Abstract
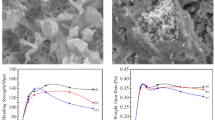
The paper presents the results of the study of structural, morphological, optical, and mechanical properties of lithium-containing ceramics obtained using the method of mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis. The purpose of this work is to assess the possibility of obtaining lithium-containing ceramics of the two-phase type, as well as the formation effect of the cubic phase of LiTiO2 on changes in the properties of ceramics. The relevance of this study is to obtain new data on the properties of lithium-containing ceramics, which have great prospects in their use as blanket materials for tritium reproduction. During the study, it was found that the formation of the LiTiO2 cubic phase leads to a change in the morphological features of ceramics, with the formation of sphere-like agglomerates of a nanoscale scale. An increase in the contribution of the LiTiO2 phase leads to a shift of the fundamental absorption edge, as well as the appearance of additional absorption bands. During mechanical tests for the determination of resistance to destruction by single compression, it was found that an increase in ceramic density, which is due to an increase in the contribution of the cubic phase, leads to an increase in resistance by 70–85%.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Rais et al., Copper substitution effect on the structural properties of nickel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 40(9), 14413–14419 (2014)
M.A. Fakhri et al., Optical investigations of photonics lithium niobate. Sol. Energy 120, 381–388 (2015)
M.A. Almessiere et al., Impact of Eu3+ ion substitution on structural, magnetic and microwave traits of Ni–Cu–Zn spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 46(8), 11124–11131 (2020)
M.V. Zdorovets, A.L. Kozlovskiy, The effect of lithium doping on the ferroelectric properties of LST ceramics. Ceram. Int. 46(10), 14548–14557 (2020)
Y. Al-Douri et al., First-principles calculations to investigate the refractive index and optical dielectric. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 256(11), 1900131 (2019)
D. Prakash et al., Synthesis, purification and microstructural characterization of nickel doped carbon nanotubes for spintronic applications. Ceram. Int. 42(5), 5600–5606 (2016)
I.Z. Zhumatayeva et al., The study of the prospects for the use of Li0.15Sr0.85TiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1(9), 6764–6772 (2020)
D.S. Klygach et al., Electromagnetic properties of BaFe12O19: Ti at centimeter wavelengths. J. Alloys Compd. 755, 177–183 (2018)
M.A. Fakhri, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, Fabricated optical strip waveguide of nanophotonics lithium niobate. IEEE Photonics J. 8(2), 1–10 (2016)
M.A. Almessiere et al., Correlation between microstructure parameters and anti-cancer activity of the [Mn0.5Zn0.5](EuxNdxFe2-2x)O4 nanoferrites produced by modified sol-gel and ultrasonic methods. Ceram. Int. 46(6), 7346–7354 (2020)
Y. Al-Douri, M.A.M. Al Saadi, First-principle calculations to investigate electronic and optical properties of MgO monolayer. Mater. Express 9(2), 166–172 (2019)
S. Hadji et al., Elastic, electronic, optical and thermodynamic properties of Ba3Ca2Si2N6 semiconductor: first-principles predictions. Physica B Condens, Matter 589, 412213 (2020)
D.I. Shlimas, M.V. Zdorovets, A.L. Kozlovskiy, Synthesis and resistance to helium swelling of Li2TiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(15), 12903–12912 (2020)
M. Bouchenafa et al., Theoretical investigation of the structural, elastic, electronic, and optical properties of the ternary tetragonal tellurides KBTe2 (B= Al, In). Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 114, 105085 (2020)
Y. Yang et al., Influence of Nd-NbZn co-substitution on structural, spectral and magnetic properties of M-type calcium-strontium hexaferrites Ca0.4Sr0.6-xNdxFe12.0-x (Nb0.5Zn0.5)xO19. J. Alloys Compd. 765, 616–623 (2018)
V.A. Ketsko et al., Specifics of pyrohydrolytic and solid-phase syntheses of solid solutions in the (MgGa2O4)x (MgFe2O4)1–x system. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 55(3), 427–429 (2010)
R. Al-Gaashani et al., XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram. Int. 39(3), 2283–2292 (2013)
M.A. Benali et al., Synthesis and analysis of SnO2/ZnO nanocomposites: structural studies and optical investigations with Maxwell-Garnett model. Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122254 (2020)
M.A. Fakhri et al., Optical investigation of nanophotonic lithium niobate-based optical waveguide. Appl. Phys. B 121(1), 107–116 (2015)
S. Touam et al., "First-principles computations of Y xGa 1–x As-ternary alloys: a study on structural, electronic, optical and elastic properties. Bull. Mater. Sci. 43, 22–32 (2020)
R. Ramaraghavulu, S. Buddhudu, G. Bhaskar Kumar, Analysis of structural and thermal properties of Li2TiO3 ceramic powders. Ceram. Int. 37(4), 1245–1249 (2011)
H. Wang et al., Fabrication of nanostructured Li2TiO3 ceramic pebbles as tritium breeders using powder particles synthesised via a CTAB-assisted method. Ceram. Int. 43(7), 5680–5686 (2017)
M. Yang et al., Comparison of the microwave and conventional sintering of Li2TiO3 ceramic pebbles. Ceram. Int. 44(16), 19672–19677 (2018)
C.-H. Jung, Sintering characterization of Li2TiO3 ceramic breeder powders prepared by the solution combustion synthesis process. J. Nucl. Mater. 341(2–3), 148–152 (2005)
W. Liu, R. Zuo, A novel Li2TiO3–Li2CeO3 ceramic composite with excellent microwave dielectric properties for low-temperature confirmed ceramic applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(1), 119–123 (2018)
C.-L. Huang, Y.-W. Tseng, J.-Y. Chen, High-Q dielectrics using ZnO-modified Li2TiO3 ceramics for microwave applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32(12), 3287–3295 (2012)
M. Du et al., High-Q microwave ceramics of Li2TiO3 co-doped with magnesium and niobium. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101(9), 4066–4075 (2018)
Y. Li et al., Synthesis of Li2TiO3 ceramic breeder powders by in-situ hydrolysis and its characterization. Mater. Lett. 89, 25–27 (2012)
C.-H. Jung et al., A polymer solution technique for the synthesis of nano-sized Li2TiO3 ceramic breeder powders. J. Nucl. Mater. 373(1–3), 194–198 (2008)
Y. Wu et al., Temperature stable microwave dielectric ceramic 0.3Li2TiO3–0.7Li (Zn0.5Ti1.5)O4 with ultra-low dielectric loss. Mater. Lett. 65(17–18), 2680–2682 (2011)
C. Dang et al., A promising tritium breeding material: Nanostructured 2Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic pebbles. J. Nucl. Mater. 500, 265–269 (2018)
M. Xiang et al., Preparation of Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 core-shell ceramic pebbles with enhanced crush load by graphite bed process. J. Nucl. Mater. 466, 477–483 (2015)
T. Hoshino et al., Pebble fabrication and tritium release properties of an advanced tritium breeder. Fusion Eng. Des. 109, 1114–1118 (2016)
H. Wedemeyer, H. Werle, E. Günther, Influence of grain-size and carbonate impurities on the tritium release from lithium orthosilicate. J. Nucl. Mater. 191, 240–242 (1992)
R.A. Andrievski, Thermal and radiation stability of nanomaterials. MRS Online Proc. Library Arch. 1645, 357–369 (2014)
Q. Zhou et al., Preparation of Li2TiO3 ceramic with nano-sized pores by ultrasonic-assisted solution combustion. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37(11), 3595–3602 (2017)
J.-L. Ma et al., Microwave dielectric properties of low-fired Li2TiO3–MgO ceramics for LTCC applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 204, 15–19 (2016)
C.-L. Yu et al., Monoclinic Li2TiO3 nano-particles via hydrothermal reaction: processing and structure. Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1901–1908 (2014)
M. Yang et al., Fabrication of Li2TiO3 ceramic pebbles with fine microstructure by microwave sintering. J. Nucl. Mater. 509, 330–334 (2018)
U. Dash et al., Electrical properties of bulk and nano Li2TiO3 ceramics: a comparative study. J. Adv. Ceram. 3(2), 89–97 (2014)
G.J. Rao et al., Fabrication and characterization of Li4SiO4-Li2TiO3 composite ceramic pebbles using extrusion and spherodization technique. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38(15), 5174–5183 (2018)
Q. Zhou et al., Release kinetics of tritium generation in neutron irradiated biphasic Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 ceramic breeder. J. Nucl. Mater. 522, 286–293 (2019)
F.Z. Krimech et al., Monoclinic Li2TiO3 nano-particles via sol–gel method: structure and impedance spectroscopy. Mediterr. J. Chem. 8(3), 209–212 (2019)
M. Yang et al., Fabrication and tritium release property of Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramics. J. Nucl. Mater. 503, 151–156 (2018)
Y. Lai et al., Temperature stability and high-Qf of low temperature firing Mg2SiO4–Li2TiO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43(18), 16167–16173 (2017)
Y. Zeng et al., Fast fabrication of high quality Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic pebbles by microwave sintering: In comparison with conventional sintering. Ceram. Int. 45(15), 19022–19026 (2019)
M. Xiang et al., Preparation of Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 core–shell ceramic pebbles with enhanced crush load by graphite bed process. J. Nucl. Mater. 466, 477–483 (2015)
Q. Zhou et al., Effect of fuel-to-oxidizer ratios on combustion mode and microstructure of Li2TiO3 nanoscale powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34(3), 801–807 (2014)
Funding
This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan (No. AP08855734).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shlimas, D.I., Kozlovskiy, A.L. & Zdorovets, M.V. Study of the formation effect of the cubic phase of LiTiO2 on the structural, optical, and mechanical properties of Li2±xTi1±xO3 ceramics with different contents of the X component. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 7410–7422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05454-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05454-z