Abstract
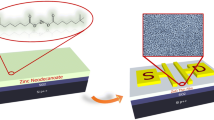
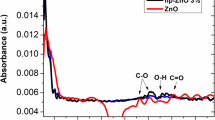
In this work, we examined the influence of In doping on the morphological and structural characteristics of ZnO active layers grown by the spin coating and the electrical performance of ZnO-based thin film transistors. XRD results indicated that the active layers were amorphous due to the absence of any sharp peaks. XPS analysis was carried out to determine indium amounts as an atomic percentage in ZnO and oxidation state of In. AFM images indicated that the roughness of the active layers decreased with increasing indium concentration in ZnO. The indium doping has dramatically improved the electrical parameters of ZnO-based transistors. The field-effect mobility of undoped TFT increased ~ 157 times by adding %3 In content. The highest field-effect mobility (μsat) of 12.9 cm2V−1 s−1 was obtained for %3 In-doped ZnO TFT (IZO3). Also IZO3 has a 6.96 V threshold voltage (Vth), 106Ion/Ioff ratio, 1.98 V/dec subthreshold slope (SS), and a high on-current of 4.6 mA. We ascribed the performance enhancement of devices with In doping due to increasing carrier concentration of channel. These results show that the low concentration of indium incorporation is very crucial to change the morphological properties of ZnO active layers and to obtain high-performance solution-processed TFTs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.Y. Won, Y.H. Han, H.J. Seol, K.J. Lee, R. Choi, J.K. Jeong, Transport property improvements of amorphous In-Zn-O transistors with printed Cu contacts via rapid temperature annealing. Thin Solid Films 603, 268–271 (2016)
T.S. Jung, S.J. Kim, C.H. Kim, J. Jung, J. Na, M.M. Sabri, H.J. Kim, Replacement and rearrangement of an oxide lattice by germanium doping in solution-processed indium-zinc-oxide thin-film. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 62, 2888–2893 (2015)
B. Du Ahn, H.J. Jeon, J. Sheng, J. Park, J.S. Park, A review on the recent developments of solution processes for oxide thin film transistors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 30, 064001 (2015)
R.A. Street, T.N. Ng, R.A. Lujan, I. Son, M. Smith, S. Kim, T. Lee, Y. Moon, S. Cho, Sol-gel solution-deposited InGaZnO thin film transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 4428–4437 (2014)
X. Li, E. Xin, J. Zhang, Effects of Hf incorporation on indium zinc oxide thin-film transistors using solution process. Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 143–148 (2015)
M.A. Islam, K.S. Rahman, F. Haque, N.A. Khan, M. Akhtaruzzaman, M.M. Alam, H. Ruslan, K. Sopian, N. Amin, Effect of Sn doping on the properties of nano-structured ZnO thin films deposited by Co-sputtering technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15, 9184–9191 (2015)
C.-Y. Tsay, K.-S. Fan, Optimization of Zr-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Mater. Trans. 49(8), 1900–1904 (2008)
R.L. Hoffman, B.J. Norris, J.F. Wager, ZnO-based transparent thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 733–735 (2003)
C.H. Ahn, S.H. Kim, Y.K. Kim, H.S. Lee, H.K. Cho, Effect of post-annealing temperatures on thin-film transistors with ZnO/Al2O3 superlattice channels. Thin solid flims (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015), pp. 336–340
L. Tian, D. Zhou, Y. Ma, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, Effects of annealing temperature on the electrical characteristics of Li–N co-doped polycrystalline ZnO thin film transistors. Superlatt. Microstruct. 109, 279–285 (2017)
S.Y. Park, B.J. Kim, K. Kim, M.S. Kang, K.-H. Lim, T. Il Lee, J.M. Myoung, H.K. Baik, J.H. Cho, Y.S. Kim, Low-temperature, solution-processed and alkali metal doped ZnO for high-performance thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 24, 834–838 (2012)
X. Zhang, H. Lee, J.-H. Kwon, E.-J. Kim, J. Park, Low-concentration indium doping in solution-processed zinc oxide films for thin-film transistors. Materials (Basel). 10, 880 (2017)
C. Klingshirn, ZnO: material, physics and applications. ChemPhysChem 8, 782–803 (2007)
R. Biswal, A. Maldonado, J. Vega-Pérez, D. Acosta, M. De La Luz Olvera, Indium doped zinc oxide thin films deposited by ultrasonic chemical spray technique, starting from zinc acetylacetonate and indium chloride. Materials (Basel). 7, 5038–5046 (2014)
S. Major, K.L. Chopra, Indium-doped zinc oxide films as transparent electrodes for solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. 17, 319–327 (1988)
C. Zhang, D. Xiong, S. Xu, W. Ouyang, L. Wang, P.K. Chu, Highly efficient field emission from indium-doped ZnO nanostructure on nanographene/macroporous electric conductive network. Mater. Lett. 222, 25–28 (2018)
R. Hadj-Tahar, A.B. Mohamed, Sol–gel processed indium-doped zinc oxide thin films and their electrical and optical properties. New J. Glas. Ceram. 4, 55–65 (2014)
C.Y. Tsay, H.C. Cheng, Y.T. Tung, W.H. Tuan, C.K. Lin, Effect of Sn-doped on microstructural and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 517, 1032–1036 (2008)
S. Krehula, M. Ristić, M. Reissner, S. Kubuki, S. Musić, Synthesis and properties of indium-doped hematite. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1900–1907 (2017)
J.-S. Hong, B.-R. Rhee, J.-J. Kim, S.-H. Park, H.-M. Kim, J.-S. Ahn, Highly transparent and conducting In$_2$O$_3$-ZnO thin films prepared by electron-beam evaporation technique. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 45, 712–715 (2004)
C.-H. Wu, K.-M. Chang, Y.-M. Chen, B.-W. Huang, Y.-X. Zhang, S.-J. Wang, Using KrF ELA to improve gate-stacked LaAlO3/ZrO2 indium gallium zinc oxide thin-film transistors with novel atmospheric pressure plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 1917–1921 (2017)
J. Park, T.-J. Ha, W.-J. Cho, Improvement of air stability on solution-processed InZnO thin-film transistors by microwave irradiation and Zn composition ration. Phys. Status Solidi. 212, 1719–1724 (2015)
J. Choi, J. Park, K.H. Lim, N.K. Cho, J. Lee, S. Jeon, Y.S. Kim, Photosensitivity of InZnO thin-film transistors using a solution process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 132105 (2016)
Y. Caglar, M. Caglar, S. Ilican, XRD, SEM, XPS studies of Sb doped ZnO films and electrical properties of its based Schottky diodes. Optik (Stuttg). 164, 424–432 (2018)
J. Kim, J.H. Choi, H. Chae, H. Kim, Effect of indium doping on low-voltage ZnO nanocrystal field-effect transistors with ion-gel gate dielectric. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 071101 (2014)
S. Ruzgar, M. Caglar, The effect of Sn on electrical performance of zinc oxide based thin film transistor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 485–490 (2019)
G. Singh, S.B. Shrivastava, D. Jain, S. Pandya, T. Shripathi, V. Ganesan, Effect of indium dop ing on zinc oxide films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. 33, 581–587 (2010)
J.H. Lee, B.O. Park, Transparent conducting ZnO:Al, and Sn thin films deposited by the sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 426, 94–99 (2003)
F. Liu, C. Qian, J. Sun, P. Liu, Y. Huang, Y. Gao, J. Yang, Solution-processed lithium-doped zinc oxide thin-film transistors at low temperatures between 100 and 300 °C. Appl. Phys. A 122, 311 (2016)
J. Yang, Y. Jiang, L. Li, M. Gao, Structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO transparent conducting thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 421, 446–452 (2017)
S.H. Jeong, B.N. Park, S.B. Lee, J.H. Boo, Study on the doping effect of Li-doped ZnO film. Thin Solid Films 516, 5586–5589 (2008)
G.H. Kim, B. Du Ahn, H.S. Shin, W.H. Jeong, H.J. Kim, H.J. Kim, Effect of indium composition ratio on solution-processed nanocrystalline InGaZnO thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 233501 (2009)
I. Noviyana, A.D. Lestari, M. Putri, M.-S. Won, J.-S. Bae, Y.-W. Heo, H.Y. Lee, High mobility thin film transistors based on amorphous indium zinc tin oxide. Materials (Basel). 10, 702 (2017)
K.B. Park, J.B. Seon, G.H. Kim, M. Yang, B. Koo, H.J. Kim, M.K. Ryu, S.Y. Lee, High electrical performance of wet-processed indium zinc oxide thin-film transistors. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 311–313 (2010)
Z. Yang, J. Yang, T. Meng, M. Qu, Q. Zhang, Influence of channel layer thickness on the stability of amorphous indium zinc oxide thin film transistors. Mater. Lett. 166, 46–50 (2016)
M. Kumar, H. Jeong, D. Lee, Sol-gel derived Hf- and Mg-doped high-performance ZnO thin film transistors. J. Alloys Compd. 720, 230–238 (2017)
B.Y. Su, S.Y. Chu, Y. Der Juang, Improved electrical and thermal stability of solution-processed Li-doped ZnO thin-film transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices. 59, 700–704 (2012)
A.B. Cheremisin, S.N. Kuznetsov, G.B. Stefanovich, Effect of indium low doping in ZnO based TFTs on electrical parameters and bias stress stability. AIP Adv. 5, 117124 (2015)
J.H. Shim, H. Kim, J.H. Lim, J.H. Choi, C.M. Lee, K. Park, J. Joo, H. Kim, H.-J. Lee, M.R. Moon, D. Jung, Fabrication and comparison of the properties of SnInZnO and InZnO TFTs processed by using the flexible and stretchable electronics view project LG chem view project fabrication and comparison of the properties of SnInZnO and InZnO TFTs processed by using the sol–gel method. Artic. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 57, 1847–1851 (2010)
S. Amano, H. Harada, K. Akimoto, J. Sakata, T. Nishi, K. Moriya, K. Wakimoto, J. Koyama, S. Yamazaki, Y. Oikawa, T. Ikeyama, M. Sakakura, Low power LC display using In-Ga-Zn-oxide TFTs based on variable frame frequency. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 41, 626 (2010)
M. Kumar, H. Jeong, D. Lee, Solution-processed undoped and Indium doped ZnO thin film transistors: role of Ag nanowires into InZnO channel layer. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34, 075019 (2019)
Z. Zhu, B. Li, J. Wen, Z. Chen, Z. Chen, R. Zhang, S. Ye, G. Fang, J. Qian, Indium-doped ZnO horizontal nanorods for high on-current field effect transistors. RSC Adv. 7, 54928–54933 (2017)
Y. Wu, E. Girgis, V. Ström, W. Voit, L. Belova, K.V. Rao, Ultraviolet light sensitive In-doped ZnO thin film field effect transistor printed by inkjet technique. Phys. Status Solidi. 208, 206–209 (2011)
J. Il Song, J.S. Park, H. Kim, Y.W. Heo, J.H. Lee, J.J. Kim, G.M. Kim, B.D. Choi, Transparent amorphous indium zinc oxide thin-film transistors fabricated at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 022106 (2007)
Z. Yang, N. Wang, M. Qu, H. Pu, Q. Zhang, Preparation and characterization of molybdenum-doped indium-zinc-oxide thin film transistors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 30(4), 045008 (2015)
R. Xu, J. He, W. Li, D.C. Paine, Performance enhancement of amorphous indium-zinc-oxide thin film transistors by microwave annealing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 1915–1919 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Eskisehir Technical University Commission of Scientific Research Projects under Grant No. 1706F385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruzgar, S., Caglar, Y. & Caglar, M. The influence of low indium composition ratio on sol–gel solution-deposited amorphous zinc oxide thin film transistors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 11720–11728 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03723-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03723-x