Abstract
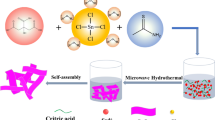
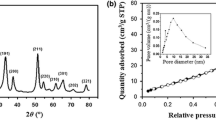
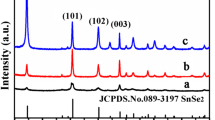
The SnO2 nanoflakes were prepared by simple one-step facile microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis. The as-prepared SnO2 nanoflakes were systematically studied using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM). From FE-SEM images seen that SnO2 nanoparticles are stocked between the SnO2 nanoflakes and also, pores are existed between the SnO2 flakes. TEM results reveal that the SnO2 nanoflakes were formed due to the self-assembly of very thin SnO2 nanosheets and also pores coexist between the sheets. The prepared SnO2 nanoflakes are used as an anode material for the fabrication of lithium-ion battery (LIB). The SnO2 nanoflakes electrode was found to show a stable reversible lithium storage capacity of 567 mA h g−1 even at a current density of 500 mA g−1 after 50 cycles. The enhanced properties in terms of reversible capacity and cycle ability of the SnO2 nanoflakes as an anode material are owing to its porous nature, which facilitates more lithium storage and interconnection between the flakes and particles enhance the kinetic properties of the electrode material. Hence, the developed SnO2 nanoflakes by simple one-step facile microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis can be a stable and high rate anode material for lithium-ion batteries.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Kang, G. Ceder, Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging. Nature 458, 19–24 (2009)
Y. Yao, M.T. Mc Dowell, I. Ryu, H. Wu, N. Liu, L. Hu, W.D. Nix, Y. Cui, Interconnected silicon hollow nanospheres for lithium-ion battery anodes with long cycle life. Nano Lett. 11, 2949–2948 (2011)
H.X. Ji, X.L. Wu, L.Z. Fan, C. Krien, I. Fiering, Y.G. Guo, Y. Mei, O.G. Schmidt, Self-wound composite nanomembranes as electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 22, 4591–4595 (2010)
G.-L. Xu, S.-R. Chen, J.-T. Li, F.-S. Ke, L. Huang, S.-G. Sun, A composite material of SnO2/ordered mesoporous carbon for the application in Lithium-Ion Battery. J. Electroanal. Chem 656, 185–187 (2011)
M.S. Dresselhaus, I.L. Thomas, Alternative energy technologies. Nature 414, 332–336 (2001)
Y. Idota, T. Kubota, A. Matsufuji, Y. Maekawa, T. Miyasaka, Tin-Based amorphous oxide: a high-capacity lithium-ion-storage. Mater. Sci. 276, 1395–1403 (1997)
L. Ma, X.-P. Zhou, L.-M. Xu, X.-Y. Xu, L.-L. Zhang, Biopolymer-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 porous nanospheres and their photocatalytic properties. Ceram. Int. 40, 13659–13667 (2014)
H. Bian, J. Zhang, M.-F. Yuen, W. Kang, Y. Zhan, D.Y.W. Yu, Z. Xu, Y.Y. Li, Anodic nanoporous SnO2 grown on Cu foils as superior binder-free Na-Ion battery anodes. J. Power Sources 307, 634–637 (2016)
M.-S. Park, G.-X. Wang, Y.-M. Kang, D. Wexler, S.-X. Dou, H.-K. Liu, Preparation and electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanowires for application in Lithium-Ion batteries. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 46, 750–754 (2007)
P. Gurunathan, P.M. Ette, K. Ramesha, Synthesis of hierarchically porous SnO2 microspheres and performance evaluation as Li-Ion battery anode by using different Binders. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 16556–16559 (2014)
C. Zhang, X. Peng, Z. Guo, C. Cai, Z. Chen, D. Wexler, S. Li, H. Liu, Carbon-coated SnO2/graphene nanosheets as highly reversible anode materials for Lithium-Ion batteries. Carbon 50, 1897–1903 (2012)
J. Liang, Y. Zhao, L. Guo, L. Li, Flexible free-standing graphene/SnO2 nanocomposites paper for Li-Ion battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 5742–5747 (2012)
S. Han, B. Jang, T. Kim, S.M. Oh, T. Hyeon, simple synthesis of hollow tin dioxide microspheres and their application to Lithium-Ion battery anodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 1845–1846 (2005)
D. Narsimulu, S. Vinoth, E.S. Srinadhu, N. Satyanarayana, Surfactant-free microwave hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanosheets as an anode material for lithium battery applications. Ceram. Int. 44, 201–207 (2018)
L. Li, X. Yin, S. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Chen, T. Wang, Electrospun porous SnO2 nanotubes as high capacity anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 12, 1383–1384 (2010)
X. Yin, L. Chen, C. Li, Q. Hao, S. Liu, Q. Li, E. Zhang, T. Wang, Synthesis of mesoporous SnO2 spheres via self-assembly and superior lithium storage properties. Electrochim. Acta 56, 2358–2366 (2011)
P. Lian, X. Zhu, S. Liang, Z. Li, W. Yang, H. Wang, High reversible capacity of SnO2/graphene nanocomposite as an anode material for Lithium-Ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 56, 4532–4538 (2011)
Y. Zhu, H. Guo, H. Zhai, C. Cao, Microwave-assisted and gram-scale synthesis of ultrathin SnO2 nanosheets with enhanced lithium storage properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2745–2749 (2015)
C. He, Y. Xiao, H. Dong, Y. Liu, M. Zheng, K. Xiao, X. Liu, H. Zhang, B. Lei, Mosaic-structured SnO2@C porous microspheres for high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials. Electrochim Acta 142, 157–210 (2014)
N.R. Srinivasan, S. Mitra, R. Bandyopadhyaya, Improved electrochemical performance of SnO2–mesoporous carbon hybrid as a negative electrode for lithium ion battery applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 16, 6630–6711 (2014)
M. Liu, X. Li, H. Ming, J. Adkins, X. Zhao, L. Su, Q. Zhou, J. Zheng, TiN surface-modified SnO2 as an efficient anode material for lithium ion batteries. New J. Chem. 37, 2096–2097 (2013)
G.Z. Xing, Y. Wang, J.I. Wong, Y.M. Shi, Z.X. Huang, S. Li, H.Y. Yang, Hybrid CuO/SnO2 nanocomposites: towards cost-effective and high performance binder free lithium ion batteries anode materials. Appl. Phys. Lett 105, 143905–143906 (2014)
X. Zhang, J. Liang, G. Gao, S. Ding, Z. Yang, W. Yu, B.Q. Li, The preparation of mesoporous SnO2 nanotubes by carbon nanofibers template and their lithium storage properties. Electrochim. Acta 98, 263–265 (2013)
X. Ye, W. Zhang, Q. Liu, S. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Wei, One-step synthesis of Ni-doped SnO2 nanospheres with enhanced lithium ion storage performance. New J. Chem. 39, 130–135 (2015)
J. Yue, W. Wang, N. Wang, X. Yang, J. Feng, J. Yang, Y. Qian, Triple-walled SnO2@N-doped carbon@SnO2 nanotubes as an advanced anode material for lithium and sodium storage. J. Mater. Chem. 3, 23194–23197 (2015)
D. Narsimulu, E.S. Srinadhu, N. Satyanarayana, Surfactant-free microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 flower-like structures as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Materialia 4, 276–286 (2018)
P. Wu, N. Du, H. Zhang, J. Yu, Y. Qi, D. Yang, Carbon-coated SnO2 nanotubes: template-engaged synthesis and their application in lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale 3, 746–756 (2011)
M.-S. Park, Y.-M. Kang, G.-X. Wang, S.-X. Dou, H.-K. Liu, The effect of morphological modification on the electrochemical properties of SnO2 nanomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater 18, 455–457 (2008)
L. Yin, S. Chai, F. Wang, J. Huang, J. Li, C. Liu, X. Kong, Ultrafine SnO2 nanoparticles as a high performance anode material for lithium ion battery. Ceram. Int. 42, 9433–9435 (2016)
C.-C. Hou, S. Brahma, S.-C. Weng, C.-C. Chang, J.-L. Huang, Facile, low temperature synthesis of SnO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 413, 160–168 (2017)
Z. Yang, G. Du, Z. Guo, X. Yu, S. Li, Z. Chen, P. Zhang, H. Liu, Plum-branch-like carbon nanofibers decorated with SnO2 nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2, 1011–1017 (2010)
D. Narsimulu, S. Vadnala, E. Srinadhu, N. Satyanarayana, Electrospun Sn–SnO2/C composite nanofibers as an anode material for lithium battery applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 11117–11127 (2018)
Z. Wen, Q. Wang, Q. Zhang, J. Li, In Situ growth of mesoporous SnO2 on multiwalled carbon nanotubes: a novel composite with porous-tube structure as anode for lithium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17, 2772–2777 (2007)
O. Lupan, L. Chow, G. Chai, A. Schulte, S. Park, H. Heinrich, A rapid hydrothermal synthesis of rutile SnO2 nanowires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 157, 101–104 (2009)
J. Yan, E. Khoo, A. Sumboja, P.S. Lee, Facile coating of Manganese oxide on tin oxide nanowires with high-performance capacitive behavior. ACS Nano 4, 4247–4249 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Prof NS is gratefully acknowledging UGC, Govt. of India for awarding BSR Faculty fellowship: No. F.18-1/2011(BSR), Date: 07-03-2019. Authors also acknowledge CIF, Pondicherry University for using the characterization facilities. Authors are also thankful to Dr.S.M. Shiva Prasad, Professor Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) Jakkur, Bangalore-0560064, for providing TEM measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narsimulu, D., Naresh, N., Rao, B.N. et al. Rational design of SnO2 nanoflakes as a stable and high rate anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 8556–8563 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03391-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03391-x