Abstract
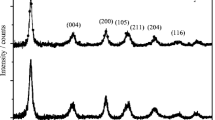
0.5 wt% Pd-doped titanium oxide thin films were obtained by dip-coating on silicon substrates. The films were compacted by annealing in air at 300 and 500 °C. Temperature dependent electrical conductivity measurements were performed in the temperature range 373–623 K, in different environments (air, methane, acetone, ethanol, formaldehyde and liquefied petroleum gas), to test the films sensing gas properties. Formaldehyde was found to be the test gas that produces the most significant changes in the electrical conductivity of the studied films. This was the reason why it was chosen to investigate its effect on their electrical conductivity. A model was proposed, the model of the potential fluctuations at grain boundaries. A comparison between some parameters obtained in the proposed model was performed as a function of annealing temperature, and as a function of gas atmosphere. The values of the mean barrier height and the standard deviation were estimated to range between 0.336–0.588 eV and 0.175–0.199 eV, respectively. It was found that formaldehyde leads to a rather sharp decrease in the values of the barrier height and the standard deviation, and to an increase in the conductivity. We have observed the best sensing gas performance for the films annealed at 300 °C, comparing to their counterparts annealed at 500 °C, explained by the lowest values of the barrier energy height and the standard deviation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Formaldehyde Epidemiology, Toxicology and Environmental Group, Formaldehyde and Facts About Health Effects (2002). http://www2.dupont.com/Plastics/en_US/assets/downloads/processing/FETEG_Facts.pdf
L. Feng, Y.J. Liu, X.D. Zhou, J.M. Hu, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284, 378 (2005)
O. Hernandez, L. Rhomberg, K. Hogan, C. Siegel-Scott, D. Lai, G. Grindstaff, M. Henry, J.A. Cotruvo, J. Hazard. Mater. 39(2), 161 (1994)
J. Flueckiger, F.K. Ko, K.C. Cheung, Sensors 9, 9196 (2009)
N. Iftimie, M. Crisan, A. Braileanu, D. Crisan, A. Nastuta, G.B. Rusu, P.D. Popa, D. Mardare, J. Optoelectron. Adv. M. 10, 9–2363 (2008)
H. Tang, K. Prasad, R. Sanjinès, F. Lévy, Sensor Actuat. B 26–27, 71 (1995)
F. Cosandey, G. Skandan, A. Singhal, JOM-e, 52(10) (2000), http://www.tms.org/pubs/journals/JOM/0010/Cosandey/Cosandey-0010.html
W.K. Choi, S.K. Song, J.S. Cho, Y.S. Yoon, D. Choi, H.-J. Jung, S.K. Koh, Sensor Actuat. B 40, 21 (1997)
N. Yamazoe, Sensor Actuat. B 5, 7 (1991)
A. Yildiz, S.B. Lisesivdin, M. Kasap, D. Mardare, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 4944 (2008)
A. Yildiz, S.B. Lisesivdin, M. Kasap, D. Mardare, Physica B 404, 1423 (2009)
A. Yildiz, S.B. Lisesivdin, M. Kasap, D. Mardare, J. Mater, Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 692 (2010)
A. Yildiz, N. Serin, M. Kasap, T. Serin, D. Mardare, J. Alloys Compd. 493, 227 (2010)
T. Serin, A. Yildiz, N. Serin, N. Yıldırım, F. Özyurt, M. Kasap, J. Electron. Mater. 39, 1152 (2010)
A. Yildiz, A.A. Alsaç, T. Serin, N. Serin, J. Electron. Mater (2011). doi:10.1007/s10854-010-0228-2
A. Yildiz, F. Iacomi, D. Mardare, J. Appl. Phys 108, 083701 (2010)
H.J. Höfler, H. Hahn, R.S. Averback, Defect Diffus. Forum 75, 195 (1991)
J.Y.W. Seto, J. Appl. Phys 46, 5247 (1975)
J.H. Werner, Solid State Phenom. 37, 213 (1994)
D. Crisan, N. Dragan, M. Crisan, M. Raileanu, A. Braileanu, M. Anastasescu, A. Ianculescu, D. Mardare, D. Luca, V. Marinescu, A. Moldovan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 2548 (2008)
D. Mardare, G.I. Rusu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 28–30, 1395 (2010)
T. Wolkenstein, Electronic Process on Semiconductor Surfaces During Chemisorption (Consultats Bureau, New York, 1991)
S. Seeger, R. Mientus, J. Röhrich, E. Strub, W. Bohne, K. Ellmer, Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 218 (2005)
F. Kopnov, A. Yoffe, G. Leitus, R. Tenne, Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 243, 1229 (2006)
J.R. Ares, A. Pascual, I.J. Ferrer, C.R. Sanchez, Thin Solid Films 451, 233 (2004)
Acknowledgments
D. Mardare acknowledges the financial support from the grants PCCE-ID_76 and 12-128/2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yildiz, A., Crisan, D., Dragan, N. et al. Effect of formaldehyde gas adsorption on the electrical conductivity of Pd-doped TiO2 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 22, 1420–1425 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0324-y