Abstract
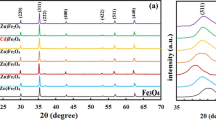
Nanocrystalline samples of Nd0.7Bi0.3Fe1−xNixO3 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) are synthesized using sol-gel auto-combustion process to investigate their structural, electrical, magnetic, and thermal properties. Phase purity and crystallinity of the samples are determined through x-ray diffraction (XRD) data. XRD patterns along with Rietveld refinement reveal orthorhombic structure with Pbnm space group. Unit cell parameters, bond angles, and bond lengths for all the samples have been determined. Crystallite size calculated by Scherrer equation is found to be in the range of 15–21 nm. The characteristic bands in the FTIR spectra further confirm the formation of our samples. FE-SEM images indicate the homogeneous distribution of particles on large scale and Ni-doped samples show some wall-like nanostructure in the morphology. EDX spectra confirm the elemental composition without any impurity element. The polarization versus electric field (P-E) and magnetization versus magnetic field (M-H) loops exhibit the multiferroic nature of the material. The sample with concentration x = 0.2 shows the maximum value of polarization (Pm) while maximum magnetization is achieved for x = 0.1 concentration. The specific heat capacity (Cp), endothermic, and exothermic peaks of the materials have been determined in the broad temperature range with the help of DTA measurements in the controlled nitrogen atmosphere. The Néel temperature of the parent system is found to be 742 K and that decreases up to 573 K on Ni doping.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Aparnadevi, K. Saravana Kumar, M. Manikandan, D. Paul Joseph, C. Venkateswaran, Room temperature dual ferroic behaviour of ball mill synthesized NdFeO3 orthoferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 120, 034101–034108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4954842
M. Yousefi, S. Soradi Zeid, M. Khorasani-Motlagh, Synthesis and characterization of nano-structured perovskite type neodymium orthoferrite NdFeO3. Curr. Chem. Lett. 6, 23–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ccl.2016.10.002
S.C. Parida, S. Dash, Z. Singh, R. Prasad, K.T. Jacob, V. Venugopal, Thermodynamic studies on NdFeO3(s). J. Solid State Chem. 164, 34–41 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.2001.9445
C. Tongyun, S. Liming, L.I.U. Feng, Z.H.U. Weichang, NdFeO3 as anode material for S/O2 solid oxide fuel cells. J. Rare Earth. 30, 1138–1141 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60194-X
S. Singh, A. Singh, B.C. Yadav, P.K. Dwivedi, Fabrication of nanobeads structured perovskite type neodymium iron oxide film: Its structural, optical, electrical and LPG sensing investigations. Sen. Actuators B: Chem. 177, 730–739 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.096
S. Chanda, S. Saha, A. Dutta, T.P. Sinha, Raman spectroscopy and dielectric properties of nanoceramic NdFeO3. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1688–1693 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.12.075
T. Murtaza, M.S. Khan, J. Ali, T. Hussain, K. Asokan, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of multiferroic NdFeO3–SrTiO3 composites. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 29, 18573–18580 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9975-2
S. Manzoor, S. Husain, A. Somvanshi, M. Fatema, N. Zarrin, Exploring the role of Zn doping on the structure, morphology, and optical properties of LaFeO3. Appl. Phys. A. 125, 509 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2806-3
W. Sławiński, R. Przeniosło, I. Sosnowska, E. Suard, Spin reorientation and structural changes in NdFeO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, 4605–4614 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/29/002
K.E. Babu, V.V. Kumar, K.B. Kumari, K. Neeraja, N.G. Praveena, V. Veeraiah, Electronic structure and magnetic properties of cubic perovskite PrFeO3 and NdFeO3: a first-principles study. AIP Conf. Proc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5048001
S.J. Yuan, W. Ren, F. Hong, Y.B. Wang, J.C. Zhang, L. Bellaiche, S.X. Cao, G. Cao, Spin switching and magnetization reversal in single-crystal NdFeO3. Phys. Rev. 87, 184405 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.184405
M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Azab, A.H. El-Khawas, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Bi doped LaFeO3 nano-crystals, synthesized by auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 26, 8765–8773 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3556-4
Nancy, R. Shukla, R. Dhaka, S. Dash, S.C. Sahoo, B. Bahera, P.D. Babu, R. Choudhary, A.K. Patra, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Bi-Mn doped SmFeO3. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.112
O. Rosales-González, F. Sánchez-De Jesús, F. Pedro-García, C.A. Cortés-Escobedo, M. Ramírez-Cardona, A.M. Bolarín-Miró, Enhanced multiferroic properties of YFeO3 by doping with Bi3+. Materials 12(13), 2054 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132054
P. Suresh, K. Vijaya Laxmi, P.S. Anil Kumar, Enhanced room temperature multiferroic characteristics in hexagonal LuFe1 – xNixO3 (x = 0 – 0.3) nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 448, 117–122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.05.052
S. A. Mir, M. Ikram, K. Asokan, Structural, optical and dielectric properties of Ni substituted NdFeO3. Optik 125, 6903–6908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.050
J. Shanker, G. Narsinga Rao, K. Venkataramana, D. Suresh Babu, Investigation of structural and electrical properties of NdFeO3 perovskite nanocrystalline. Phys. Lett. A. 382, 2974–2977 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2018.07.002
M.D. Luu, N.N. Dao, D. Van Nguyen, N.C. Pham, T.N. Vu, T.D. Doan, A new perovskite-type NdFeO3 adsorbent: synthesis, characterization, and As(V) adsorption. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci Nanotechnol. 7(2), 025015 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/7/2/025015
M. Khorasani-Motlagh, M. Noroozifar, M. Yousefi, S. Jahani, Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of Perovskite NdFeO3 Nanocrystals via a Co-Precipitation Method. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 7–14 (2013). http://www.ijnnonline.net/article_3874.html
Z. Zhou, L. Guo, H. Yang, Q. Liu, F. Ye, Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of multiferroic rare-earth orthoferrites. J. Alloy Compd. 583, 21–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.129
J. Agus, S. Samnur, K. Triyana, E.H. Sujiono, Effect of sintering temperature on crystal structure and surface morphology of NdFeO3 oxide alloy materials prepared by solid reaction method. Key Eng. Mater. 811, 158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.811.158
A. Somvanshi, S. Manzoor, S. Husain, Influence of Mn doping on structural, dielectric and optical properties of neodymium orthoferrite. AIP Conf. Proc. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032578
R. Punia, R.S. Kundu, S. Murugavel, N. Kishore, Hopping conduction in bismuth modified zinc vanadate glasses: An applicability of Mott’s model. J. Appl. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4768898
Y. Du, Z.X. Cheng, X.-L. Wang, S.X. Dou, Structure, magnetic, and thermal properties of Nd1 – xLaxCrO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0). J. Appl. Phys. 108, 093914 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3505800
A. Somvanshi, S. Husain, W. Khan, Investigation of structure and physical properties of cobalt doped nano-crystalline neodymium orthoferrite. J. Alloy Compd. 778, 439–451 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.095
L.B. McCusker, R.B. Von Dreele, D.E. Cox, D. Louër, P. Scardi, Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 32, 36–50 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889898009856
A. Somvanshi, S. Husain, Study of structural, dielectric and optical properties of NdMnO3. AIP Conf. Proc. 1953, 030242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032577
N. Zarrin, S. Husain, Study of structural, morphological, optical, and dielectric behaviour of zinc-doped nanocrystalline lanthanum chromite. Appl. Phys. A. 124, 730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2139-7
R.J. Wiglusz, K. Kordek, M. Małecka, A. Ciupa, M. Ptak, R. Pazik, P. Pohl, D. Kaczorowski, A new approach in the synthesis of La1 – xGdxFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles – structural and magnetic characterization. Dalton Trans. 44, 20067–20074 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5DT03378K
A. Alqahtani, S. Husain, A. Somvanshi, W. Khan, Structural, morphological, thermal and optical investigations on Mn doped GdCrO3. J. Alloy Compd. 804, 401–414 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.028
X.G. Li, A. Chiba, S. Takahashi, M. Sato, Oxidation characteristics and magnetic properties of iron ultrafine particles. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 3871–3875 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.366619
R. Mathur, D.R. Sharma, S.R. Vadera, S.R. Gupta, B.B. Sharma, N. Kumar, Room temperature synthesis of nanocomposites of Mn-Zn ferrites in a polymer matrix. Nanostruct. Mater. 11, 677–686 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(99)00356-6
C. Shivakumara, A.K. John, S. Behera, N. Dhananjaya, R. Saraf, Photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties of Eu3+-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the nitrate-citrate gel combustion method. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11304-5
K. Yao, C. Zhao, N. Sun, W. Lu, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Wang, Freestanding CuS nanowalls: Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis and prominent catalytic performance for the decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. CrystEngComm. 19(34), 5048–5057 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ce01119a
N. Choudhary, M.K. Verma, N.D. Sharma, S. Sharma, D. Singh, Superparamagnetic nanosized perovskite oxide La0.5Sr0.5Ti0.5Fe0.5O3 synthesized by modified polymeric precursor method: effect of calcination temperature on structural and magnetic properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 86, 73–82 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4593-2
C. Padurariu, L. Padurariu, L. Curecheriu, C. Ciomaga, N. Horchidan, C. Galassi, L. Mitoseriu, Role of the pore interconnectivity on the dielectric, switching and tunability properties of PZTN ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 5767–5773 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.01.123
Y. Zhang, J. Roscow, R. Lewis, H. Khanbareh, V.Y. Topolov, M. Xie, C.R. Bowen, Understanding the effect of porosity on the polarisation-field response of ferroelectric materials. Acta Mater. 154, 100–112 (2018).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.05.007
I. Sosnowska, E. Steichele, A. Hewat, Reorientation phase transition in NdfeO3. Physica B + C 136, 394–396 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4363(86)80099-7
A. Somvanshi, S. Husain, S. Manzoor, N. Zarrin, W. Khan, Structure of nanocrystalline Nd0.5R0.5FeO3 (R = La, Pr, and Sm) intercorrelated with optical, magnetic and thermal properties. J. Alloy Compd. 806, 1250–1259 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.333
P.R. Vanga, R.V. Mangalaraja, M. Ashok, Effect of (Nd, Ni) co-doped on the multiferroic and photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3. Mater. Res. 72, 299 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.08.015
J. Zhao, X. Zhang, S. Liu, W. Zhang, Z. Liu, Effect of Ni substitution on the crystal structure and magnetic properties of BiFeO3. J. Alloy Compd. 557, 120–123 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.005
P. Kaur, K.K. Sharma, R. Pandit, R. Kumar, R.K. Kotnala, J. Shah, Temperature dependent dielectric and magnetic properties of GdFe1–xNixO3 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.3) orthoferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 224102 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4882115
M. Idrees, M. Nadeem, M. Mehmood, M. Atif, K.H. Chae, Impedance spectroscopic investigation of delocalization effects of disorder induced by Ni doping in LaFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 44(10), 105401 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/10/105401
S. Manzoor, S. Husain, Analysis of Zn substitution on structure, optical absorption, magnetization, and high temperature specific heat anomaly of the nano-crystalline LaFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 065110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5025252
S. Husain, A.O.A. Keelani, W. Khan, Influence of Mn substitution on morphological, thermal and optical properties of nanocrystalline GdFeO3 orthoferrite. Nano-Struct. Nano-Object. 15, 17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2018.03.002
S.A. Mir, M. Ikram, K. Asokan, Effect of Ni doping on optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Nd orthoferrite. J. Phys Conf. Ser. 534, 012017 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/534/1/012017
Acknowledgements
One of the authors A. Somvanshi is thankful for financial support provided by UGC-DAE CSR, Mumbai under the project CRS-M-271. Authors are grateful to Dr. Shalendra Kumar, Electronic Materials & Nanomagnetism Lab, Amity University Gurgaon and Mr. Anuj Kumar, Department of Physics, IIT Roorkee for providing P-E and M-H characterizations respectively. Ms. Babli Debnath, Department of Physics, Tripura University is thankfully acknowledged for her immense help in FE-SEM characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somvanshi, A., Husain, S., Manzoor, S. et al. Room temperature dual ferroic behavior induced by (Bi, Ni) co-doping in nanocrystalline Nd0.7Bi0.3Fe1−xNixO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.3). J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11010–11020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03649-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03649-4