Abstract
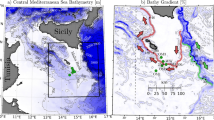
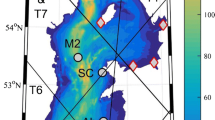
The Luzon Strait is blocked by two meridional ridges at depths, with the east ridge somewhat higher than the west ridge in the middle reaches of the Strait. Previous numerical models identified the Luzon Strait as the primary generation site of internal M2 tides entering the northern South China Sea (Niwa and Hibiya, 2004), but the role of the west-versus-east ridge was uncertain. We used a hydrostatic model for the northern South China Sea and a nonhydrostatic, process-oriented model to evaluate how the west ridge of Luzon Strait modifies westward propagation of internal tides, internal bores and internal solitary waves. The dynamic role of the west ridge depends strongly on the characteristics of internal waves and is spatially inhomogeneous. For M2 tides, both models identify the west ridge in the middle reaches of Luzon Strait as a dampener of incoming internal waves from the east ridge. In the northern Luzon Strait, the west ridge is quite imposing in height and becomes a secondary generation site for M2 internal tides. If the incoming wave is an internal tide, previous models suggested that wave attenuation depends crucially on how supercritical the west ridge slope is. If the incoming wave is an internal bore or internal solitary wave, our investigation suggests a loss of sensitivity to the supercritical slope for internal tides, leaving ridge height as the dominant factor regulating the wave attenuation. Mechanisms responsible for the ridge-induced attenuation are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chao, S. Y. and P. T. Shaw (2006): Reflection and diffraction of internal solitary waves by a circular island. J. Oceanogr., 52, 811–823.
Global Ocean Associates (2004): An Atlas of Internal Solitary-like Waves and Their Properties. 2nd ed. (http://www.internal waveatlas.com/).
Johnston, T. M. S. and M. A. Merrifield (2003): Internal tide scattering at seamounts, ridges and islands. J. Geophys. Res., 108, doi:10.1029/2002JC001528.
Ko, D. S., P. J. Martin, C. D. Rowley and R. H. Preller (2007): A real-time coastal ocean prediction experiment for MREA04. J. Mar. Syst., doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.02.022.
Liu, C.-T., R. Pinkel, M.-K. Hsu, J. M. Klymak, H.-W. Chen and C. Villanoy (2006): Nonlinear internal waves from the Luzon Strait. EOS, 87, No. 42, 449–451.
Lynch, J. F., S. R. Ramp, C.-S. Chiu, T. Y. Tang, Y.-J. Yang and J. A. Simmen (2004): Research highlights from the Asian Seas International Acoustics Experiment in the South China Sea. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng., 29, 1067–1074.
Müller, P. and X. Liu (2000): Scattering of internal waves at finite topography in two dimensions: I. Theory and case studies. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 30, 532–549.
Nash, J. D., M. H. Alford and E. Kunze (2005): On estimating internal wave energy fluxes in the ocean. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 22, 1551–1570.
Niwa, Y. and T. Hibiya (2004): Three-dimensional numerical simulation of M2 internal tides in the East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res., 109, C04027, doi:10.1029/2003JC001923.
Shaw, P. T. and S. Y. Chao (2006): A nonhydrostatic primitive equation model for studying small-scale processes: an object-oriented approach. Cont. Shelf Res., 26, 1416–1432.
Yang, Y. J., T. Y. Tang, M. H. Chuang, A. K. Liu, M.-K. Hsu and S. R. Ramp (2004): Soliton northeast of Tung-Sha Island, Pilot study of ASIAEX. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng., 29, 1182–1199.
Zhao, Z., V. Klemas, Q. Zheng and X.-H. Yan (2004): Remote sensing evidence for baroclinic tide origin of internal solitary waves in the northeastern South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, doi: 10.1029/2003GL019077.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, SY., Ko, DS., Lien, RC. et al. Assessing the west ridge of Luzon Strait as an internal wave mediator. J Oceanogr 63, 897–911 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-007-0076-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-007-0076-8