Abstract
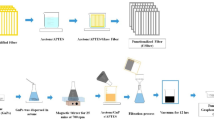
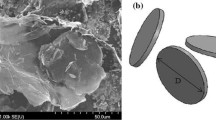
We investigated the effect of graphene nanoplatelets (GnPs) with two different lateral dimensions on the morphology, flexural, and thermo-mechanical properties of multiscale GnPs/glass fiber/epoxy composites. First, 3 and 5 wt% of GnP-C750 (<1 µm in diameter) and GnP-5 (5 µm in diameter) were individually integrated into epoxy suspension through a combination of calendaring and sonication processes. The GnPs/glass fiber/epoxy composites were then fabricated by incorporating glass fibers into the GnPs/epoxy mixture. Results showed that the flexural modulus of the GnPs/glass fiber/epoxy composites was improved by 11.5 and 26.3 % with the addition of 5 wt% GnP-C750 and GnP-5, respectively. At the same filler content, the storage modulus of the glass/epoxy composites incorporated with GnP-C750 and GnP-5 at 30 °C was enhanced by 10.2 and 28.2 %, respectively. The flexural strength of the 3 wt% GnP-5-reinforced glass fiber/epoxy composite is 16.2 % higher than that of the glass fiber/epoxy composite. The dispersion results of GnPs in the composites and the interfacial interactions between fibers and modified matrix were evaluated by scanning electron microscopy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soutis C (2005) Fibre reinforced composites in aircraft construction. Prog Aero Sci 41:143–151
Zhang J, Ju S, Jiang D, Peng HX (2013) Reducing dispersity of mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy composites by introducing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos B 54:371–376
Loyola BR, Saponara VL, Loh KJ (2010) In situ strain monitoring of fiber-reinforced polymers using embedded piezoresistive nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45:6786–6798. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4775-y
Garg M, Sharma S, Mehta R (2015) Pristine and amino functionalized carbon nanotubes reinforced glass fiber epoxy composites. Compos A 76:92–101
Li J, Wu Z, Huang C, Li L (2014) Multiscale carbon nanotube-woven glass fiber reinforced cyanate ester/epoxy composites for enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Compos Sci Technol 104:81–88
Umboh MK, Adachi T, Oishi K, Higuchi M, Major Z (2013) Mechanical properties of nano-silica particulate-reinforced epoxy composites considered in terms of crosslinking effect in matrix resins. J Mater Sci 48:5148–5156. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7300-2
Schilde C, Schlömann M, Overbeck A, Linke S, Kwade A (2015) Thermal, mechanical and electrical properties of highly loaded CNT-epoxy composites-A model for the electric conductivity. Compos Sci Technol 117:183–190
Zaman I, Phan TT, Kuan HC, Meng QS, La LTB, Lee L, Youssf O, Ma J (2011) Epoxy/graphene platelets nanocomposites with two levels of interface strength. Polymer 52:1603–1611
Ahmadi-Moghadam B, Sharafimasooleh M, Shadlou S, Taheri F (2015) Effect of functionalization of graphene nanoplatelets on the mechanical response of graphene/epoxy composites. Mater Des 66:142–149
Ahmadi-Moghadam B, Taheri F (2014) Effect of processing parameters on the structure and multi-functional performance of epoxy/GNP-nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 49:6180–6190. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8332-y
Rahman MM, Zainuddin S, Hosur MV, Malone JE, Salam MBA, Kumar A, Jeelani S (2012) Improvements in mechanical and thermo-mechanical properties of e-glass/epoxy composites using amino functionalized MWCNTs. Compos Struct 94:2397–2406
King JA, Klimek DR, Miskioglu I, Odegard GM (2013) Mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites. Appl Polym Sci 128(6):4217–4223
Kim M, Park YB, Okoli OI, Zhang C (2009) Processing, characterization, and modeling of carbon nanotube-reinforced multiscale composites. Compos Sci Technol 69:335–342
Chatterjee S, Wang JW, Kuo WS, Tai NH, Salzmann C, Li WL, Hollertz R, Nüesch FA, Chu BTT (2012) Mechanical reinforcement and thermal conductivity in expanded graphene nanoplatelets reinforced epoxy composites. Chem Phys Lett 531:6–10
Bozkurt E, Kaya E, Tanoğlu M (2007) Mechanical and thermal behavior of non-crimp glass fiber reinforced layered clay/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 67:3394–3403
Xu Y, Hoa SV (2008) Mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy/clay nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 68:854–861
Norkhairunnisa M, Azhar AB, Shyang CW (2007) Effects of organo-montmorillonite on the mechanical and morphological properties of glass/epoxy fiber composites. Polym Int 56:512–517
Lee JH, Rhee KY, Park SJ (2011) Silane modification of carbon nanotubes and its effects on the material properties of carbon/CNT/epoxy three-phase composites. Compos A 42:478–483
Ruoff RS, Lorents DC (1995) Mechanical and thermal properties of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 33(7):925–930
Yu MF, Lourie O, Dyer MJ, Moloni K, Kelly TF, Ruoff RS (2000) Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 287(5453):637–640
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Hiura H, Bennett JW, Ghaemi HF, Thio T (1996) Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotube. Nature 382:54–56
Chandrasekaran VCS, Advani SG, Santare MH (2010) Role of processing on interlaminar shear strength enhancement of epoxy/glass fiber/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid composites. Carbon 48:3692–3699
Kim MT, Rhee KY, Lee JH, Hui D, Lau AKT (2011) Property enhancement of a carbon fiber/epoxy composite by using carbon nanotubes. Compos B 42:1257–1261
Li M, Gu Y, Liu Y, Li Y, Zhang Z (2013) Interfacial improvement of carbon fiber/epoxy composites using a simple process for depositing commercially functionalized carbon nanotubes on the fibers. Carbon 52:109–121
Lee C, Wei X, Kysar JW, Hone J (2008) Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321:385–388
Du X, Skachko I, Barker A, Andrei EY (2008) Approaching ballistic transport in suspended graphene. Nat Nanotechnol 3:491–495
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183–191
Wang FZ, Drzal LT, Qin Y, Huang ZX (2015) Multifunctional graphene nanoplatelets/cellulose nanocrystals composite paper. Compos B 79:521–529
Wang FZ, Drzal LT, Qin Y, Huang ZX (2015) Processing and characterization of high content multi-layer graphene/epoxy composites with high electrical conductivity. Polym Compos. doi:10.1002/pc.23487
Li B, Zhong WH (2011) Review on polymer/graphite nanoplatelet nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 46:5595–5614. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5572-y
Wang FZ, Drzal LT, Qin Y, Huang ZX (2015) Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites. J Mater Sci 50(3):1082–1093. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8665-6
Wang Y, Yu J, Dai W, Song Y, Wang D, Zeng L, Jiang N (2015) Enhanced thermal and electrical properties of epoxy composites reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Polym Compos 36:556–565
Park YT, Qian Y, Chan C, Suh T, Nejhad MG, Macosko CW, Stein A (2015) Epoxy toughening with low graphene loading. Adv Funct Mater 25(4):575–585
Rafiee MA, Rafiee J, Wang Z, Song H, Yu ZZ, Koratkar N (2009) Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocomposites at low graphene content. ACS Nano 3:3884–3890
Gojny FH, Wichmann MHG, Fiedler B, Bauhofer W, Schulte K (2005) Influence of nano-modification on the mechanical and electrical properties of conventional fiber-reinforced composites. Compos A 36:1525–1535
Zhu J, Imam A, Crane R, Lozano K, Khabashesku VN, Barrera EV (2007) Processing a glass fiber reinforced vinyl ester composite with nanotube enhancement of interlaminar shear strength. Compos Sci Technol 67(7):1509–1517
Zhang J, Qipeng G, Huson M, Slota J, Fox BL (2010) Interphase study of thermoplastic modified epoxy matrix composites: phase behaviour around a single fibre influenced by heating rate and surface treatment. Compos A 41(6):787–794
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Rich Mike, Brian Rook, and Per Askeland, research assistants in Composite Materials and Structures Center (CMSC), for their training and guidance. We would like to acknowledge China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Drzal, L.T., Qin, Y. et al. Size effect of graphene nanoplatelets on the morphology and mechanical behavior of glass fiber/epoxy composites. J Mater Sci 51, 3337–3348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9649-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9649-x