Abstract
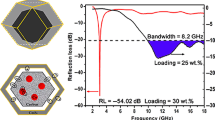
A growing number of core–shell structured microwave absorbents have been reported; nevertheless, there are few studies accessible about one-dimensional core–shell electromagnetic nanocomposites as microwave absorption materials. In this work, we have developed two kinds of novel electromagnetic nanocomposites, namely yolk–shell Fe3O4@void@SiO2 nanochains and Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains. Their components and morphologies have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectra, scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms have demonstrated their specific surface areas and porosity, and the magnetic properties have been recorded by the vibrating sample magnetometer. Investigation of microwave absorbing properties manifests that Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains have stronger absorption capability and broader effective absorption bandwidth than Fe3O4@void@SiO2 nanochains, which is caused by the introduction of polypyrrole shells, giving rise to the addition of conductive loss and the enhancement of dipole polarizations, interfacial polarizations, multiple reflection and absorption. Specifically, the minimum reflection loss value is − 54.2 dB (17.70 GHz) and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth can reach 5.90 GHz (11.49–17.39 GHz); thus, Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains will become promising microwave absorption candidates. This research once more demonstrates that necklace-like core–shell magnetic–dielectric complex benefit to enhancement of microwave absorption performance, and establishes a good foundation for exploiting the high-effective microwave absorbing materials.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Man HS, Koo CM, Gogotsi Y (2016) Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304):1137–1140
Herzer G (1996) Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. J Magn Magn Mater s 157–158(5):133–136
Chen ZP, Xu C, Ma CQ, Ren WC, Cheng HM (2013) Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 25(9):1296–1300
Wang GZ, Gao Z, Tang SW, Chen CQ, Duan FF, Zhao SC, Lin SW, Feng YH, Zhou L, Qin Y (2012) Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12):11009–11017
Watts CM, Liu XL, Padilla WJ (2012) Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater 24(23):OP98–OP120
You WB, Bi H, She W, Zhang Y, Che RC (2017) Dipolar-distribution cavity γ-Fe2O3@C@α-MnO2 nanospindle with broadened microwave absorption bandwidth by chemically etching. Small 13(5):1602779
Zhang HX, Jia ZR, Feng AL, Zhou ZH, Chen L, Zhang CH, Liu XH, Wu GL (2020) In situ deposition of pitaya-like Fe3O4@C magnetic microspheres on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for electromagnetic wave absorber. Compos Part B 199:108261
Liu QH, Cao Q, Bi H, Liang CY, Yuan KP, She W, Yang YJ, Che RC (2016) CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@ Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv Mater 28(3):486–490
Chen C, Liu QH, Bi H, You WB, She W, Che RC (2016) Fabrication of hierarchical TiO2 coated Co20Ni80 particles with tunable core sizes as high-performance wide-band microwave absorbers. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(38):26712–26718
Chen YJ, Gao P, Wang RX, Zhu CL, Wang LJ, Cao MS, Jin HB (2009) Porous Fe3O4/SnO2 core/shell nanorods: synthesis and electromagnetic properties. J Phys Chem C 113(23):10061–10064
Du YC, Liu WW, Qiang R, Wang Y, Han XJ, Ma J, Xu P (2014) Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core–shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6(15):12997–13006
Liu JW, Che RC, Chen HJ, Zhang F, Xia F, Wu QS, Wang M (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8(8):1214–1221
Zhao B, Guo XQ, Zhao WY, Deng JS, Shao G, Fan BB, Bai ZY, Zhang R (2016) Yolk–shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8(42):28917–28925
Zhao B, Shao G, Fan BB, Zhao WY, Zhang R (2015) Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core–shell structure. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(4):2531–2539
Ding D, Wang Y, Li XD, Qiang R, Xu P, Chu WL, Han XJ, Du YC (2017) Rational design of core-shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 111:722–732
Zhou WC, Hu XJ, Bai XX, Zhou SY, Sun CH, Yan J, Chen P (2011) Synthesis and electromagnetic, microwave absorbing properties of core-shell Fe3O4-poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Inter 3(10):3839–3845
Feng JT, Hou YH, Wang YC, Li LC (2017) Synthesis of hierarchical ZnFe2O4@SiO2@RGO core-shell microspheres for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9(16):14103–14111
Han R, Li W, Pan WW, Zhu MG, Zhou D, Li FS (2014) 1D Magnetic materials of Fe3O4 and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption fabricated by electrospinning method. Sci Rep 4(1):7493
Zhang XF, Li YX, Liu RG, Rao Y, Rong HW, Qin GW (2016) High-magnetization FeCo nanochains with ultrathin interfacial gaps for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption at gigahertz. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8(5):3494–3498
Hou Y, Cheng LF, Zhang YN, Yang Y, Deng CR, Yang ZH, Chen Q, Wang P, Zheng LX (2017) Electrospinning of Fe/SiC hybrid fibers for highly efficient microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9(8):7265–7271
Li N, Huang GW, Li YQ, Xiao HM, Feng QP, Hu N, Fu SY (2017) Enhanced microwave absorption performance of coated carbon nanotubes by optimizing the Fe3O4 nanocoating structure. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9(3):2973–2983
Kong LB, Li ZW, Liu L, Huang R, Abshinova M, Yang ZH, Tang CB, Tan PK, Deng CR, Matitsine S (2013) Recent progress in some composite materials and structures for specific electromagnetic applications. Int Mater Rev 58(4):203–259
Chiu SC, Yu HC, Li YY (2010) High electromagnetic wave absorption performance of silicon carbide nanowires in the gigahertz range. J Phys Chem C 114(4):1947–1952
Liu J, Cao MS, Luo Q, Shi HL, Wang WZ, Yuan J (2016) Electromagnetic property and tunable microwave absorption of 3D nets from nickel chains at elevated temperature. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8(34):22615–22622
Qiao MT, Lei XF, Ma Y, Tian LD, He XW, Su KH, Zhang QY (2017) Application of yolk-shell Fe3O4@N-doped carbon nanochains as highly effective microwave-absorption material. Nano Res 11(3):1500–1519
Ma ML, Li WT, Tong ZY, Yang YY, Ma Y, Cui ZH, Wang RZ, Lu P, Huang WB (2020) 1D flower-like Fe3O4@SiO2@MnO2 nanochains inducing RGO self-assembly into aerogels for high-efficient microwave absorption. Mater Des 188:108462
Guo J, Song HX, Liu H, Luo CJ, Ren YR, Ding T, Khan MA, Young DP, Liu XY, Zhang X, Kong J, Guo ZH (2017) Polypyrrole-interface-functionalized nano-magnetite epoxy nanocomposites as electromagnetic wave absorbers with enhanced flame retardancy. J Mater Chem C 5:5334–5344
Liu YL, Li CM, Zhang HT, Fan XL, Liu Y, Zhang QY (2015) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of highly monodisperse water-dispersible hollow magnetic microspheres and construction of photonic crystals. Chem Eng J 259:779–786
Ma ML, Zhang QY, Dou JB, Zhang HP, Yin DZ, Geng WC, Zhou YY (2012) Fabrication of one-dimensional Fe3O4/P (GMA–DVB) nanochains by magnetic-field-induced precipitation polymerization. J Colloid Interf Sci 374(1):339–344
Ma ML, Zhang QY, Dou JB, Zhang HP, Yin DZ, Chen SJ (2012) Fabrication of 1D Fe3O4/P(NIPAM-MBA) thermosensitive nanochains by magnetic-field-induced precipitation polymerization. Colloid Polym Sci 290(12):1207–1213
Qiao MT, Lei XF, Ma Y, Tian LD, Su KH, Zhang QY (2016) Well-defined core–shell Fe3O4@polypyrrole composite microspheres with tunable shell thickness: synthesis and their superior microwave absorption performance in the Ku band. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(22):6263–6275
Yang M, Ma J, Niu Z, Dong X, Xu H, Meng Z, Jin Z, Lu Y, Hu Z, Yang Z (2005) Synthesis of spheres with complex structures using hollow latex cages as templates. Adv Funct Mater 15(9):1523–1528
Li GL, Liu G, Kang ET, Neoh KG, Yang X (2008) pH-responsive hollow polymeric microspheres and concentric hollow silica microspheres from silica-polymer core−shell microspheres. Langmuir 24(16):9050–9055
Li GL, Kang ET, Neoh KG, Yang X (2009) Concentric hollow nanospheres of mesoporous silica shell-titania core from combined inorganic and polymer syntheses. Langmuir 25(8):4361–4364
Qiao MT, Lei XF, Ma Y, Tian LD, Wang WB, Su KH, Zhang QY (2017) Facile synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption performance for porous core-shell Fe3O4@MnO2 composite microspheres with lightweight feature. J Alloy Compd 693:432–439
Liu W, Tan SJ, Yang ZH, Ji GB (2018) Enhanced low-frequency electromagnetic properties of MOF-derived cobalt through interface design. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(37):31610–31622
Zhao B, Song Q, Liu W, Sun Y (2014) Overview of dual-active-bridge isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter for high-frequency-link power-conversion system. IEEE T Power Electr 29(8):4091–4106
Ma F, Qin Y, Li YZ (2010) Enhanced microwave performance of cobalt nanoflakes with strong shape anisotropy. Appl Phys Lett 96(20):3262
Zhao B, Zhao WY, Shao G, Fan BB, Zhang R (2015) Morphology-control synthesis of a core-shell structured NiCu alloy with tunable electromagnetic-wave absorption capabilities. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(23):12951–12960
Fleming J, Koman R (1998) Web navigation: designing the user experience. O'reilly Sebastopol, CA
Zhou XF, Jia ZR, Feng AL, Wang KK, Liu XH, Chen L, Cao HJ, Wu GL (2020) Dependency of tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance on morphology-controlled 3D porous carbon fabricated by biomass. Compos Commun 21:100404
Xu W, Pan YF, Wei W, Wang GS (2018) Nanocomposites of oriented nickel chains with tunable magnetic properties for high-performance broadband microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Inter 1(3):1116–1123
He S, Wang GS, Lu C, Liu J, Wen B, Liu H, Guo L, Cao MS (2013) Enhanced wave absorption of nanocomposites based on the synthesized complex symmetrical CuS nanostructure and poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Mater Chem A 1(15):4685–4692
Zhang WL, Jiang D, Wang X, Hao BN, Liu YD, Liu J (2017) Growth of polyaniline nanoneedles on MoS2 nanosheets, tunable electro-response and electromagnetic wave attenuation analysis. J Phys Chem C 121(9):4989–4998
Song NN, Yang HT, Liu HL, Ren X, Ding HF, Zhang XQ, Cheng ZH (2013) Exceeding natural resonance frequency limit of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles via superparamagnetic relaxation. Sci Rep 3(1):3161
Lv HL, Ji GB, Liu W, Zhang HQ, Du YW (2015) Achieving hierarchical hollow carbon@Fe@Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight feature. J Mater Chem C 3(39):10232–10241
Lv HL, Zhang HQ, Zhao J, Ji GB, Du YW (2016) Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures. Nano Res 9(6):1813–1822
Zhou XF, Jia ZR, Feng AL, Qu SL, Wang XA, Liu XH, Wang BB, Wu GL (2020) Synthesis of porous carbon embedded with NiCo/CoNiO2 hybrids composites for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J Colloid Interf Sci 575:130–139
Tian CH, Du YC, Xu P, Qiang R, Wang Y, Ding D, Xue JL, Ma J, Zhao HT, Han XJ (2015) Constructing uniform core–shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(36):20090–20099
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51433008), National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Grant No. 51503116) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3102017jc01001). The authors thank the Analytical & Testing Center of Northwestern Polytechnical University for the SEM and TEM test.
Funding
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling Editor: Dale Huber.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, M., Wei, D., He, X. et al. Novel yolk–shell Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains toward microwave absorption application. J Mater Sci 56, 1312–1327 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05313-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05313-y