–1720
Otero-de-la-Roza A, Lua\(\tilde{n}\)a V (2011) Equations of state and thermodynamics of solids using empirical corrections in the quasiharmonic approximation. Phys Rev B 84:184103(1)–184103(20)
Pankovc JI (1971) Optical processes in semiconductors. Solid state physical electronics series. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Penn DR (1962) Wave-number-dependent dielectric function of semiconductors. Phys Rev 128:2093–2097
Mubarak AA (2014) Ab initio study of the structural, electronic and optical properties of the fluoropervskite SrXF\(_3\) Li, Na, K and Rb) compounds. Comp Mater Sci 81:478–482
Li D, Zhang X, Zhu Z, Zhang H (2011) First-principles calculation of structural, electronic, and optical properties of zinc-blende Al\(_x\)Ga\(_{1-x}\)N alloys. Sol Sta Sci 13:1731–1734
Othman M, Kasap E, Korozlu N (2010) The structural, electronic and optical properties of In\(_x\)P alloys. Phys B 405:23572361
Swalin RA (1972) Thermodynamics of solids, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
López-Pérez W, Simon-Olivera N, González-Hernández R (2013) Theoretical prediction of structural parameters, band-gap energies, and mixing enthalpies of Sc\(_{1-x}\)In\(_x\)As alloys. J Mater Sci 48:4899–4907
Phillips JM (1995) Substrate selection for thin-film growth. MRS Bull 20:35–39
Khare N (2005) Handbook of High-Temperature Superconductor Electronics. Marcel Deker Inc, New York
Höglund C, Birch J, Alling B, Bareño J, Czigány Z, Persson PO, Wingqvist G, Zukauskaite A, Hultman L (2010) Wurtzite structure Sc\(_{1-x}\)N solid solution films grown by reactive magnetron sputter epitaxy: structural characterization and first-principles calculations. J Appl Phys 107:123515(1)–123515(7)
Höglund C, Bareño J, Birch J, Alling B, Czigány Z, Hultman L (2009) Cubic Sc\(_{1-x}\)N solid solution thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputter epitaxy onto ScN(111). J Appl Phys 105:113517(1)–113517(7)
Alling B, Odn M, Hultman L, Abrikosov IA (2009) Pressure enhancement of the isostructural cubic decomposition in Ti\(_{1-x}\)N. Appl Phys Lett 95:181906(1)–181906(3)
Haddou A, Khachai H, Khenata R, Litimein F, Bouhemadou A, Murtaza G, Alahmed Z, Bin-Omran S, Abbar B (2013) Elastic, optoelectronic, and thermal properties of cubic CSi\(_2\)N\(_4\): an ab initio study. J Mater Sci 48:8235–8243
Hacini K, Ghemid S, Meradji H, El Haj Hassan F (2011) Theoretical study of structural, electronic and thermal properties of Zn\(_{1-x}\)Be\(_x\)S ternary alloy. Comp Mat Sci 50:3080–3084
Acknowledgements
This work has been carried out with the financial support of Universidad del Norte and Colciencias (Administrative Department of Science, Technology and Research of Colombia) under “Convocatoria 658 - Convocatoria para proyectos de investigación en ciencias básicas año 2014.” The calculations reported in this paper were performed using the machines of the computational laboratory at the Universidad del Norte. The authors thank DIDI office for their useful management in the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramírez-Montes, L., López-Pérez, W., González-García, A. et al. Structural, optoelectronic, and thermodynamic properties of Y\(_x\)Al\(_{1-x}\)N semiconducting alloys. J Mater Sci 51, 2817–2829 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9590-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9590-z